Showing 21–40 of 194
-
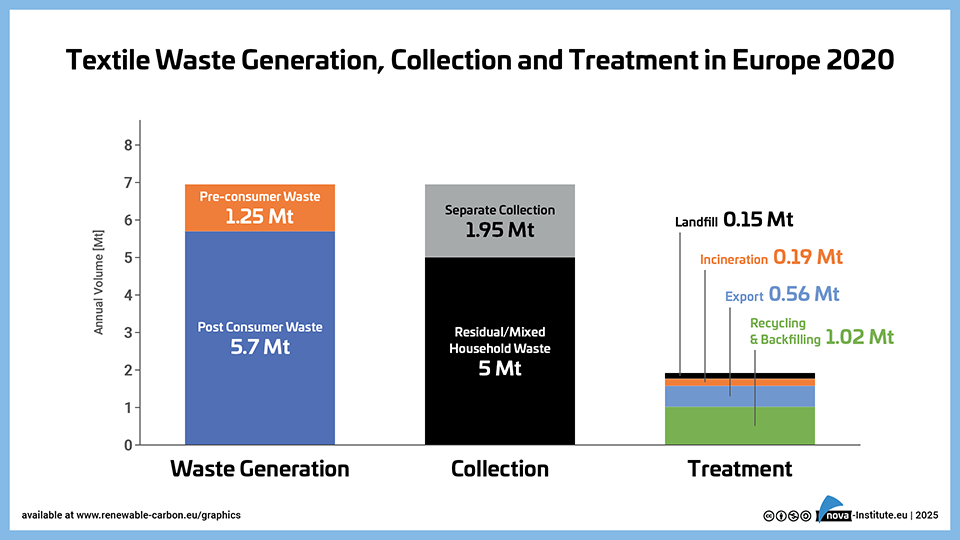
Textile-Waste-Generation-Collection-and-Treatment-in-Europe-2020 (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
42 Downloads
42 Downloads
2025-02
FREE
42
Downloads -
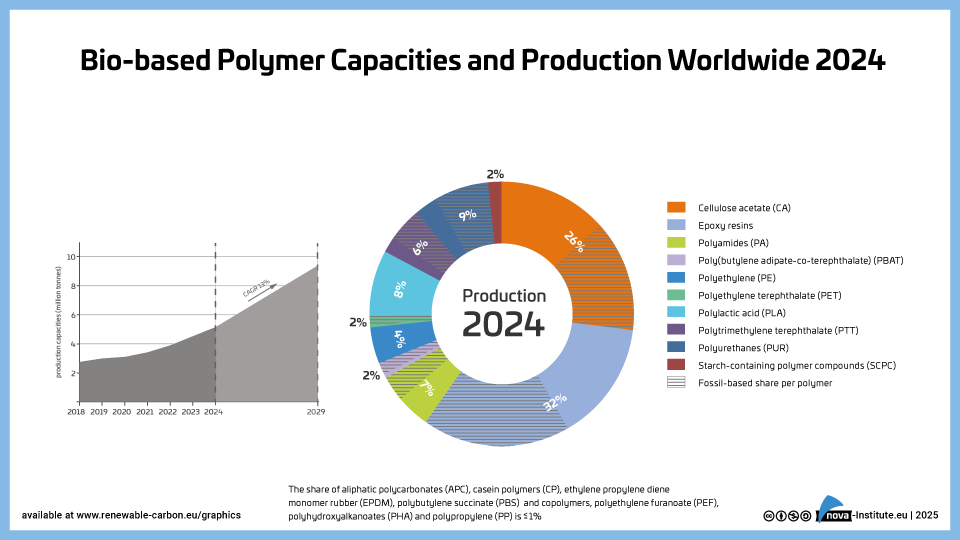
Bio-based-Polymer-Production-and-Bio-based-shares-2024 (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
99 Downloads
99 Downloads
2025-02
FREE
99
Downloads -
