Showing 41–60 of 531
-
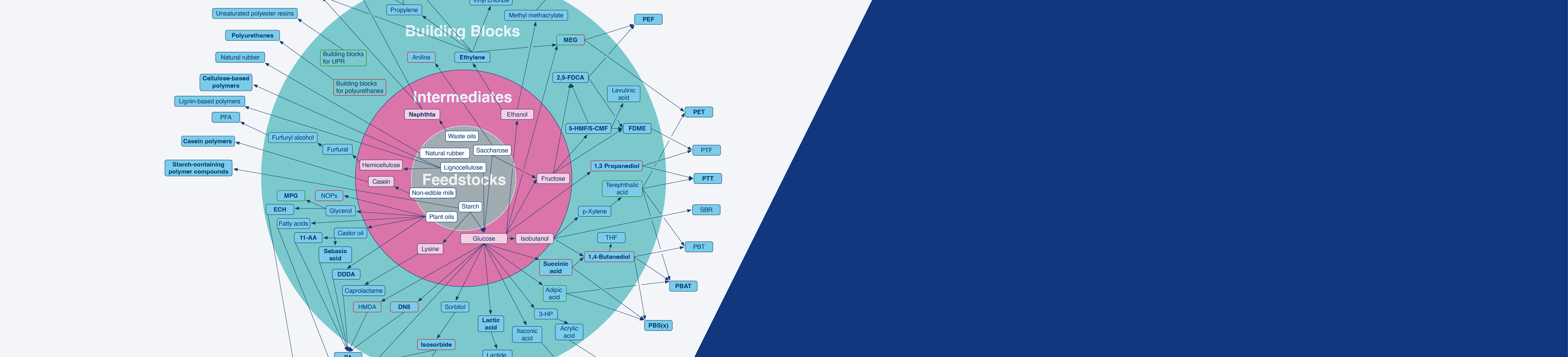
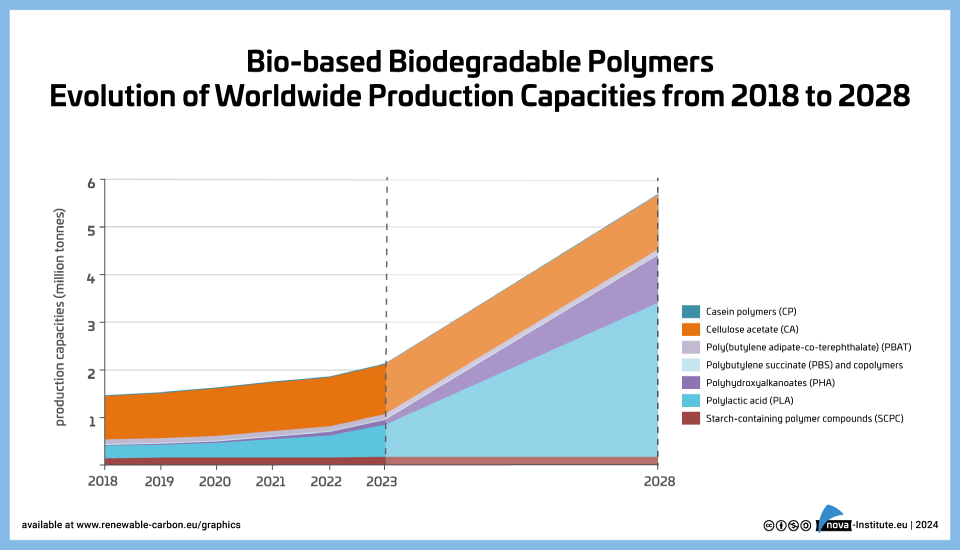
Bio-based Biodegradable Polymers Worldwide Production Capacities 2018-2028 (PNG)
Markets & Economy
1 Page
248 Downloads
248 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
248
Downloads -
EU27+3 Advanced Recycling Waste Input Capacity (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Technology
1 Page
82 Downloads
82 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
82
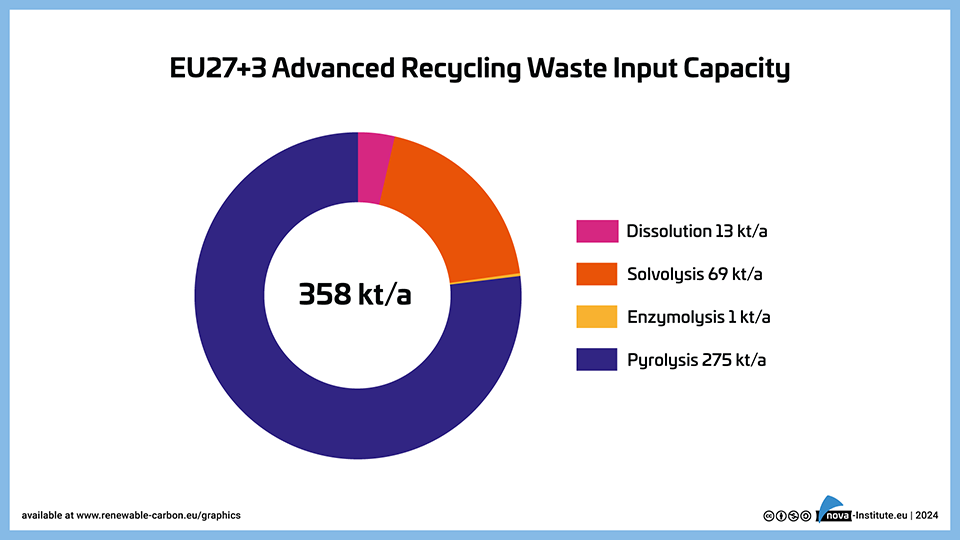
