Showing 1–20 of 325
-
Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) Webinar slides – April 2024 (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Technology
43 Pages
3 Downloads
3 Downloads
2024-05
FREE
Free Shipping3
DownloadsThis document contains a generic set of slides to introduce the concept of renewable carbon and the Renewable Carbon Initiative. The focus of this webinar was the upcoming position paper on Chemical and Physical Recycling.
In addition, RCI member BASF, in person of Christian Krueger (Chemical Recycling | BASF Net Zero Accelerator) was a speaker at this webinar, given the focus topic of this webinar and BASF’s expertise in the
recycling industry. -
CO2-based Fuels and Chemicals Conference 2024 (Proceedings, PDF)
NewMarkets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2024-05
150 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Add to
cartThe proceedings of the CO2-based Fuels and Chemicals Conference 2024 (17-18 April 2024, https://co2-chemistry.eu) contain all released presentations, the conference journal, and the press release of the three winners of the Innovation Award “Best CO2 Utilisation 2024″.
-
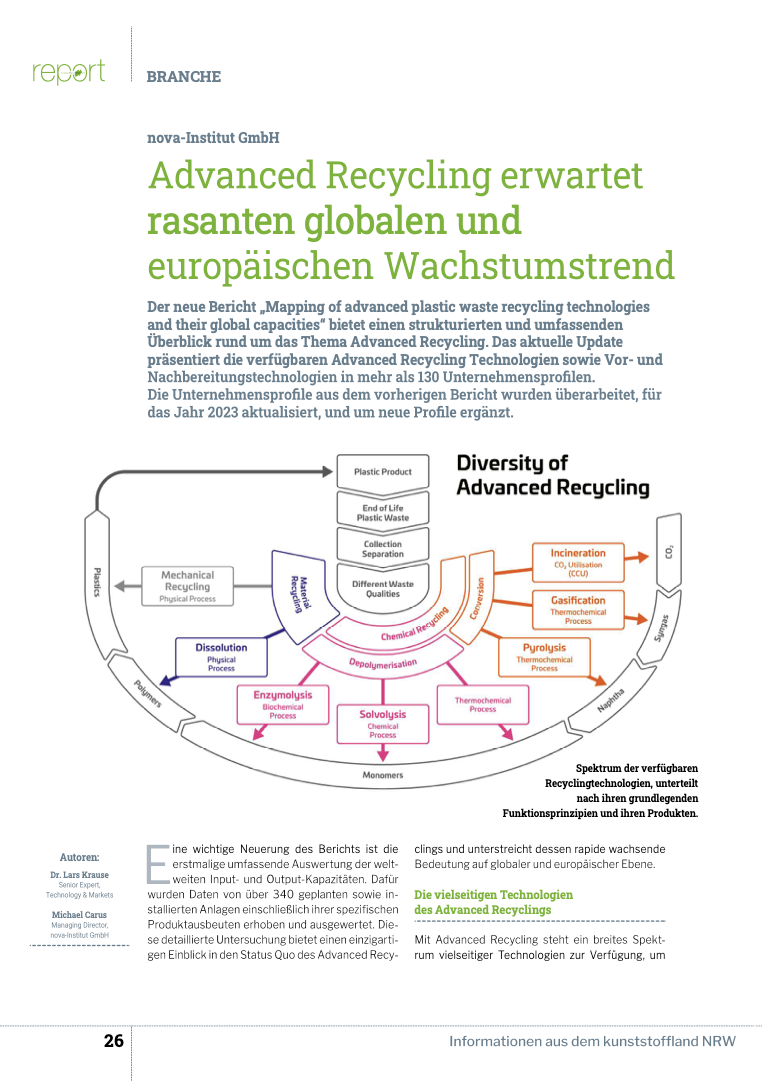
Advanced Recycling erwartet rasanten globalen und europäischen Wachstumstrend (PDF)
Markets & Economy
3 Pages
17 Downloads
17 Downloads
2024-04
FREE
17
DownloadsDer neue Bericht „Mapping of advanced plastic waste recycling technologies and their global capacities“ bietet einen strukturierten und umfassenden Überblick rund um das Thema Advanced Recycling. Das aktuelle Update präsentiert die verfügbaren Advanced Recycling Technologien sowie Vor- und Nachbereitungstechnologien in mehr als 130 Unternehmensprofilen. Die Unternehmensprofile aus dem vorherigen Bericht wurden überarbeitet, für das Jahr 2023 aktualisiert, und um neue Profile ergänzt.
