Showing 101–120 of 234
-
RCI’s scientific background paper: “Making a case for Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) – It is much more than just a carbon removal technology” (July 2023)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
48 Pages
2083 Downloads
2083 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
Free Shipping2083
DownloadsThis scientific background paper highlights the importance of Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) and the need for more political recoginition and support for CCU.
CCU enables the substitution of fossil carbon in sectors where carbon is necessary, supports the full defossilisation of the chemical and derived material industries, creates a circular economy, reduces the emission gap, promotes sustainable carbon cycles, fosters innovation, generates local value and stimulates job growth.
CCU is much more than a carbon removal technology: the technology offers multiple solutions to pressing problems of our modern world and can support several Sustainable Development Goals if implemented properly.
In total, 14 different benefits and advantages of CCU are described and discussed in the paper. A key advantage is that CCU supplies renewable carbon to – and thereby substitutes fossil carbon in – sectors that will require carbon in the long run. This includes the chemical sectors and products like polymers, plastics, solvents, paints, detergents, cosmetics or pharmaceuticals. But CCU is also essential to a long-term net-zero strategy, crucial for creating a sustainable circular economy, providing solutions for scaling up the renewable energy system, and bringing multiple benefits for innovation and business.
The relevance of the technology is not yet accepted in Europe, but the RCI wants to make a very clear statement: CCU is a central pillar for the biggest transformation of the chemical and material industry since the industrial revolution.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/VYKR3129
-
180 Downloads
2023-07
FREE
180
DownloadsThis short document contains seven key policy messages the RCI advocates for to shape the future of the chemical and material industry. These seven messages are:
- Renewable carbon and comprehensive carbon management need to become integral guiding principles of policies to achieve truly sustainable carbon cycles.
- Adopt a precise definition of “non-fossil, sustainable” carbon and then adopt a legally binding target for 20% sustainable, non-virgin-fossil carbon content
- Suitable measures to support the 20% goal would be
- material- and product focused policies that promote all three renewable carbon sources,
- CCU receiving at least the same support as CCS and
- recognition and promotion of chemical recycling technologies
- Support the transformation of existing chemical infrastructure from fossil to renewable carbon and support the transformation of biofuels plants into chemical suppliers
- Support the massive expansion of renewable energies
- Develop standards, certificates and labels for renewable carbon
- Phase out financial support, tax advantages and tax exemptions for fossil feedstocks
-
Proceedings: nova-Session on Policies for Chemicals and Plastics in a Net-Zero Economy (PDF)
Policy
7 Downloads
7 Downloads
2023-06
FREE
Plus 19% MwSt.7
DownloadsAre you ready to join the conversation on Europe’s clean future? The EU has recently introduced a series of key policies aimed at achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, which will have a significant impact on the way companies operate. To help you understand these policies and their implications specifically for chemicals and plastics, nova-Institute hosted an online workshop on “Policies for Chemicals and Plastics in a Net-Zero Economy” in June 2023.
The proceedings includs four presentations of:
- Luciano Proto Cassina, and Nico Hark, nova-Institute: Overview of EU initiatives impacting renewable carbon chemicals and plastics
- Larry Sullivan, KBR: What does the US’s Inflation Reduction Act mean for the EU?
- Carla Benauges, DG CLIMA, European Commission: The EU’s answer to the IRA, the Net-Zero Industry Act
-
Yield of Fermentable Sugars (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
152 Downloads
152 Downloads
2023-06
FREE
152
Downloads -
Graphic of the scientific paper „The Use of Food and Feed Crops for Bio-based Materials and the Related Effects on Food Security“ (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
113 Downloads
113 Downloads
2023-06
FREE
113
DownloadsPromoting Evidence-based Debates and Recognising Potential Benefits
The graphic shows the multiple potential benefits of using food and feed crops for bio-based materials, in terms of climate, land productivity, environment, farmers, market stability, feed security and food security.
- The climate wins – Bio-based materials are part of the solution to achieve climate change mitigation.
- Land productivity wins – The competition between applications is not for the type of crop grown, but for the land
- The environment wins – due to increased resource efficiency and productivity of food and feed crops.
- Farmers win – because they have more options for selling stock to different markets.
- Market stability wins – due to increased global availability of food and feed crops.
- Feed security wins – due to the high value of the protein-rich co-products of food and feed crops.
- Food security wins – due to the increased overall availability of edible crops that can be stored and flexibly distributed.