DownloadsInstalled input capacities for different advanced recycling technologies in EU27+3.
-
Installed and Future Advanced Recycling Production Capacities EU 27+3 (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Technology
1 Page
113 Downloads
113 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
113
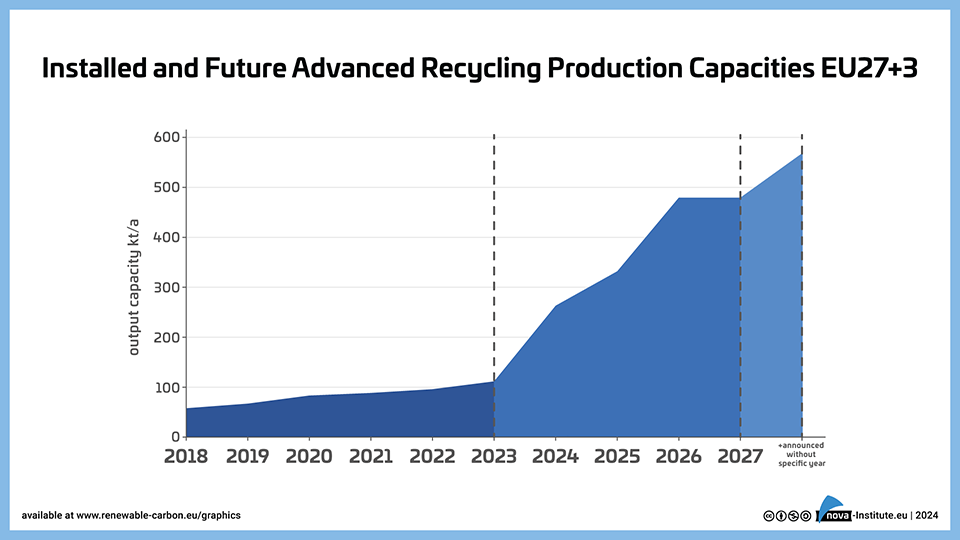
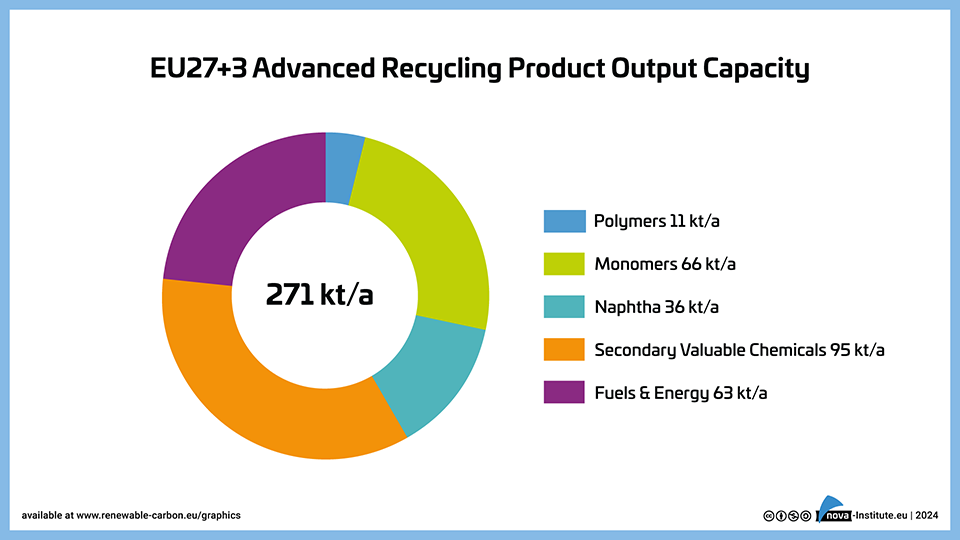
DownloadsInstalled and future production capacities of naphtha, monomers and polymers through advanced recycling in the EU27+3.