Quelle: Advanced Recycling erwartet rasanten globalen und europäischen Wachstumstrend – aus kunststoffland NRW report 01/2024, 26-28
-
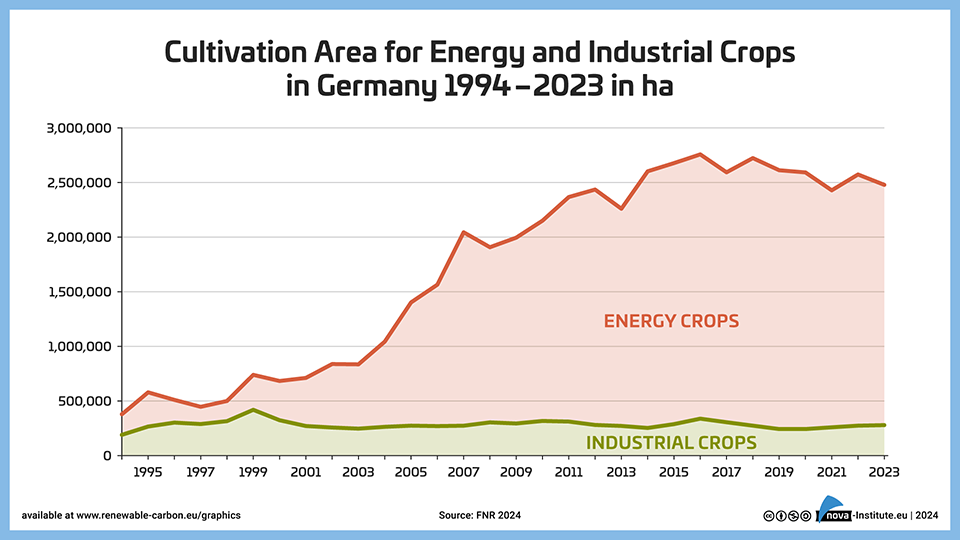
Cultivation Area for Energy and Industrial Crops in Germany 1994-2023 in ha − Graphic
Markets & Economy
1 Page
437 Downloads
437 Downloads
2024-04
FREE
437
Downloads -
Cellulose Fibres Conference 2024 (Proceedings, PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2024-04
150 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Add to
cartThe conference covered the entire value chain, from lignocellulose, chemical pulp, cellulose fibres such as rayon, viscose, modal or lyocell and new developments to a wide range of applications:
Textiles from renewable fibres, non-wovens such as wet wipes as well as new areas such as composites, hygiene, packaging or nanocellulose in the food industry. The conference offered deep insights into the promising future of cellulose fibres, which perfectly fits the current trends of circular economy, recycling and sustainable carbon cycles.The Cellulose Fibres Conference Proceedings (https://cellulose-fibres.eu, 13-14 March 2024, Cologne, hybrid) include all released conference presentations, the conference journal, sponsor documents, a Fiber2Fashion Knowledgepaper and the conference press release.
