Showing 121–140 of 426
-
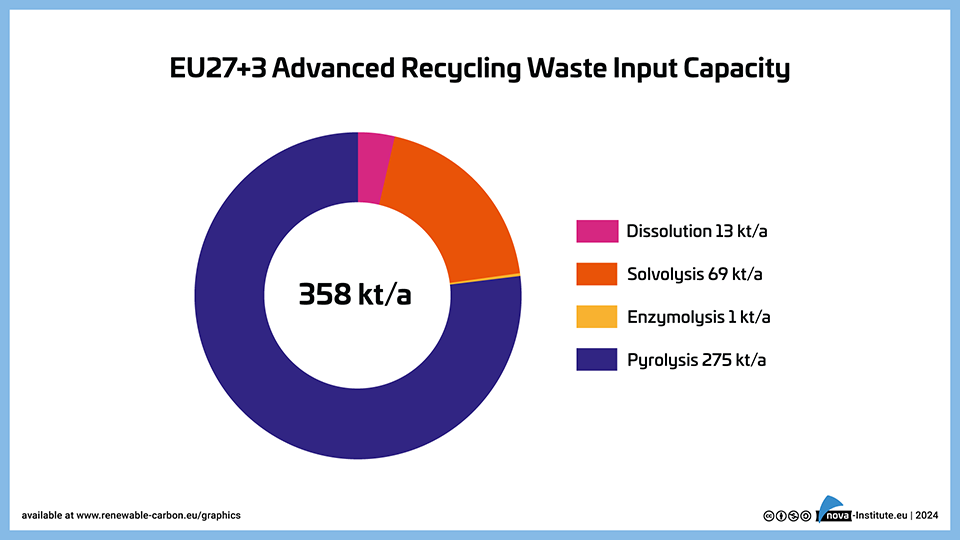
EU27+3 Advanced Recycling Waste Input Capacity (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Technology
1 Page
139 Downloads
139 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
139
DownloadsInstalled input capacities for different advanced recycling technologies in EU27+3.
-
Mapping of Advanced Plastic Waste Recycling Technologies and their Global Capacities (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Technology
276 Pages

2024-02
3,000 € – 10,000 €Price range: 3,000 € through 10,000 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Select
licenceAdvanced recycling technologies are developing at a fast pace, with new players constantly appearing on the market, from start-ups to giants and everything in between – new plants are being built, new capacities are being achieved, and new partnerships are established. Due to these developments, it is difficult to keep track of everything. The report “Mapping of advanced plastic waste recycling technologies and their global capacities” aims to clear up this jungle of information providing a structured, in-depth overview and insight. It has an exclusive focus on profiling available technologies and providers of advanced recycling including the addition of new technologies and updated/revised profiles. Furthermore, for the first time a comprehensive evaluation of the global input and output capacities was carried out for which more than 340 planned as well as installed and operating plants including their specific product yields were mapped.
Further information:
The new report “Mapping of advanced plastic waste recycling technologies and their global capacities” differs from the old report “Chemical Recycling – Status, Trends and Challenges” as follows:- All technology provider profiles from the old report included + updated to 2023.
- Overall >120 technologies and providers (vs. >70 technologies and providers in the old report)
- Global capacities
In summary, this report is suitable for interested readers who have already dealt with the advanced recycling topic and are looking for an up-to-date overview of all identified providers and a detailed description of the technologies.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/WQHT8696
-
Mapping of Advanced Plastic Waste Recycling Technologies and their Global Capacities – Short Version (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Technology
12 Pages
2222 Downloads
2222 Downloads
2024-02
FREE
2222
DownloadsAdvanced recycling technologies are developing at a fast pace, with new players constantly appearing on the market, from start-ups to giants and everything in between – new plants are being built, new capacities are being achieved, and new partnerships are established. Due to these developments, it is difficult to keep track of everything. The report “Mapping of advanced plastic waste recycling technologies and their global capacities” aims to clear up this jungle of information providing a structured, in-depth overview and insight. It has an exclusive focus on profiling available technologies and providers of advanced recycling including the addition of new technologies and updated/revised profiles. Furthermore, for the first time a comprehensive evaluation of the global input and output capacities was carried out for which more than 340 planned as well as installed and operating plants including their specific product yields were mapped.
Further information:
The new report “Mapping of advanced plastic waste recycling technologies and their global capacities” differs from the old report “Chemical Recycling – Status, Trends and Challenges” as follows:- All technology provider profiles from the old report included + updated to 2023.
- Overall >120 technologies and providers (vs. >70 technologies and providers in the old report)
- Global capacities
In summary, this report is suitable for interested readers who have already dealt with the advanced recycling topic and are looking for an up-to-date overview of all identified providers and a detailed description of the technologies.