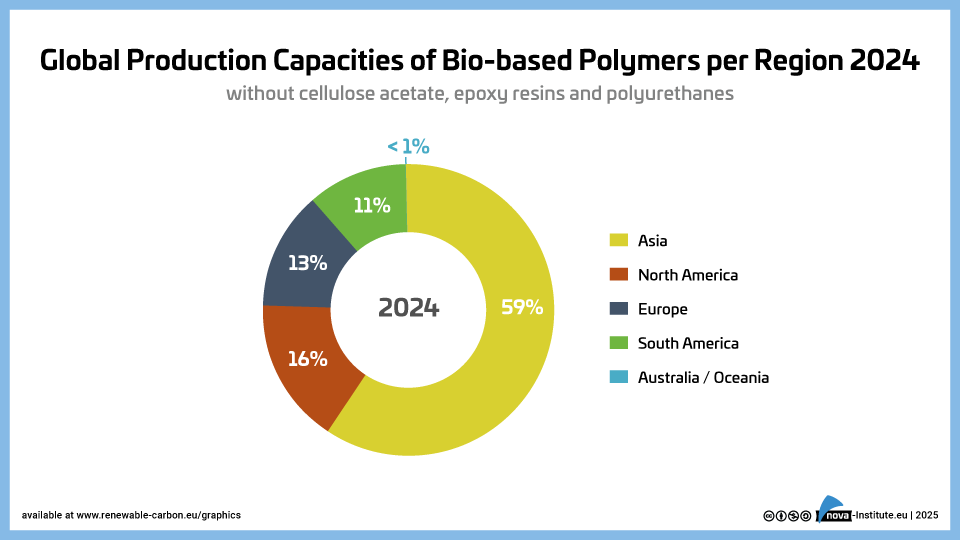
Global-Production-Capacities-of-Bio-based-Polymers-per-Region-2024 (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
31 Downloads
31 Downloads
2025-02
FREE
31
Downloads -
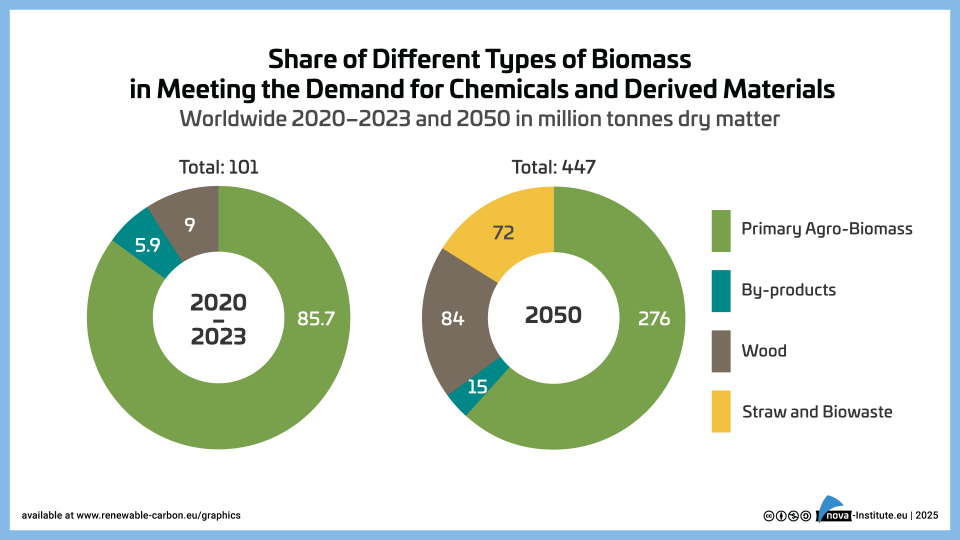
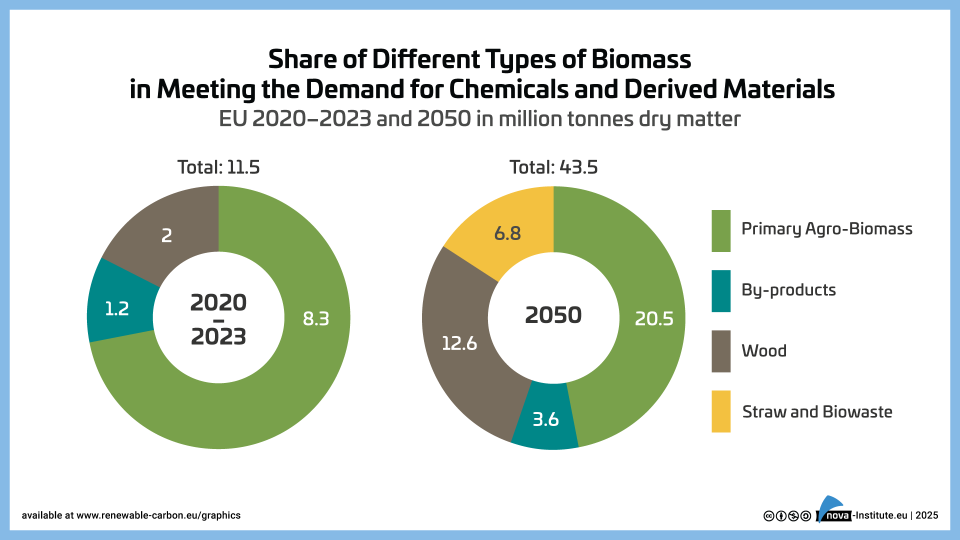
Share-of-Different-Types-of-Biomass-EU-2023–2050 – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
27 Downloads
27 Downloads
2025-02
FREE
27
Downloads -