-
EU27+3 Advanced Recycling Product Output Capacity (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Technology
1 Page
84 Downloads
84 Downloads
2024-03
FREE
84
Downloads -
Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) Webinar slides – February 2024 (PDF)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
61 Pages
1589 Downloads
1589 Downloads
2024-02
FREE
Free Shipping1589
DownloadsThis document contains a generic set of slides to introduce the concept of renewable carbon and the Renewable Carbon Initiative. The focus of this webinar was the latest scientific background report: “Non-level Playing Field for Renewable Materials vs. Fossil in Life Cycle Assessments – Critical aspects of the JRC Plastics LCA methodology and its policy implications”.
In addition, three RCI member companies shared their expertise on renewable carbon, defossilisation and sustainable carbon cycles.
AllocNow (speaker: Daniel Bochnitschek) talked about how the increasing demand for sustainable and low carbon products is driving the need for specific and comprehensive information on product carbon footprints. AllocNow discussed why standardisation of sustainability accounting methodologies is critical and how a data-driven approach can help create transparency at scale.
Econic Technologies Ltd. (speaker: Liz Manning) spoke about the opportunities and challenges of quantifying the sustainability impact of key products in complex manufacturing supply chains.
SCS Global Services (speakers: Miguel Ruiz and Jéssica Marcon Bressanin) highlighted its certification activities, focusing on biofuels and circular materials schemes, as well as greenhouse gas accounting methodologies.
More information at https://renewable-carbon-initiative.com/media/library
-
Mapping of Advanced Plastic Waste Recycling Technologies and their Global Capacities (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Technology
276 Pages

2024-02
3,000 € – 10,000 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Select
licenceAdvanced recycling technologies are developing at a fast pace, with new players constantly appearing on the market, from start-ups to giants and everything in between – new plants are being built, new capacities are being achieved, and new partnerships are established. Due to these developments, it is difficult to keep track of everything. The report “Mapping of advanced plastic waste recycling technologies and their global capacities” aims to clear up this jungle of information providing a structured, in-depth overview and insight. It has an exclusive focus on profiling available technologies and providers of advanced recycling including the addition of new technologies and updated/revised profiles. Furthermore, for the first time a comprehensive evaluation of the global input and output capacities was carried out for which more than 340 planned as well as installed and operating plants including their specific product yields were mapped.
Further information:
The new report “Mapping of advanced plastic waste recycling technologies and their global capacities” differs from the old report “Chemical Recycling – Status, Trends and Challenges” as follows:- All technology provider profiles from the old report included + updated to 2023.
- Overall >120 technologies and providers (vs. >70 technologies and providers in the old report)
- Global capacities
In summary, this report is suitable for interested readers who have already dealt with the advanced recycling topic and are looking for an up-to-date overview of all identified providers and a detailed description of the technologies.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/WQHT8696
-
Mapping of Advanced Plastic Waste Recycling Technologies and their Global Capacities – Short Version (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Technology
12 Pages
1640 Downloads
1640 Downloads
2024-02
FREE
1640
DownloadsAdvanced recycling technologies are developing at a fast pace, with new players constantly appearing on the market, from start-ups to giants and everything in between – new plants are being built, new capacities are being achieved, and new partnerships are established. Due to these developments, it is difficult to keep track of everything. The report “Mapping of advanced plastic waste recycling technologies and their global capacities” aims to clear up this jungle of information providing a structured, in-depth overview and insight. It has an exclusive focus on profiling available technologies and providers of advanced recycling including the addition of new technologies and updated/revised profiles. Furthermore, for the first time a comprehensive evaluation of the global input and output capacities was carried out for which more than 340 planned as well as installed and operating plants including their specific product yields were mapped.