-
Advanced Recycling Conference 2023 (Proceedings)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
12 Downloads
12 Downloads
2023-12
FREE
Plus 19% MwSt.12
DownloadsThe proceedings of the Advanced Recycling Conference 2023 (28-29 November, https://advanced-recycling.eu) contain conference presentations, the conference journal, sponsor documents and the press release. Download of the conference journal incl. the program.
-
RCI’s scientific background report: “The use of food and feed crops for bio-based materials and the related effects on food security – Promoting evidence-based debates and recognising potential benefits” (June 2023) Short Version
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
2 Pages
1000 Downloads
1000 Downloads
2023-11
FREE
1000
DownloadsPromoting Evidence-based Debates and Recognising Potential Benefits
This short version of the scientific paper highlights on two pages new insights into a hotly debated topic and urges for careful and evidence-based debates.
The paper aims to show that the well-known biomass debate is flawed, subjective and not fully based on evidence. What is detrimental to food security are, according to the World Food Programme in 2023, climate change, conflict, extreme inequalities in wealth distribution, heavy dependence on food imports from industrial countries, overconsumption of meat, losses along the value chain and the impact of the COVID pandemic. Competition between biomass uses is not mentioned among the relevant causes.
The use of biomass for industrial applications, does have the potential to replace fossil feedstocks and thus contribute to the urgently needed reduction of fossil carbon emissions into our atmosphere to mitigate climate change.
While not denying the dire need to combat world hunger, the authors of the paper argue that using food and feed crops for chemicals and materials will not necessarily exacerbate food insecurity, and in fact has the potential to cause multiple benefits for local and global food security, climate mitigation and other factors:
- The climate wins – Bio-based materials are part of the solution to achieve climate change mitigation.
- Land productivity wins – The competition between applications is not for the type of crop grown, but for the land.
- The environment wins – due to increased resource efficiency and productivity of food and feed crops.
- Farmers win – because they have more options for selling stock to different markets.
- Market stability wins – due to increased global availability of food and feed crops.