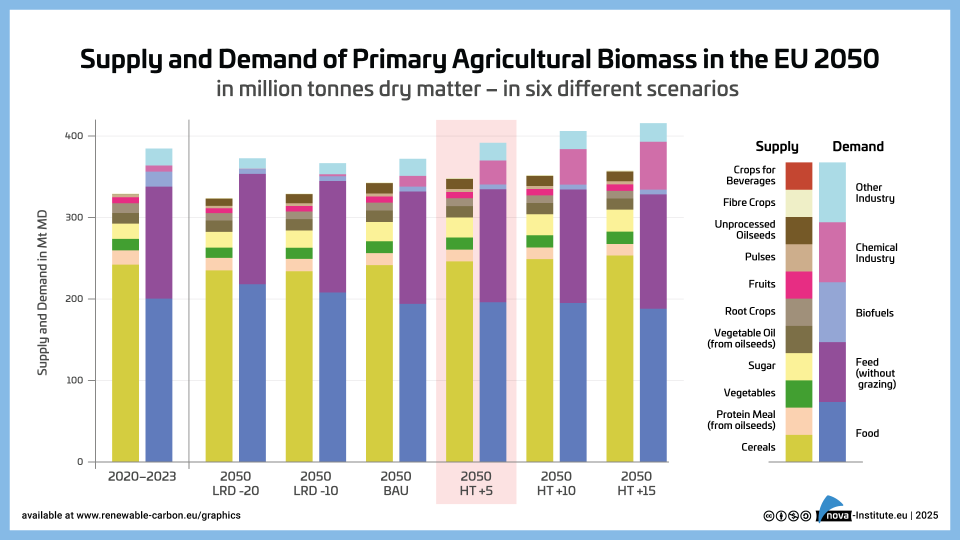
Supply and Demand of Agriculture Biomass in the EU 2050 – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
29 Downloads
29 Downloads
2025-02
FREE
29
Downloads -
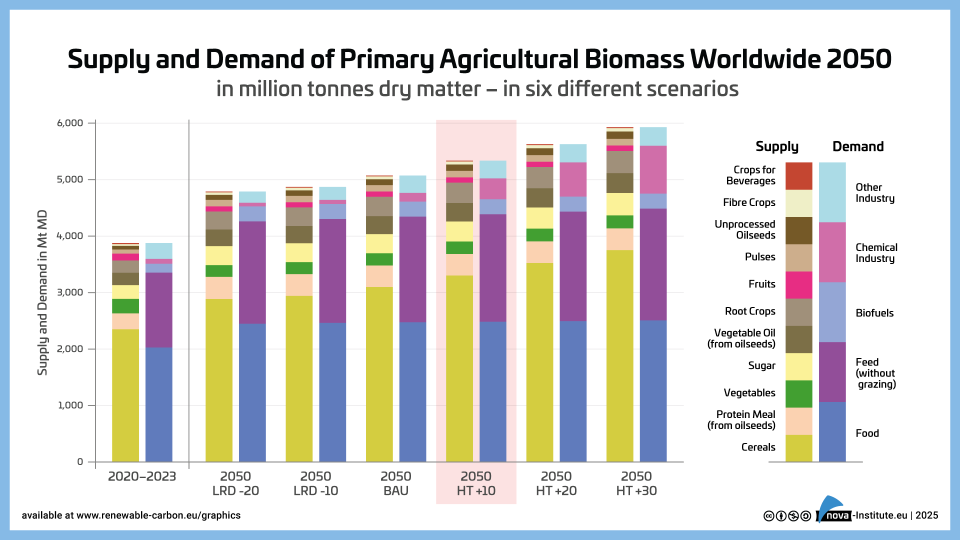
Supply and Demand of Agriculture Biomass Worldwide 2050 – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
27 Downloads
27 Downloads
2025-02
FREE
27
Downloads -
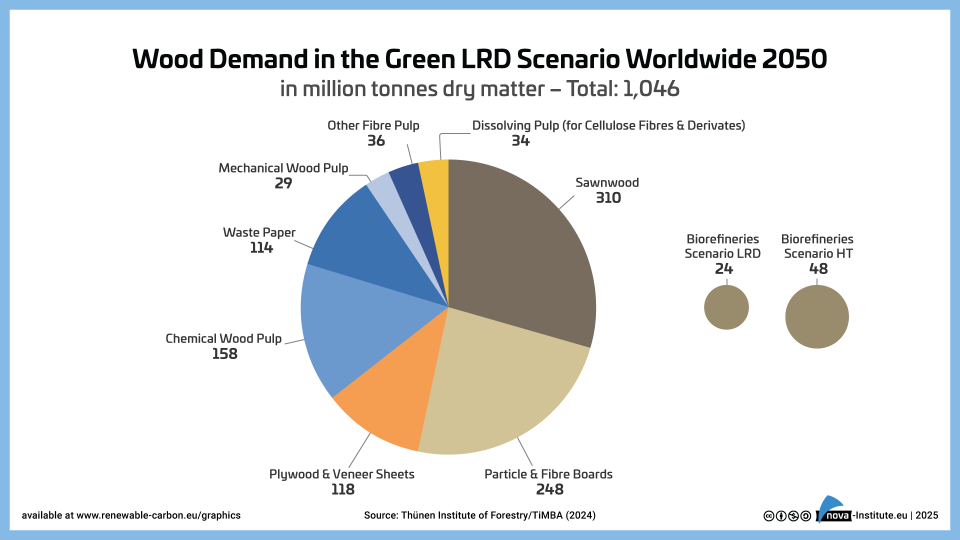