Further information:
The new report “Mapping of advanced plastic waste recycling technologies and their global capacities” differs from the old report “Chemical Recycling – Status, Trends and Challenges” as follows:- All technology provider profiles from the old report included + updated to 2023.
- Overall >120 technologies and providers (vs. >70 technologies and providers in the old report)
- Global capacities
In summary, this report is suitable for interested readers who have already dealt with the advanced recycling topic and are looking for an up-to-date overview of all identified providers and a detailed description of the technologies.
-
RCI’s Internal Survey: „How to enable the transition from fossil to renewable carbon in the chemical and material sector“ (January 2024)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
3 Pages
509 Downloads
509 Downloads
2024-01
FREE
509
DownloadsIn a comprehensive member survey in summer 2023, the Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) has collected ideas and opinions on what is needed to enable the transition from fossil to renewable carbon in Europe. The feedback paints a clear picture and is a call to action.
The European chemicals and materials sector is under pressure. RCI members, representing a wide range of these sectors, see many common elements in the key challenges and how to address them. High energy and raw material prices, as well as the need to defossilise carbon demand to meet CO2 emission targets, particularly in so-called “Scope 3” emissions, are some of the issues frequently raised.
-
1143 Downloads
2024-01
FREE
1143
Downloads -
Nora and her flyphone on renewable carbon (Comic)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
2 Pages
686 Downloads
686 Downloads
2024-01
FREE
686
Downloads -
RCI’s scientific background report: “Non-level playing field for renewable materials vs. fossil in Life Cycle Assessments” (January 2024)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
44 Pages
1287 Downloads
1287 Downloads
2024-01
FREE
1287
DownloadsCritical aspects of the JRC Plastics LCA methodology and its policy implications
This RCI Scientific Background Report was mainly motivated by a study published by JRC in 2021 with the title: “LCA of alternative feedstocks for plastic products”, commonly referred to as the JRC Plastics LCA Method (Nessi et al. 2021).
Alternative feedstocks refer to the same three feedstocks that RCI defines as renewable carbon: biomass, CO2 utilisation and recycling. The study describes a methodology developed by the JRC to compare the environmental performance of alternative feedstocks with fossil-based plastic products. However, the methodology has also been subject to criticism from various stakeholders, mainly from the bio-based sector, eliciting responses from the JRC.
This RCI report is mainly aiming to provide additional context to highlight issues that might arise with implementation of the JRC Plastics LCA methodology, and dives deeper into five aspects:
- The fossil footprint is likely underestimated, not transparent and lacks regional differentiation
- Renewable feedstocks are more cirtically evaluated than fossil feedstocks
- Methodological inconsistency and different regulatory support between energy and material use of renewable feedstocks
- Biogenic/Atmospheric carbon uptake cannot be transparently visualised at factory in PEF / JRC Plastics LCA methodologies
- The methodology should acknowledge the wider interface of sustainability assessment, policy design and landscape
The report contains several recommendations to remedy the above-mentioned aspects.
-
Advanced Recycling Conference 2023 (Proceedings)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2023-12
150 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Add to
cartThe proceedings of the Advanced Recycling Conference 2023 (28-29 November, https://advanced-recycling.eu) contain conference presentations, the conference journal, sponsor documents and the press release. Download of the conference journal incl. the program.