-
RCI’s scientific background report: “The use of food and feed crops for bio-based materials and the related effects on food security – Promoting evidence-based debates and recognising potential benefits” (June 2023) Long Version
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
36 Pages
1709 Downloads
1709 Downloads
2023-06
FREE
1709
DownloadsPromoting Evidence-based Debates and Recognising Potential Benefits
This scientific paper highlights new insights into a hotly debated topic and urges for careful and evidence-based debates.
The paper aims to show that the well-known biomass debate is flawed, subjective and not fully based on evidence. What is detrimental to food security are, according to the World Food Programme in 2023, climate change, conflict, extreme inequalities in wealth distribution, heavy dependence on food imports from industrial countries, overconsumption of meat, losses along the value chain and the impact of the COVID pandemic. Competition between biomass uses is not mentioned among the relevant causes.
The use of biomass for industrial applications, does have the potential to replace fossil feedstocks and thus contribute to the urgently needed reduction of fossil carbon emissions into our atmosphere to mitigate climate change.
While not denying the dire need to combat world hunger, the authors of the paper argue that using food and feed crops for chemicals and materials will not necessarily exacerbate food insecurity, and in fact has the potential to cause multiple benefits for local and global food security, climate mitigation and other factors:
- The climate wins – Bio-based materials are part of the solution to achieve climate change mitigation.
- Land productivity wins – The competition between applications is not for the type of crop grown, but for the land.
- The environment wins – due to increased resource efficiency and productivity of food and feed crops.
- Farmers win – because they have more options for selling stock to different markets.
- Market stability wins – due to increased global availability of food and feed crops.
- Feed security wins – due to the high value of the protein-rich co-products of food and feed crops.
- Food security wins – due to the increased overall availability of edible crops that can be stored and flexibly distributed.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/WQXU7327
-
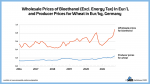
Wholesale Prices of Bioethanol and Wheat (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
84 Downloads
84 Downloads
2023-06
FREE
84
Downloads -
Global Harvested Agricultural and Grazed Biomass Demand by Sectors (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
149 Downloads
149 Downloads
2023-06
FREE
149
Downloads -
Embedded Carbon Demand for Main Sector (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
141 Downloads
141 Downloads
2023-06
FREE
141
Downloads -
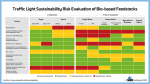
Traffic Light Sustainability Risk Evaluation of Bio-based Feedstocks (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
298 Downloads
298 Downloads
2023-06
FREE
298
Downloads -
Corn and its Applications (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
124 Downloads
124 Downloads
2023-06
FREE
124
Downloads -
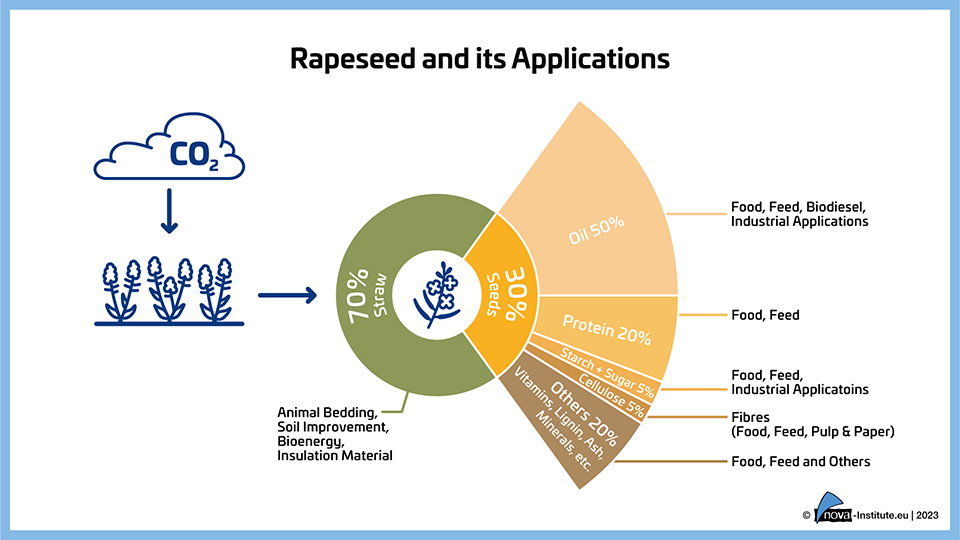
Rapeseed and its Applications (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
97 Downloads
97 Downloads
2023-06
FREE
97
Downloads -
Renewable Materials Conference 2023 Proceedings
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
228 Downloads
228 Downloads
2023-06
FREE
Plus 19% MwSt.228
DownloadsThe proceedings of the Renewable Materials Conference 2023 (23-25 May 2023, https://renewable-materials.eu) contain all released presentations of three conference days, the conference journal, and the press release of the three winners of the Innovation Award “Renewable Material of the Year 2023“.