Wood Demand in the Green LRD Scenario Worldwide 2050 – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
14 Downloads
14 Downloads
2025-02
FREE
14
Downloads -
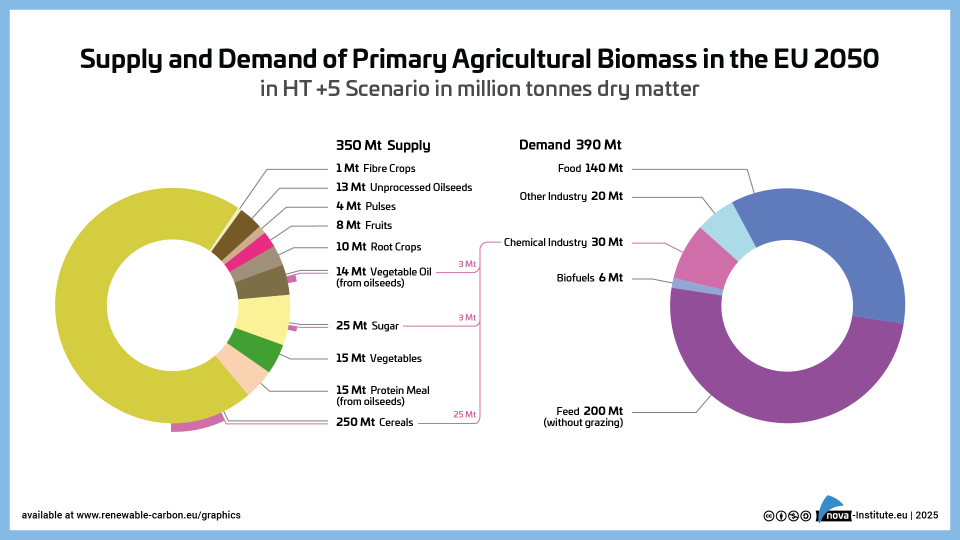
Supply and Demand of Agricultural Biomass in the EU 2050 in HT +5 Scenario – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
22 Downloads
22 Downloads
2025-02
FREE
22
Downloads -
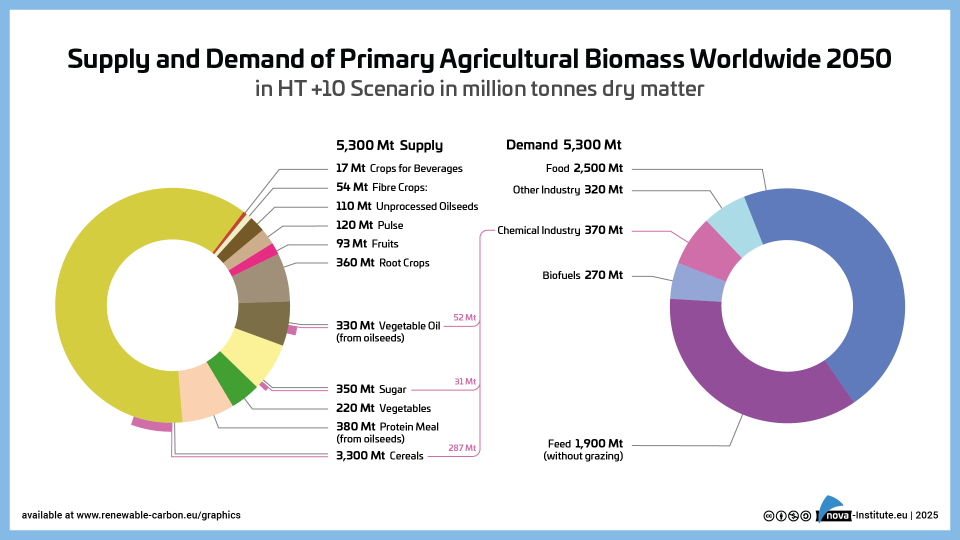