-
The Green-Claims-Directive – What Companies Need to Know (PNG)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
401 Downloads
401 Downloads
2023-12
FREE
401
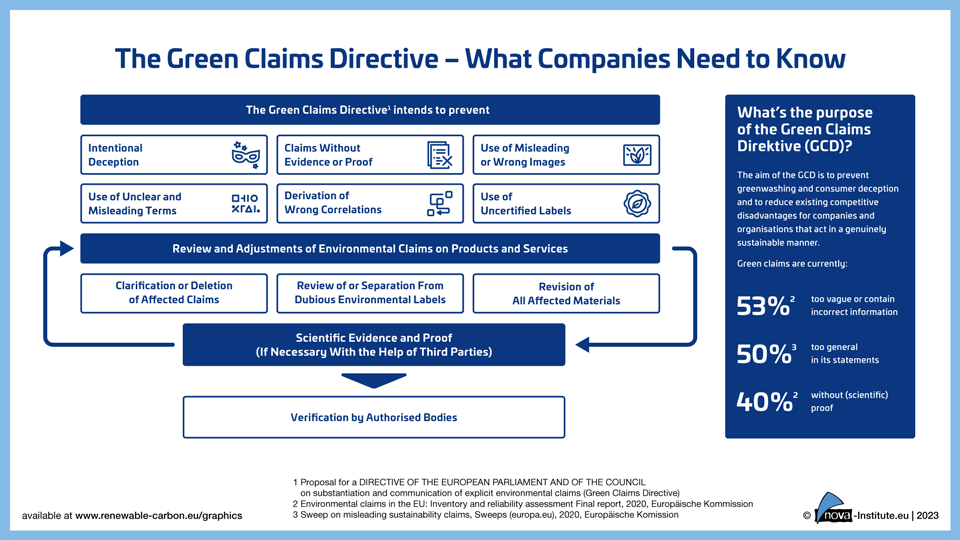
DownloadsSo far, companies can use terms such as “climate-neutral”, “recyclable”, “environmentally friendly” or self-created logos, which are intended to emphasise the environmental friendliness of a product, to advertise products and services without third-party verification. With the proposal for the Green Claims Directive, the EU wants to change this practice. The aim is to test and certify the green claims by an external testing authority. This would require a scientific verification. This graphic provides companies with an initial overview of what the new EU proposal could mean for them.
Lean more about this topic and join our nova-Session “Sustainability Claims under New EU Legislation” (7 February, 13:00-15:00 CET, online): https://events.renewable-carbon.eu/event/green-claims-directive
-
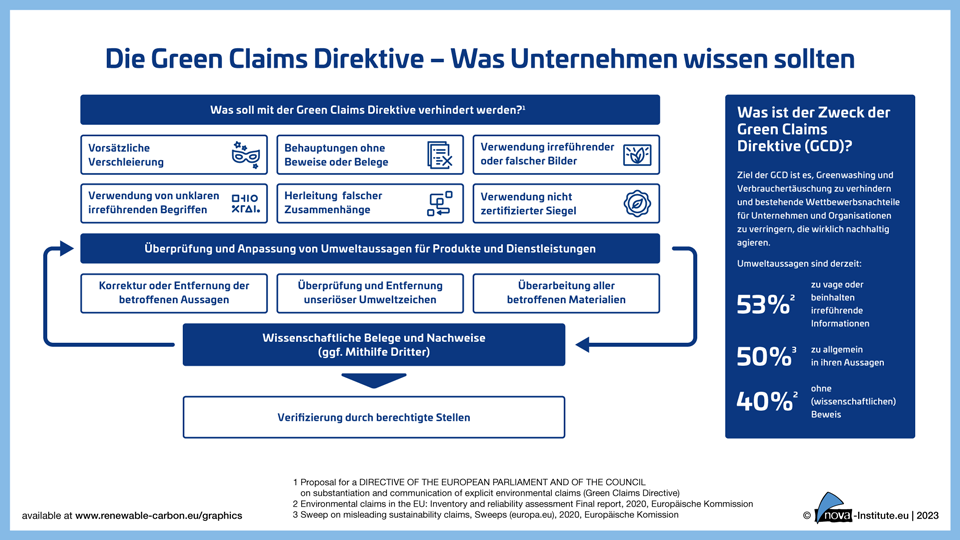
The Green-Claims-Directive – Was Unternehmen wissen sollten (PNG)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
124 Downloads
124 Downloads
2023-12
FREE
124
DownloadsBisher können Firmen Begriffe wie “klimaneutral, “recycelbar”, “umweltfreundlich” oder selbst kreierte Logos, welche die Umweltfreundlichkeit eines Produkts hervorheben sollen, ohne Prüfung durch Dritte für die Bewerbung von Produkten und Services nutzen. Mit dem Vorschlag zur Green Claims Richtlinie will die EU diese Praxis ändern. Ziel ist die Prüfung und Zertifizierung der sogenannten green claims (Umweltaussagen) durch eine externe Prüfstelle. Notwendig dafür wird dann ein wissenschaftlicher Nachweis. Mit dieser Grafik können sich Unternehmen einen ersten Überblick darüber verschaffen, was mit dem neuen Vorschlag der EU auf sie zukommen könnte.Erfahren Sie mehr über dieses Thema und besuchen Sie unsere nova-Session “Sustainability Claims under New EU Legislation” (7. Februar, 13:00-15:00 CET, online): https://events.renewable-carbon.eu/event/green-claims-directive -
RCI’s scientific background report: “The use of food and feed crops for bio-based materials and the related effects on food security – Promoting evidence-based debates and recognising potential benefits” (June 2023) Short Version
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
2 Pages
804 Downloads
804 Downloads
2023-11
FREE
804
DownloadsPromoting Evidence-based Debates and Recognising Potential Benefits
This short version of the scientific paper highlights on two pages new insights into a hotly debated topic and urges for careful and evidence-based debates.