-
RCI’s position paper: “Commission proposal for a Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation” (May 2023)
Policy
3 Pages
295 Downloads
295 Downloads
2023-05
FREE
295
DownloadsThis position paper highlights chances for the EU to lead the way to a sustainable packaging industry and to promote innovation
In November 2022, the Commission adopted the Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council on packaging and packaging waste, amending Regulation (EU) 2019/1020 and Directive (EU) 2019/904, and repealing Directive 94/62/EC. The proposed regulation includes several rules that would – if implemented – push for a much stronger circular economy in the packaging sector, due to higher re-use and refill quotas, higher use of recycled materials and mandatory composting of certain hard-to-recycle products.
The Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) welcomes this proposal and wants to offer several suggestions to strengthen it further and get implementation closer to the market realities of Europe.
1. Set ambitious targets for all types of renewable content:
A complementary renewable content target should be added to the proposal promoting the use of bio- and CO2-based feedstocks in packaging similar to recycling.2. Keep Article 8 as it is – scientific evidence shows that these products offer true environmental benefits from being compostable
The proposal, following scientific evidence, requires that certain types of tea and coffee packaging, sticky labels attached to fruit and vegetables as well as very lightweight plastic carrier bags shall be compostable in industrially controlled conditions in bio-waste treatment facilities.3. Support the market uptake of all state-of-the-art recycling technologies
To actually achieve the ambitious recycling quotas and recycled content targets, technologies will have to evolve. Advanced recycling technologies (i.e. depolymerisation) are key. -
Conference on CO2-based Fuels and Chemicals 2023 Proceedings
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
173 Downloads
173 Downloads
2023-05
FREE
Plus 19% MwSt.173
DownloadsThe proceedings of the Conference on CO2-based Fuels and Chemicals (19-20 April 2023, https://co2-chemistry.eu) contain all released presentations, the conference journal, and the press release of the three winners of the Innovation Award “Best CO2 Utilisation 2023″.
Press Release: https://renewable-carbon.eu/news/smart-carbon-capture-and-utilisation-ccu-technologies-and-materials-defossilise-the-economy
-
RCI’s position paper: “Communication on sustainable carbon cycles” (April 2023)
Policy
7 Pages
559 Downloads
559 Downloads
2023-04
FREE
Free Shipping559
DownloadsThe RCI, an interest group of leading companies and pioneers from the chemical and material sector, has a rich history of advocating for policies acknowledging the indispensable need of carbon in a broad range of chemical and material industries. The Communication on Sustainable Carbon Cycles, as published in December 2021, is a milestone in European policy as it acknowledges exactly this value of carbon as a feedstock and its unavoidability for certain sectors. The recently published position paper of the RCI highlights why this is an important step in the right direction and asks policy makers for effective follow-up.
-
Cellulose Fibres Conference 2023 (Proceedings, PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2023-03
50 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Add to
cartThe unique conference focused on cellulose fibres – in textiles, hygiene products and packaging!
The Cellulose Fibres 2023 Conference Proceedings (https://cellulose-fibres.eu, 8-9 March 2023, Cologne, hybrid) include all released conference presentations, the conference journal, sponsor documents, a Fiber2Fashion Knowledgepaper and the conference press release.
-
nova-Session: “Bio- and CO₂-based Polymers: Production, Trends 2022-2027 and the latest Policy Developments” (Proceedings, PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2023-03
50 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Add to
cartThe download of the proceedings contains all six presentations of the nova-Session (March 2023).
Bio-based and CO2-based Solutions – Where are we heading?
The only way for chemicals and plastics to become sustainable, climate-friendly and part of the circular economy is the complete substitution of fossil carbon with renewable carbon from alternative sources: biomass, CO2 and recycling. We see strong investment in all three sectors, with growth rates far exceeding that of fossil polymers – i.e. fossil polymers are being substituted in the market.
The session will focus on developments in bio- and CO2-based polymers and building blocks: Bio-based polymers are estimated to grow at a CAGR of 14 % from 2022 to 2027. Some examples: Bio-based epoxy resin production is on the rise, PTT regained attractiveness after several years of constant capacities and PE and PP made from bio based naphtha are being further established with growing volumes. Increased capacities for PLA are ongoing, after being sold out in 2019. Current and future expansions for bio based polyamides as well as PHAs are on the horizon. And also, bio-based PET is getting back in the game.