Supply and Demand of Agricultural Biomass Worldwide 2050 in HT +10 Scenario – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
32 Downloads
32 Downloads
2025-02
FREE
32
Downloads -
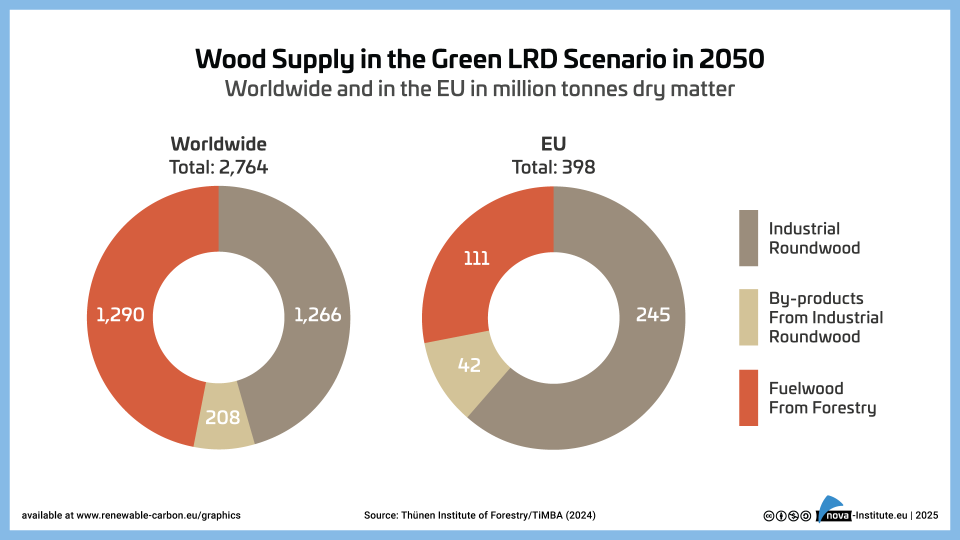
Wood Supply in the Green LRD Scenario in 2050 – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
9 Downloads
9 Downloads
2025-02
FREE
9
Downloads -
Share of Different Types of Biomass Worldwide 2023-2050 – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