The paper aims to show that the well-known biomass debate is flawed, subjective and not fully based on evidence. What is detrimental to food security are, according to the World Food Programme in 2023, climate change, conflict, extreme inequalities in wealth distribution, heavy dependence on food imports from industrial countries, overconsumption of meat, losses along the value chain and the impact of the COVID pandemic. Competition between biomass uses is not mentioned among the relevant causes.
The use of biomass for industrial applications, does have the potential to replace fossil feedstocks and thus contribute to the urgently needed reduction of fossil carbon emissions into our atmosphere to mitigate climate change.
While not denying the dire need to combat world hunger, the authors of the paper argue that using food and feed crops for chemicals and materials will not necessarily exacerbate food insecurity, and in fact has the potential to cause multiple benefits for local and global food security, climate mitigation and other factors:
- The climate wins – Bio-based materials are part of the solution to achieve climate change mitigation.
- Land productivity wins – The competition between applications is not for the type of crop grown, but for the land.
- The environment wins – due to increased resource efficiency and productivity of food and feed crops.
- Farmers win – because they have more options for selling stock to different markets.
- Market stability wins – due to increased global availability of food and feed crops.
- Feed security wins – due to the high value of the protein-rich co-products of food and feed crops.
- Food security wins – due to the increased overall availability of edible crops that can be stored and flexibly distributed.
-
RCI’s scientific background report: “Case studies based on peer-reviewed Life Cycle Assessments – Carbon footprints of different carbon-based chemicals and materials” (November 2023)
Sustainability & Health
39 Pages
1831 Downloads
1831 Downloads
2023-11
FREE
1831
DownloadsIn this brochure, the RCI (https://renewable-carbon-initiative.com) presents five peer-reviewed LCA case studies – representing the highest possible scientific standard – that examine the carbon footprint of materials and products made from renewable carbon. These case studies are on products from RCI member companies Avantium (NL), BASF (DE), IFF (US), Lenzing (AT), Neste (FI) and all LCAs have been peer-reviewed by external experts. The LCAs have been summarised by experts of nova-Institutes sustainability team.
The case studies visualise that there are not only competitive materials and products made of renewable carbon already on the market, but that they also come with significantly lower carbon footprints ranging from 30–90%.
A key aspect of replacing fossil carbon with renewable carbon is the gained circularity of carbon. The less additional fossil carbon is added to our above-ground cycle of atmosphere, biosphere and technosphere, the smaller will be the amount of carbon emissions that have to be balanced out with expensive atmospheric removal and underground storage of carbon.
It is essential to recognise that the carbon footprint of renewable carbon-based materials is not automatically close to zero for two primary reasons:
- Fossil energy in the value chain
- Ongoing innovation and optimisation
All in all, the here presented materials and products show reduced carbon footprints already today, which lowers the remaining emissions gap so that less CO2 needs to be removed from the atmosphere in the future. At the same time, these materials and products still have significant potential to further reduce emissions in the future.