Additionally, the use of CO2 as chemical feedstock for building blocks and polymers has been intensively diversified. Several successfully implemented technologies used at commercial level are in place and many more at the laboratory and pilot phase. Besides the long-established use of CO2 for the synthesis of polycarbonates, also polyurethanes are based on it. The most notable biotechnological conversion pathway of a syngas produces ethanol at commercial scale. Additionally, high interest is also observed in CO2-based methanol and in CO2-based hydrocarbons, which can be used for fuel, chemical and polymers applications. A current total production capacity of these CO2-based products of ca. 1.3 Mt/a in 2022 is observed and a strong increase in capacity is expected by 2027.
The EU policy landscape has seen significant updates in the final weeks of 2022 with the proposed Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation and the publication of the Policy Framework on bio-based, biodegradable and compostable plastics. How these updates may affect CO2 and bio-based polymers will be addressed in the session.
-
Letter to the Commission on the definition of natural polymers in the REACH microplastics restriction
Policy, Sustainability & Health
4 Pages
482 Downloads
482 Downloads
2023-02
FREE
482
DownloadsSix leading associations and stakeholders from the chemicals, polymers and plastics sectors – namely BioChem Europe (a sector group of Cefic), EDANA, EuropaBio, European BioPlastics, GO!PHA and Renewable Carbon Initiative) – express in this letter their specific concerns about the proposed definition of “natural polymers” and its impact on biopolymers in the context of the REACH restriction on microplastics.
Under the coordination of the Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) they ask the European Commission in a letter “that in the adoption of the text of the Synthetic Polymer Microparticles restrictions (REACH Microplastics Restriction), the European Commission should not use the definition of ‘natural polymer’ which refers to a polymerisation process that takes place in nature.“
-
Importance of mass balance and free attribution (MBFA) for the conversion of the chemical sector to alternative carbon sources (October 2022)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
4 Pages
764 Downloads
764 Downloads
2022-12
FREE
Free Shipping764
DownloadsA position paper of the Renewable Carbon Initiative
This position paper highlights the importance of mass balance and free attribution “MBFA” as one possible way to incentivise the transformation of the chemical sector away from fossil and on towards renewable carbon.
The term “mass balance” has become established to describe systems in which biomass, CO2 and secondary materials are used as a feedstock, but is not or not fully physically traced to the end product . It is common practice in many value chains in which large scale capacities are involved in one or more steps of the value chain that require mixing the sustainable with conventional material to fill the capacity. The approach makes it possible to substitute large quantities of fossil raw materials and attractive renewable content shares can be attributed to desired materials or products for which demand on the market exists. This incentivises a stepwise continuous transformation to increase the share of renewable carbon in particular for the large-scale chemical industry
However, the term “mass balance” is somewhat unfortunate because it is too general, and does not mention the essence of the method: the free attribution of the bio-based, CO2-based or chemically recycled share in the feedstock mix to certain selected end products.
The RCI recommends to only speak of “mass balance and free attribution (MBFA)” when talking about such cases, as this is how the complete method and its two central parts are referred to. This is transparent and honest, building trust from customers, end consumers and society in general. Both, mass balance and the free attribution are based on solid and established certifications.
Besides terminology, there is still a need for regulatory harmonisation between the schemes of the existing certification systems. MBFA cannot only be applied for bio-based feedstock, but also for CO/CO2 or feedstock from chemical recycling, both will gain strongly in importance in the coming years. Every MBFA scheme should cover these three renewable feedstocks: biomass, CO/CO2 and recycling.

![nova-Session: “Bio- and CO₂-based Polymers: Production, Trends 2022-2027 and the latest Policy Developments” (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital]](https://renewable-carbon.eu/publications/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/21-01-07_RC-Publications-Cover-Proceedings_1-100x141.png) nova-Session: “Bio- and CO₂-based Polymers: Production, Trends 2022-2027 and the latest Policy Developments” (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital]
nova-Session: “Bio- and CO₂-based Polymers: Production, Trends 2022-2027 and the latest Policy Developments” (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital] 







![Renewable Materials Conference 2023 Proceedings [Digital]](https://renewable-carbon.eu/publications/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/21-01-07_RC-Publications-Cover-Proceedings_RMC-100x141.png)

![Conference on CO2-based Fuels and Chemicals 2023 Proceedings [Digital]](https://renewable-carbon.eu/publications/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/21-01-07_RC-Publications-Cover-Proceedings_CO2-based-100x141.png)

![Cellulose Fibres Conference 2023 (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital]](https://renewable-carbon.eu/publications/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/21-01-07_RC-Publications-Cover-Proceedings_Cellulose-Fibres-100x141.png)