-
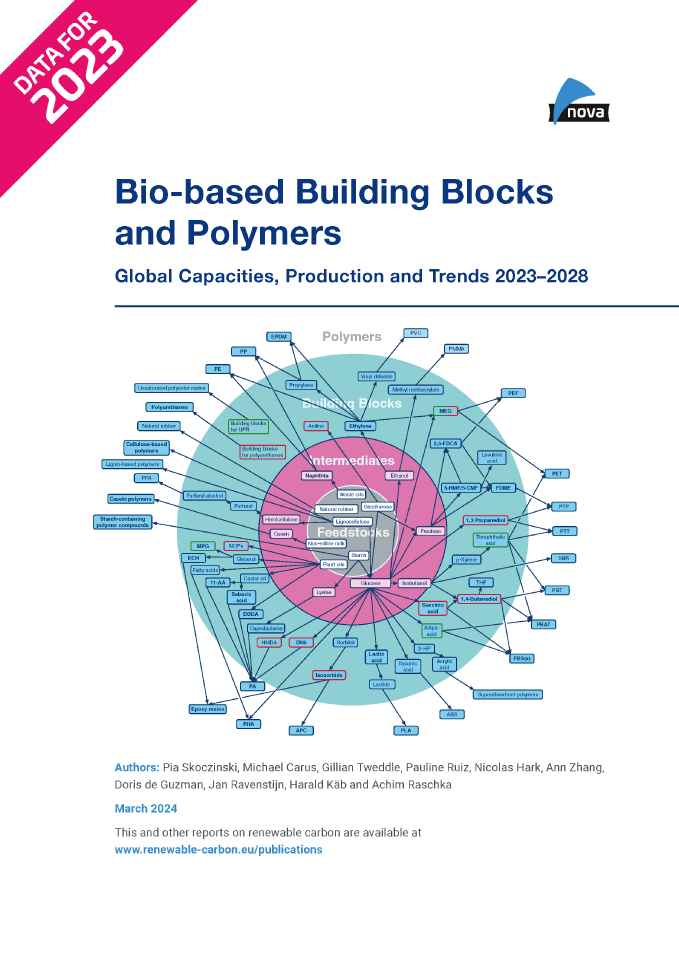
Bio-based Building Blocks and Polymers – Global Capacities, Production and Trends 2023–2028 – Short Version (PDF)
NewMarkets & Economy
28 Pages
970 Downloads
970 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
970
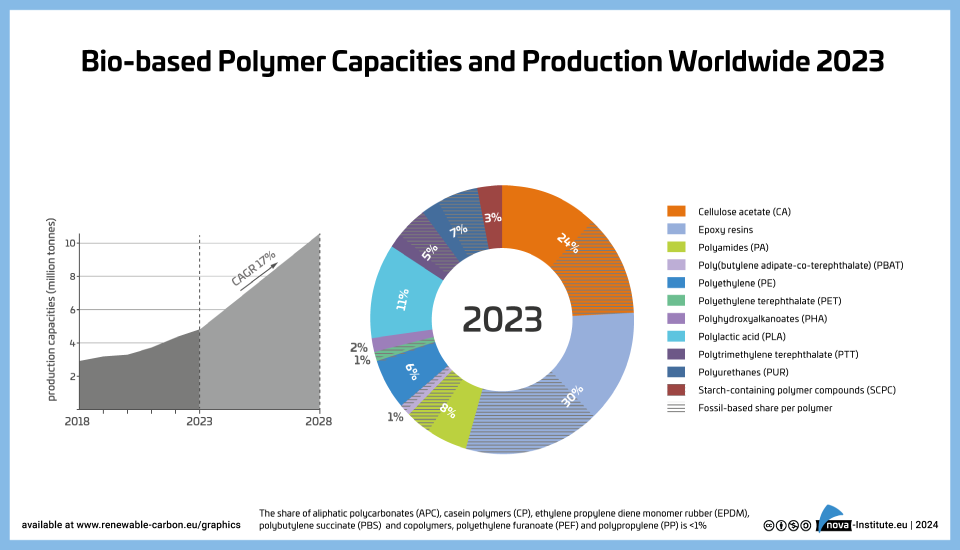
DownloadsNew report released on the global bio‑based polymer market 2023 – a deep and comprehensive insight into a dynamically growing market
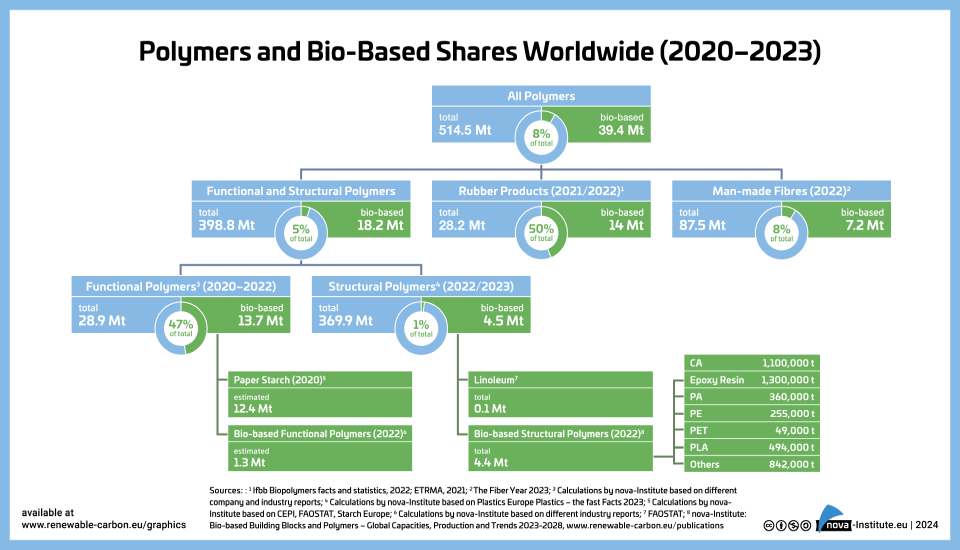
The year 2023 was a promising year for bio‑based polymers: PLA capacities have been increased by almost 50 %, and at the same time polyamide capacities are steadily increasing, as well as epoxy resin production. Capacities for 100 % bio-based PE have been