- Feed security wins – due to the high value of the protein-rich co-products of food and feed crops.
- Food security wins – due to the increased overall availability of edible crops that can be stored and flexibly distributed.
-
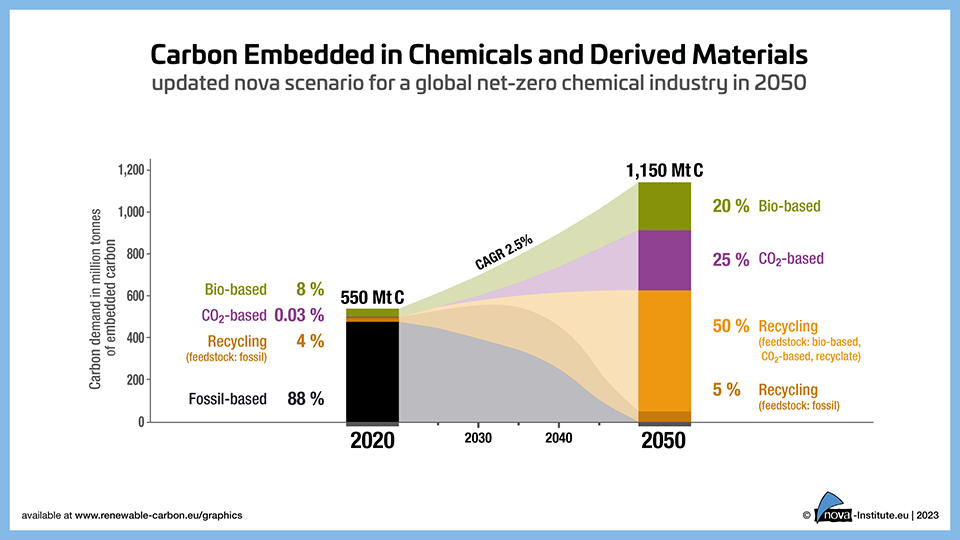
Explorative Scenario – Carbon Embedded in Chemicals and Derived Materials (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy
1 Page
1204 Downloads
1204 Downloads
2023-10
FREE
Free Shipping1204
DownloadsFigure from the RCI Carbon Flows Report 2023The nova October 2023 update shows a steady increase in the share of bio-based chemicals from 8% in 2020 to 20% in 2050. CO2-based chemicals require a lot of investment to become relevant after 2030, with strong growth between 2040 and 2050. The recycling of virgin fossil chemicals and plastics dominates the recycling sector until 2035. After 2035, bio-based, CO2-based and recyclates increasingly dominate the recycling sector. -
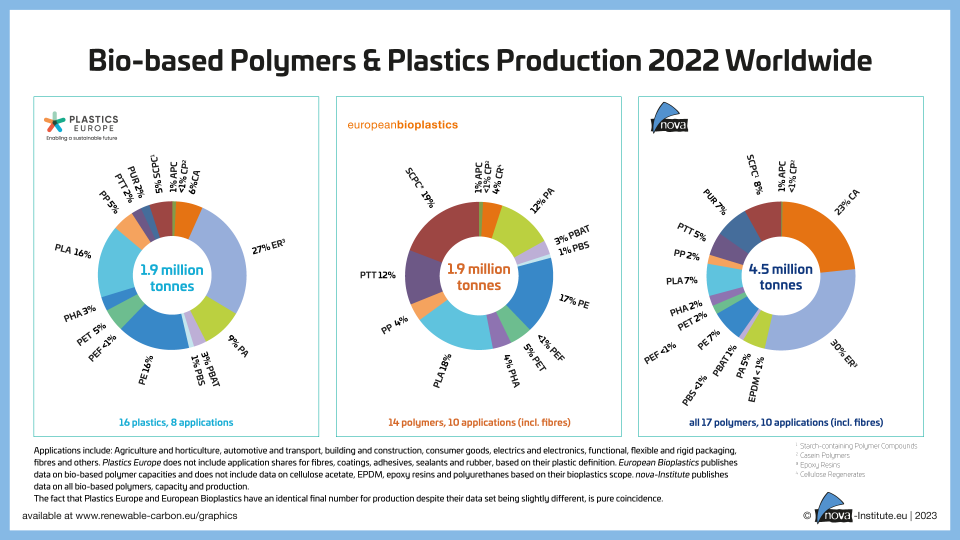
Bio-based Polymers & Plastics Production 2022 Worldwide (PNG)
Markets & Economy
1 Page
531 Downloads
531 Downloads
2023-10
FREE
531
Downloads -
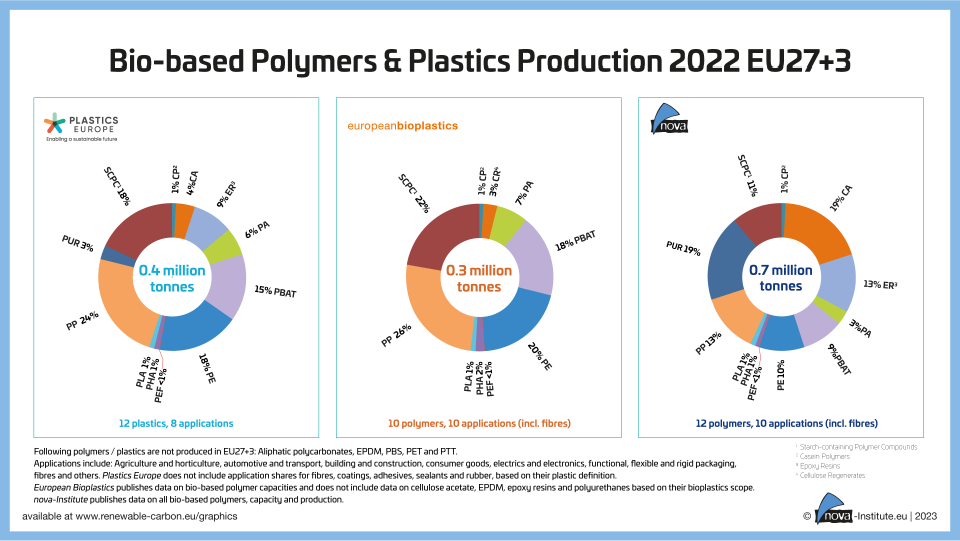
309 Downloads
2023-10
FREE
309
Downloads -
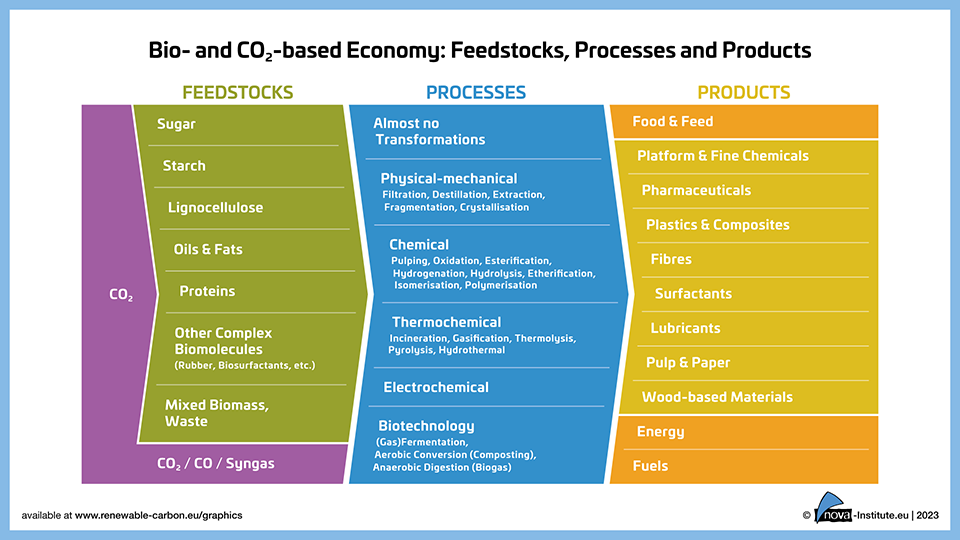