52 Downloads
52 Downloads
2025-02
FREE
52
Downloads -
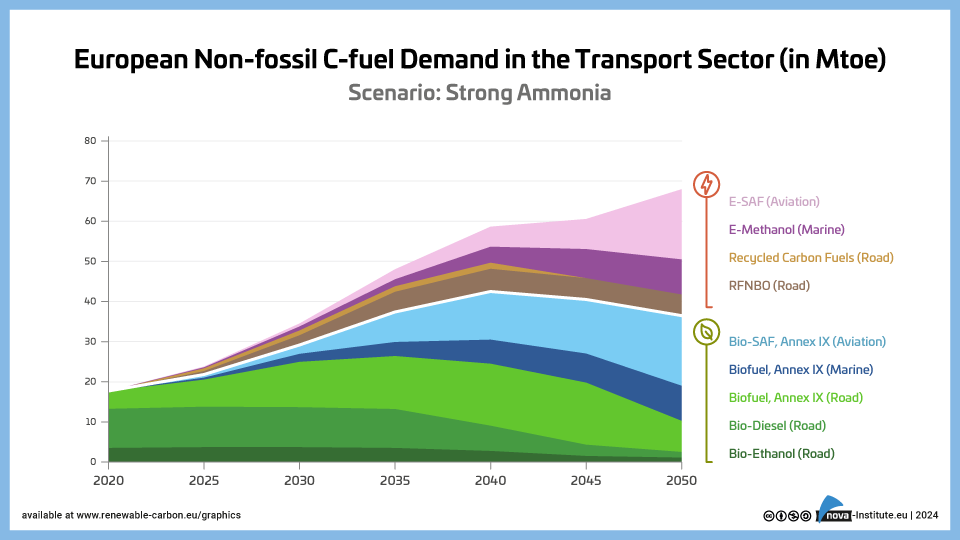
European Non-fossil C-fuel Demand in the Transport Sector – Strong Ammonia – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
8 Downloads
8 Downloads
2025-01
FREE
8
Downloads -
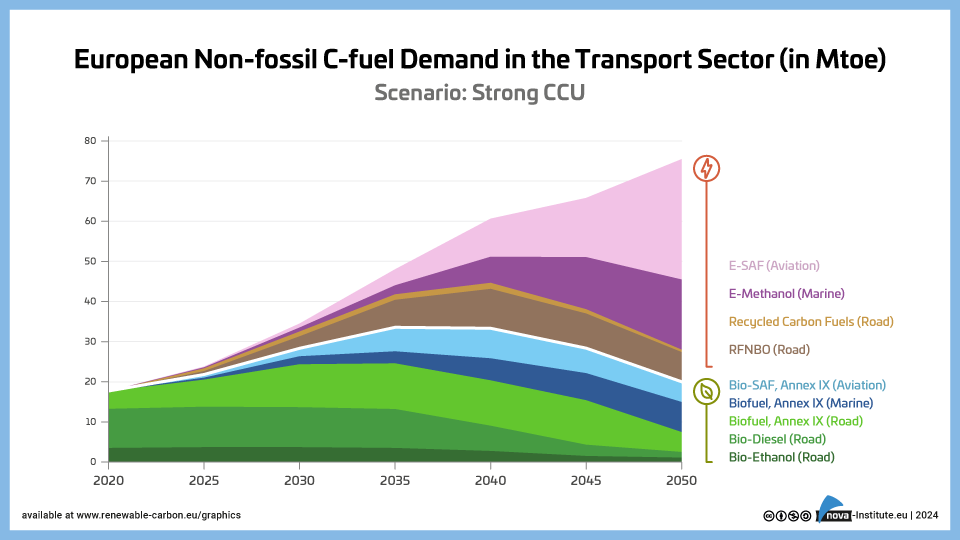
European Non-fossil C-fuel Demand in the Transport Sector – Strong CCU – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
16 Downloads