expanded and PE and PP made from bio‑based naphtha are being further established with growing volumes. Current and future expansions for PHAs are still on the horizon. After hinting at a comeback in 2022 bio-based PET production dropped in 2023 by 50 %.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/VXTH2416
-
96 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
96
Downloads -
89 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
89
Downloads -
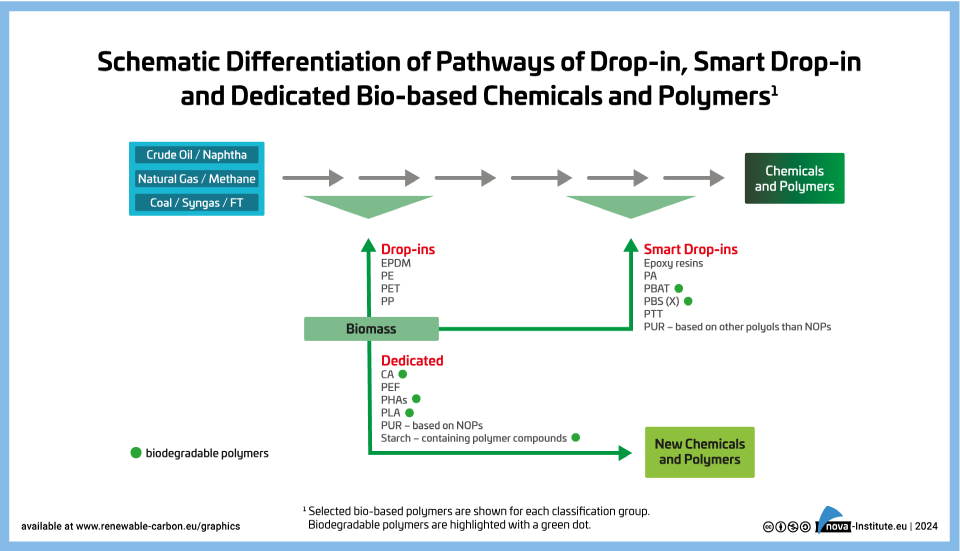
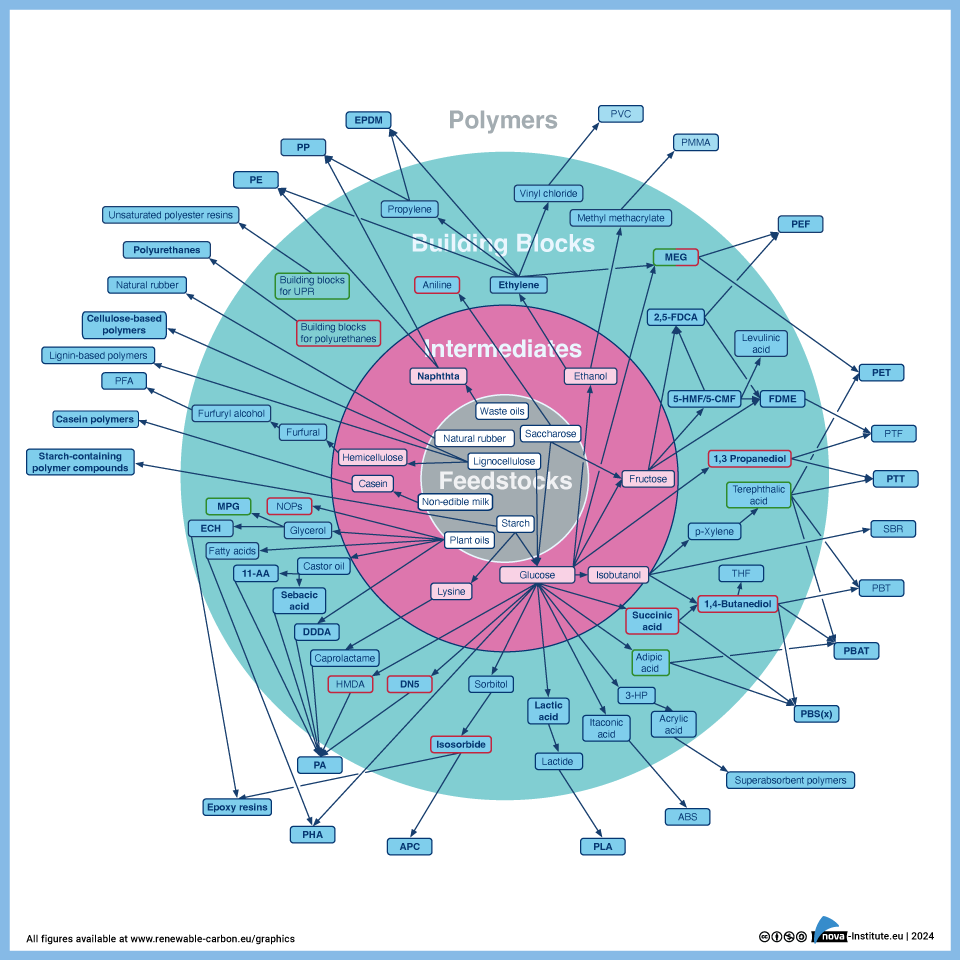
Schematic Differentiation of Pathways of Drop-in, Smart Drop-in and Dedicated Bio-based Chemicals and Polymers (PNG)
Markets & Economy
1 Page
47 Downloads
47 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