“Bio- and CO2-based Economy: feedstocks, processes and products” − Graphic – Update
Markets & Economy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
3411 Downloads
3411 Downloads
2023-09
FREE
3411
Downloads -
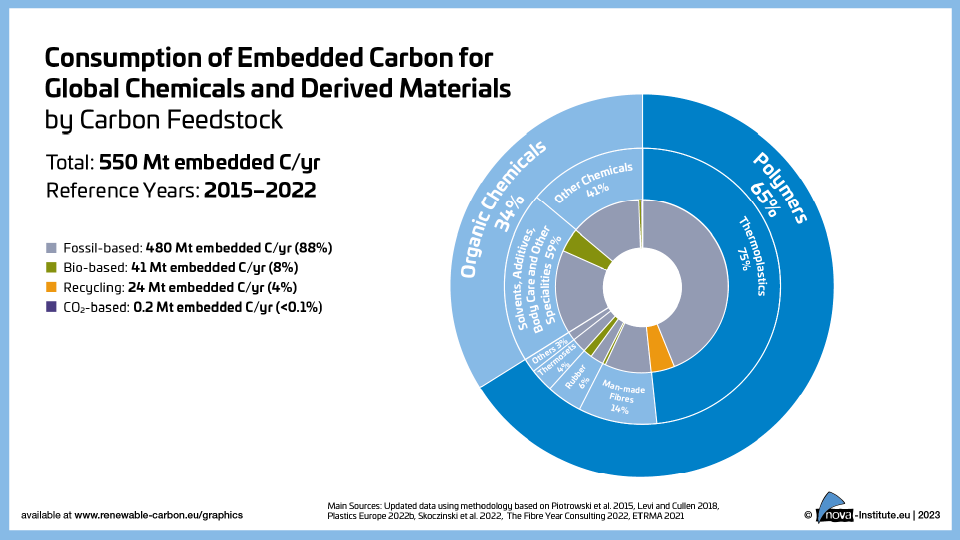
Consumption of Embedded Carbon for Global Chemicals and Derived Materials by Carbon Feedstock (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy
1 Page
120 Downloads
120 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping120
DownloadsFigure from the RCI Carbon Flows Report 2023
-
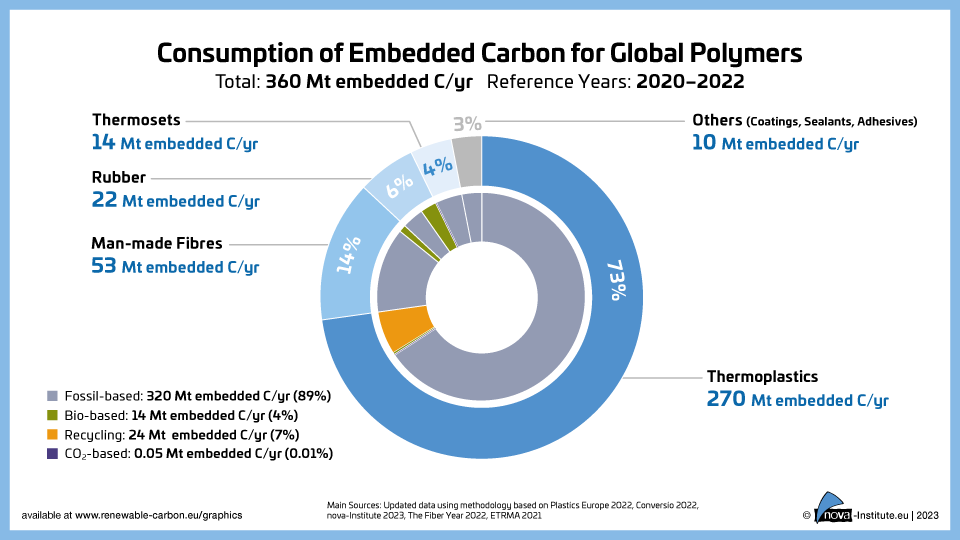
Consumption of Embedded Carbon for Global Polymers (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy
1 Page
134 Downloads
134 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping134
DownloadsFigure from the RCI Carbon Flows Report 2023
-
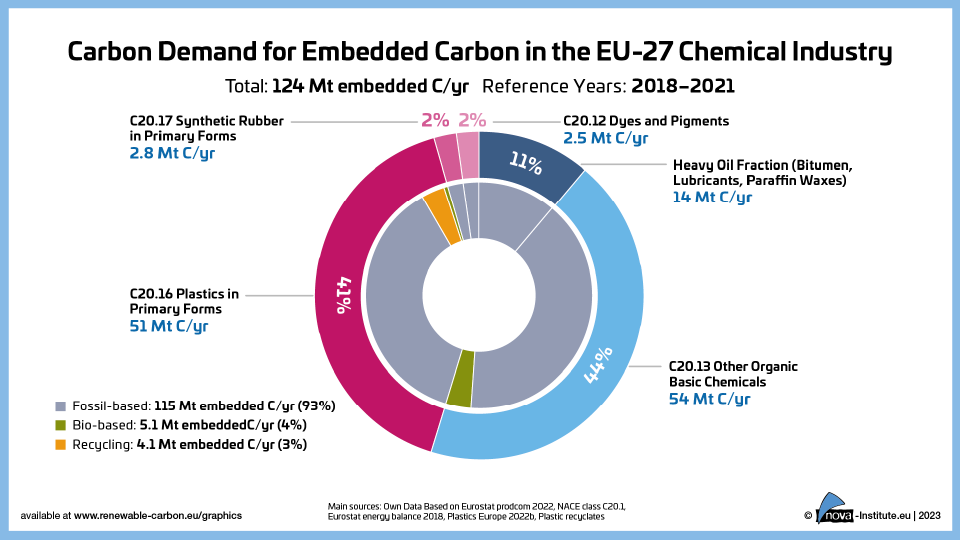
Carbon Demand for Embedded Carbon in the EU-27 Chemical Industry (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy
1 Page
154 Downloads
154 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping154
DownloadsFigure from the RCI Carbon Flows Report 2023
-
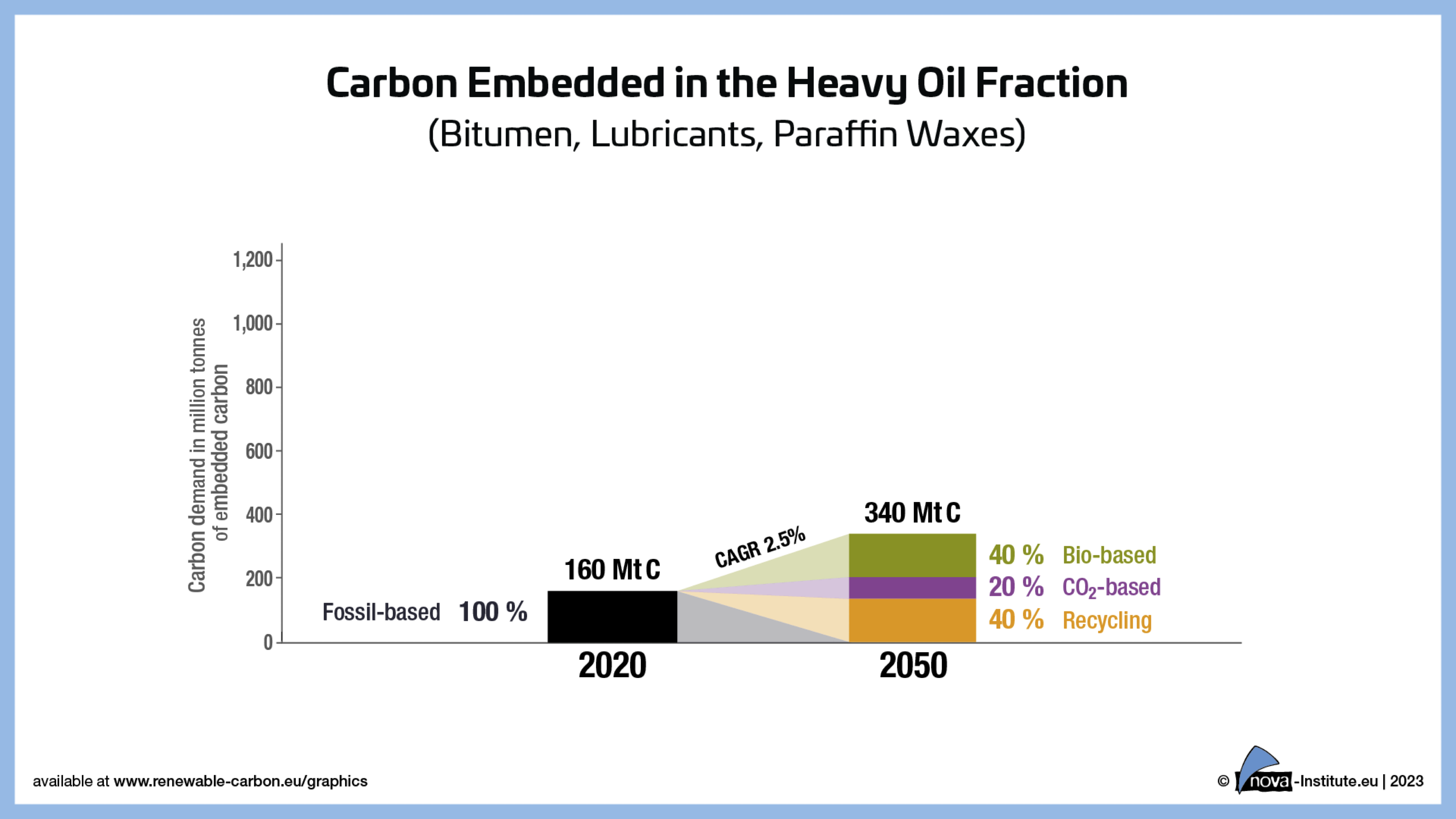
Explorative Scenario – Carbon Embedded in the Heavy Oil Fraction. (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy
1 Page
56 Downloads
56 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping56
DownloadsFigure from the RCI Carbon Flows Report 2023
-
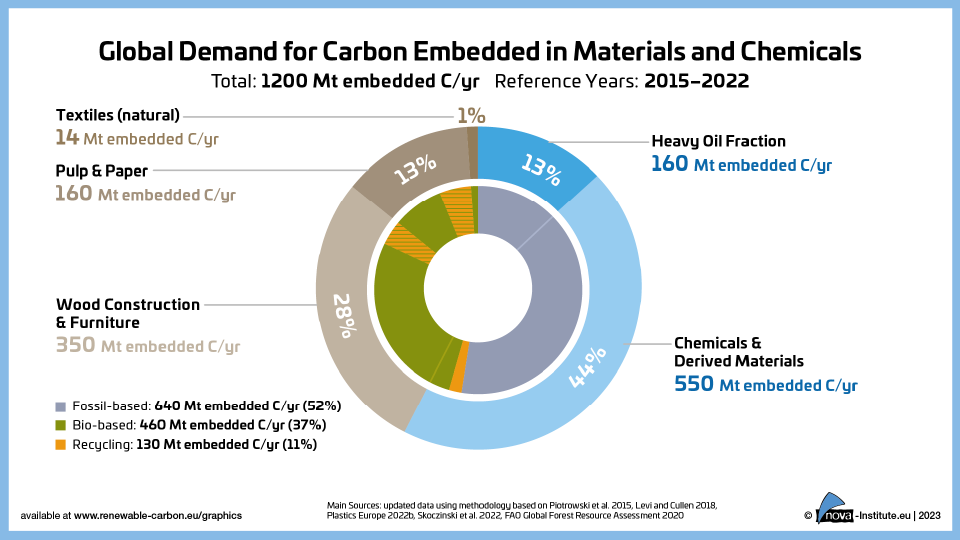
Global Demand for Carbon Embedded in Materials and Chemicals (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy
1 Page
265 Downloads
265 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping265
DownloadsFigure from the RCI Carbon Flows Report 2023
-
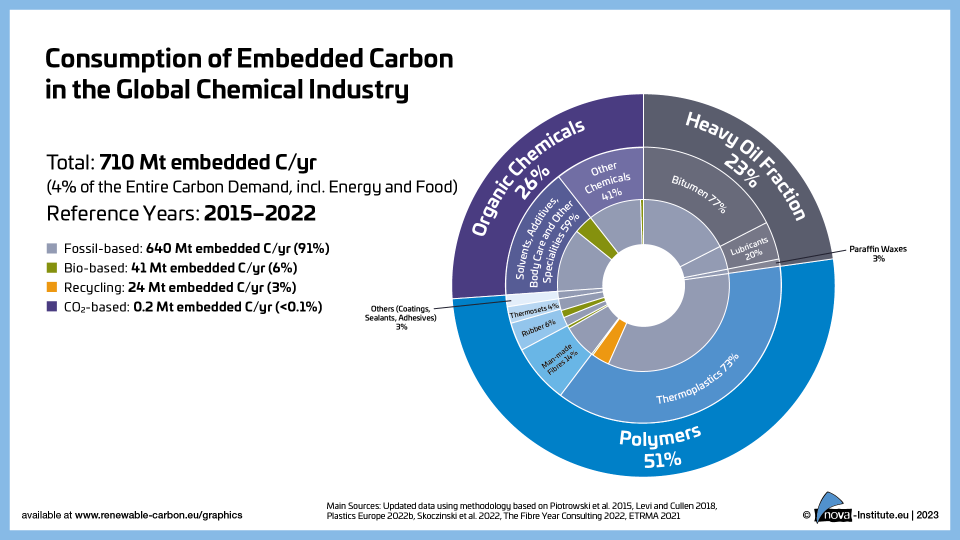
Consumption of Embedded Carbon in the Global Chemical Industry (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy
1 Page
140 Downloads
140 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping140
DownloadsFigure from the RCI Carbon Flows Report 2023
-
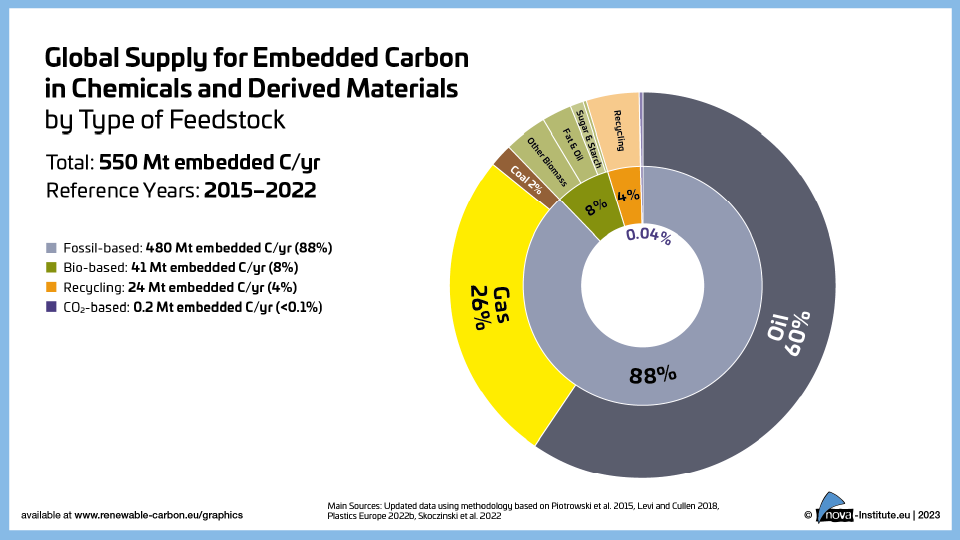
Global Supply for Embedded Carbon in Chemicals and Derived Materials by Type of Feedstock (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy
1 Page
181 Downloads
181 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping181
DownloadsFigure from the RCI Carbon Flows Report 2023
-
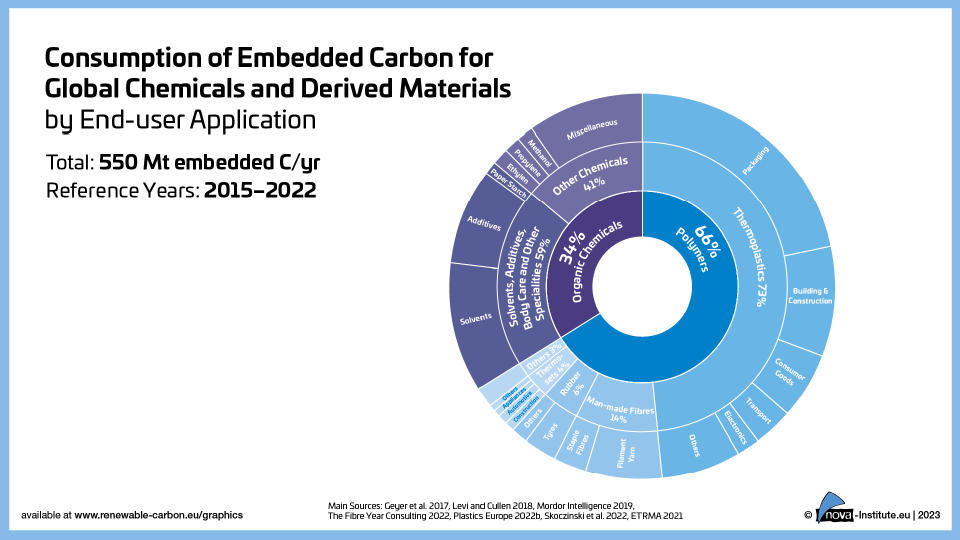
Consumption of Embedded Carbon for Global Chemicals and Derived Materials by End-user Application (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy
1 Page
125 Downloads
125 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping125
DownloadsFigure from the RCI Carbon Flows Report 2023
-
Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) Shapes the Future of the Chemicals and Materials Sector
Markets & Economy, Policy
3 Pages
139 Downloads
139 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping139
DownloadsFrom international brands to leading chemical and bioeconomy companies to innovative start-ups for CO2 utilisation, companies are collaborating to guide a smart transition from fossil carbon to renewable carbon. The Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) (www.renewable-carbon-initiative.com) was created after observing the struggles of the chemical and material industriesin facing the enormous challenges to meet the climate goals set by the European Union and the sustainability expectations held by societies around the globe. It was clear that the industry has to go beyond using renewable energy and also consider their raw materials. Because decarbonisation is not an option for the chemical and material sector, as it is entirely based on the use of carbon, an alternative strategy is required: defossilisation through renewable carbon – carbon from above the ground: biomass, CO2 and recycling.