-
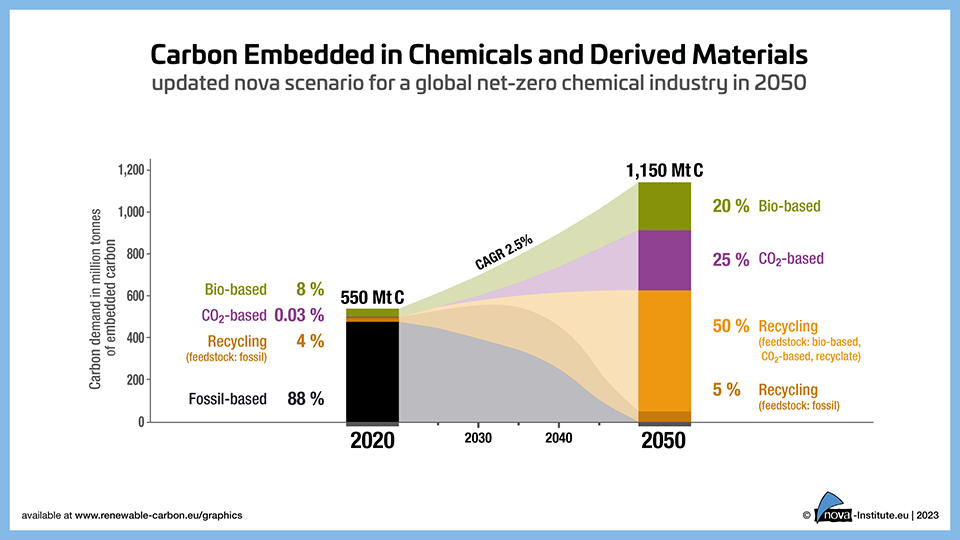
Explorative Scenario – Carbon Embedded in Chemicals and Derived Materials (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy
1 Page
776 Downloads
776 Downloads
2023-10
FREE
Free Shipping776
DownloadsFigure from the RCI Carbon Flows Report 2023The nova October 2023 update shows a steady increase in the share of bio-based chemicals from 8% in 2020 to 20% in 2050. CO2-based chemicals require a lot of investment to become relevant after 2030, with strong growth between 2040 and 2050. The recycling of virgin fossil chemicals and plastics dominates the recycling sector until 2035. After 2035, bio-based, CO2-based and recyclates increasingly dominate the recycling sector. -
162 Downloads
2023-10
FREE
162
Downloads -
334 Downloads
2023-10
FREE
334
DownloadsThis position paper describes that our understanding that new thinking and terminology are required to achieve climate targets and secure a sustainable carbon supply
Comprehensive carbon management goes beyond CO2 emissions, capture and long-term storage, to which it is often reduced to. It decouples the whole industry from fossil feedstock, eliminates the use of fossil carbon wherever possible and allocates renewable carbon (from biomass, CO2 and recycling) as efficiently and effectively as possible where carbon use is unavoidable. The aim is to achieve the lowest possible CO2 emissions, reducing the need for Carbon Dioxide Removal to achieve net zero, and to provide a secure supply of renewable carbon to all dependent industries such as chemicals and materials. Only when carbon is recognised as a raw material in carbon management strategies can truly sustainable carbon cycles be achieved. With a proper comprehensive carbon management, the carbon-reliant material and energy sectors will be defossilised and the remaining energy sector will be decarbonised. And only for the remaining share of truly unavoidable emissions, carbon dioxide removal and carbon capture and storage should come into play.
-
Joint Letter: Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) should be recognised as a Strategic Net Zero Technology in the EU Net Zero Industry Act (PDF)
Policy
2 Pages
63 Downloads
63 Downloads
2023-10
FREE
63
DownloadsA co-signed letter with CO2 Value Europe, Cefic – European Chemical Industry Council, the European Cement Association (CEMBUREAU), The Confederation of European Waste-to-Energy Plants (CEWEP), UPEI – the Voice of Europe’s Independent Fuel Suppliers, eFuel Alliance, Eurogas, The European Steel Association (EUROFER), FuelsEurope, Methanol Institute and the European Confederation of Fuel Distributors (ECFD) that calls on Members of the EU Parliament and EU Member States to take position to include CCU technologies as part – along with CCS – of the list of strategic net-zero technologies in the Net Zero Industry Act (NZIA).