47
Downloads -
Bio-based Building Blocks and Polymers – Global Capacities, Production and Trends 2023–2028 (PDF)
NewMarkets & Economy
438 Pages

2024-03
3,000 € – 10,000 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Select
licenceNew report released on the global bio‑based polymer market 2023 – a deep and comprehensive insight into a dynamically growing market
The year 2023 was a promising year for bio‑based polymers: PLA capacities have been increased by almost 50 %, and at the same time polyamide capacities are steadily increasing, as well as epoxy resin production. Capacities for 100 % bio-based PE have been expanded and PE and PP made from bio‑based naphtha are being further established with growing volumes. Current and future expansions for PHAs are still on the horizon. After hinting at a comeback in 2022 bio-based PET production dropped in 2023 by 50 %.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/VXTH2416
-
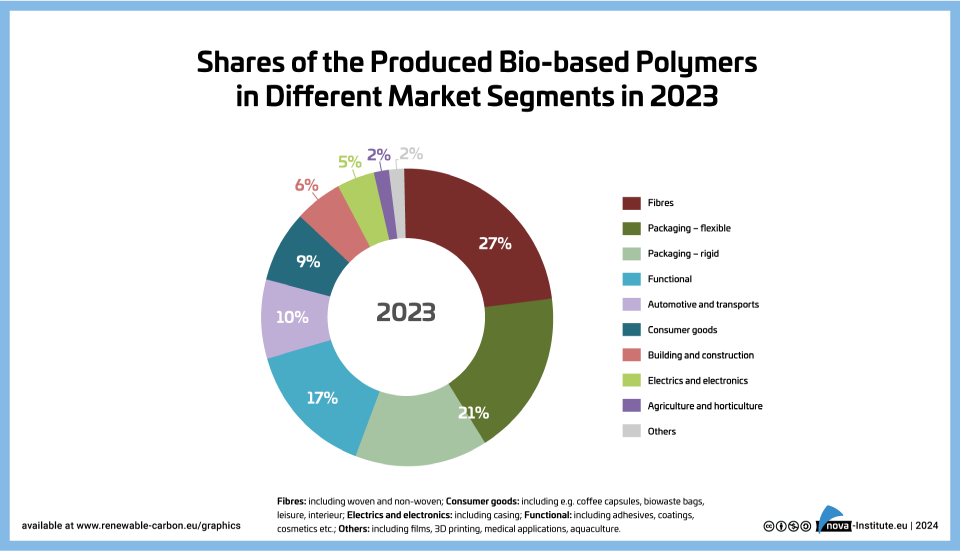
Shares of Produced bio-based polymers in different market segments (PNG)
Markets & Economy
1 Page
81 Downloads
81 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
81
Downloads -
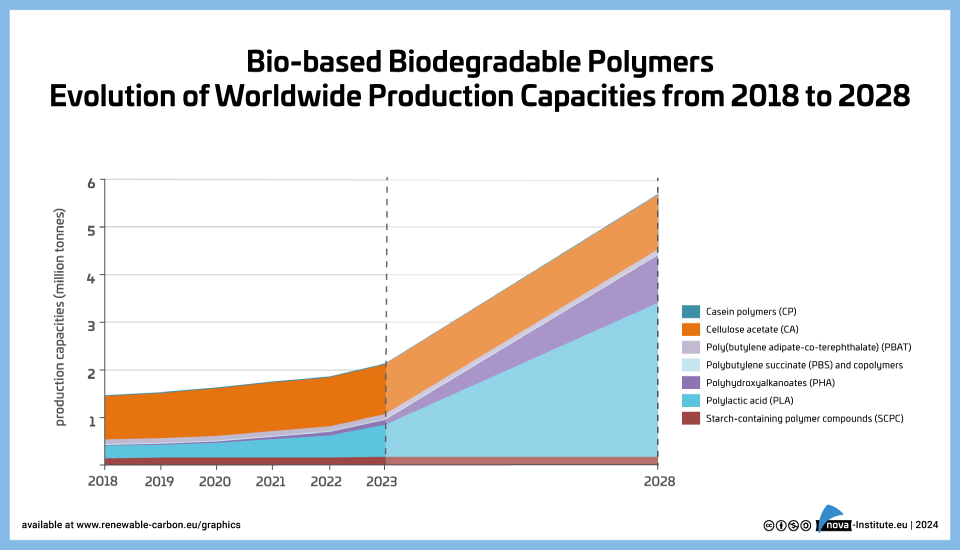
Bio-based Biodegradable Polymers Worldwide Production Capacities 2018-2028 (PNG)
Markets & Economy
1 Page
79 Downloads
79 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
79
Downloads -
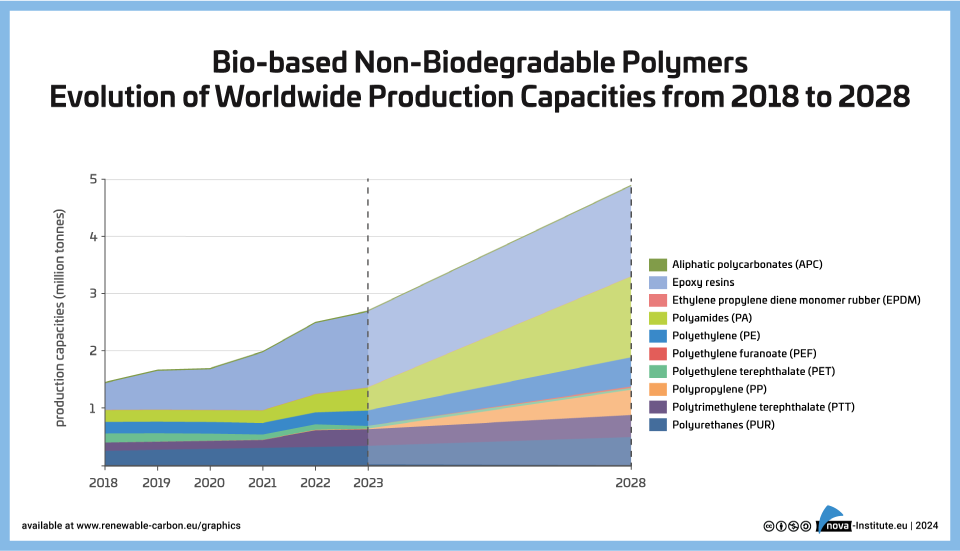