-
RCI’s scientific background paper: “Making a case for Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) – It is much more than just a carbon removal technology” (July 2023)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
48 Pages
2113 Downloads
2113 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping2113
DownloadsThis scientific background paper highlights the importance of Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) and the need for more political recoginition and support for CCU.
CCU enables the substitution of fossil carbon in sectors where carbon is necessary, supports the full defossilisation of the chemical and derived material industries, creates a circular economy, reduces the emission gap, promotes sustainable carbon cycles, fosters innovation, generates local value and stimulates job growth.
CCU is much more than a carbon removal technology: the technology offers multiple solutions to pressing problems of our modern world and can support several Sustainable Development Goals if implemented properly.
In total, 14 different benefits and advantages of CCU are described and discussed in the paper. A key advantage is that CCU supplies renewable carbon to – and thereby substitutes fossil carbon in – sectors that will require carbon in the long run. This includes the chemical sectors and products like polymers, plastics, solvents, paints, detergents, cosmetics or pharmaceuticals. But CCU is also essential to a long-term net-zero strategy, crucial for creating a sustainable circular economy, providing solutions for scaling up the renewable energy system, and bringing multiple benefits for innovation and business.
The relevance of the technology is not yet accepted in Europe, but the RCI wants to make a very clear statement: CCU is a central pillar for the biggest transformation of the chemical and material industry since the industrial revolution.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/VYKR3129
-
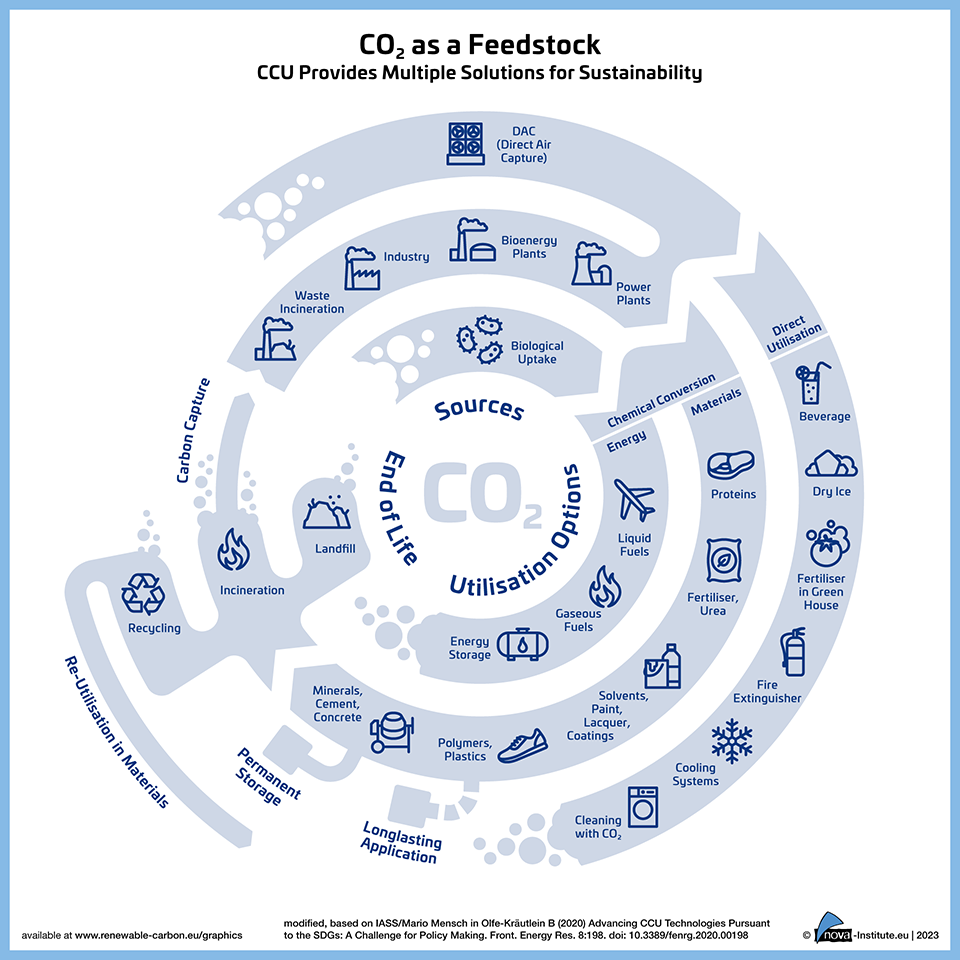
565 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping565
DownloadsCarbon Capture and Utilization (CCU) provides multiple solutions for sustainability