Bio-based Non-Biodegradable Polymers Evolution of Worldwide Production Capacities (PNG)
Markets & Economy
1 Page
44 Downloads
44 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
44
Downloads -
60 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
60
Downloads -
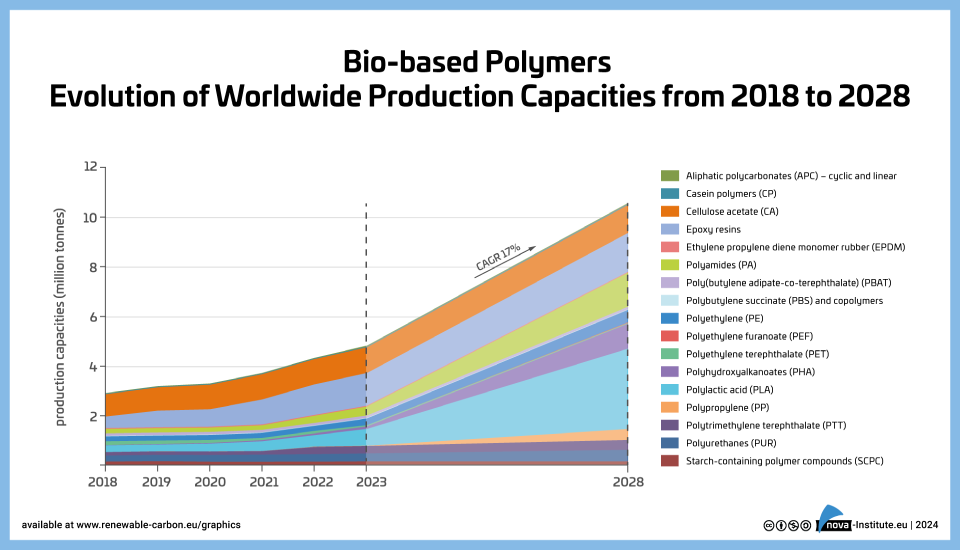
Bio-based Polymers – Evolution of worldwide production capacities from 2018 to 2028 (PNG)
Markets & Economy
1 Page
74 Downloads
74 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
74
Downloads -
83 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
83
Downloads -
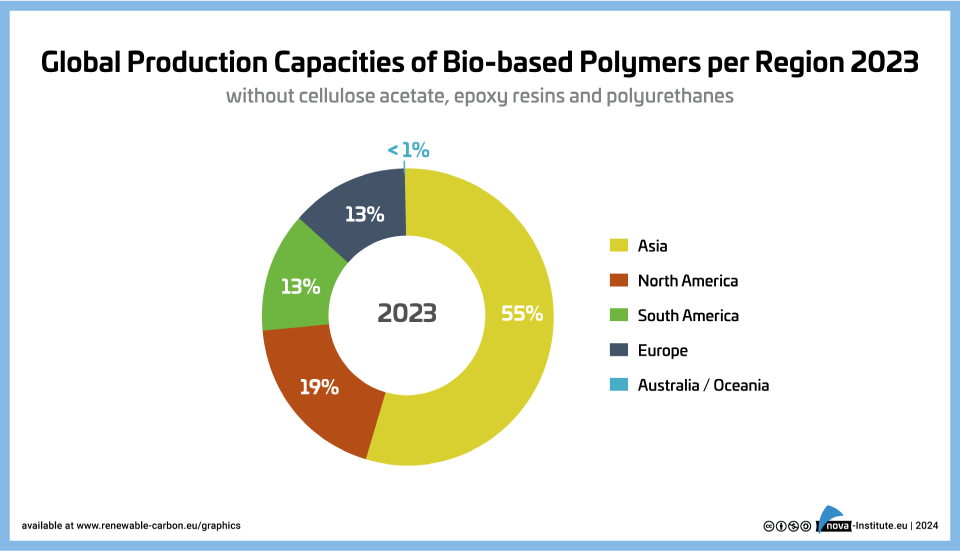
Global Production Capacities of Bio-based Polymers per Region 2022 (PNG)
Markets & Economy
1 Page
45 Downloads
45 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
45
Downloads -
121 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
121
Downloads -
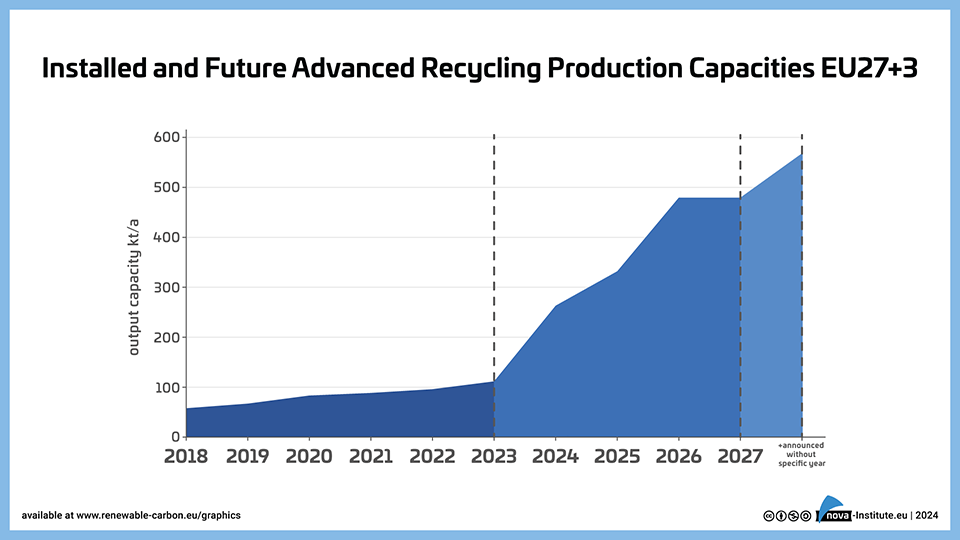
Installed and Future Advanced Recycling Production Capacities EU 27+3 (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Technology
1 Page
37 Downloads
37 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
37
DownloadsInstalled and future production capacities of naphtha, monomers and polymers through advanced recycling in the EU27+3.
-
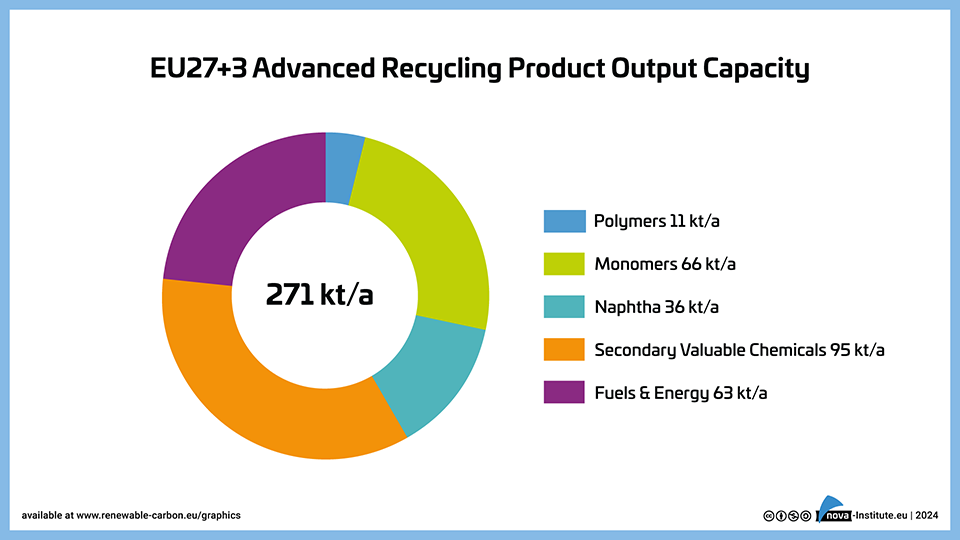
EU27+3 Advanced Recycling Product Output Capacity (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Technology
1 Page
31 Downloads
31 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
31
Downloads