16 Downloads
2025-01
FREE
16
Downloads -
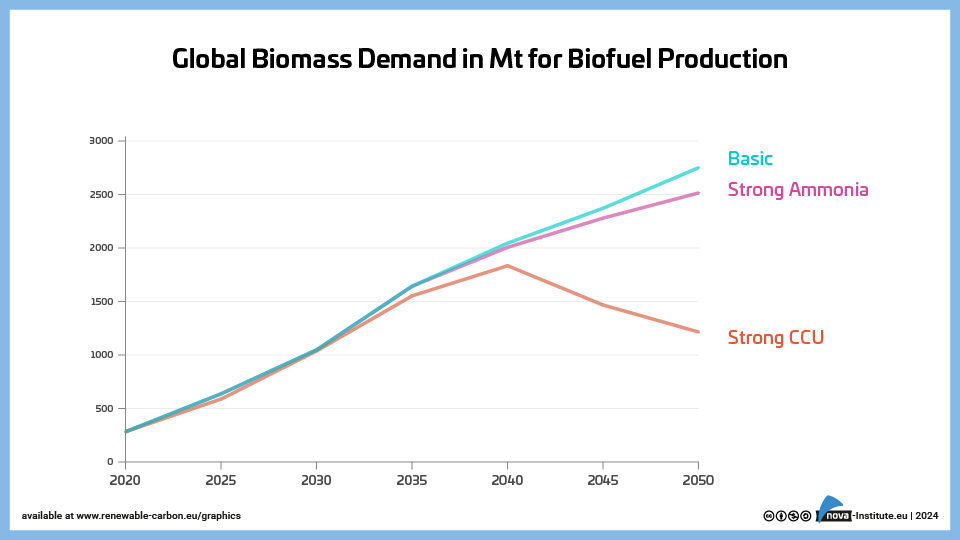
Global Biomass Demand in Mt for Biofuel Production – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
22 Downloads
22 Downloads
2025-01
FREE
22
Downloads -
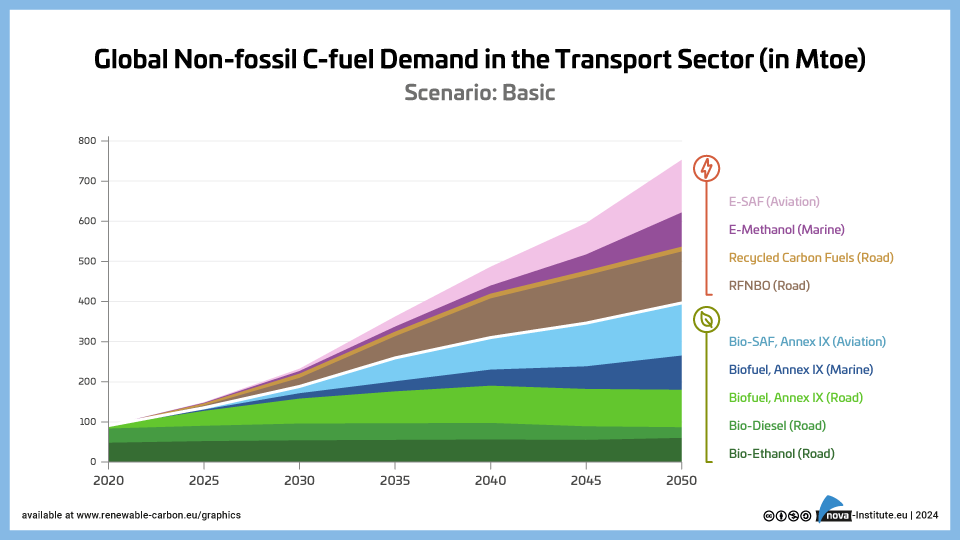
Global Non-fossil C-fuel Demand in the Transport Sector – Basic – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
22 Downloads
22 Downloads
2025-01
FREE
22
Downloads -
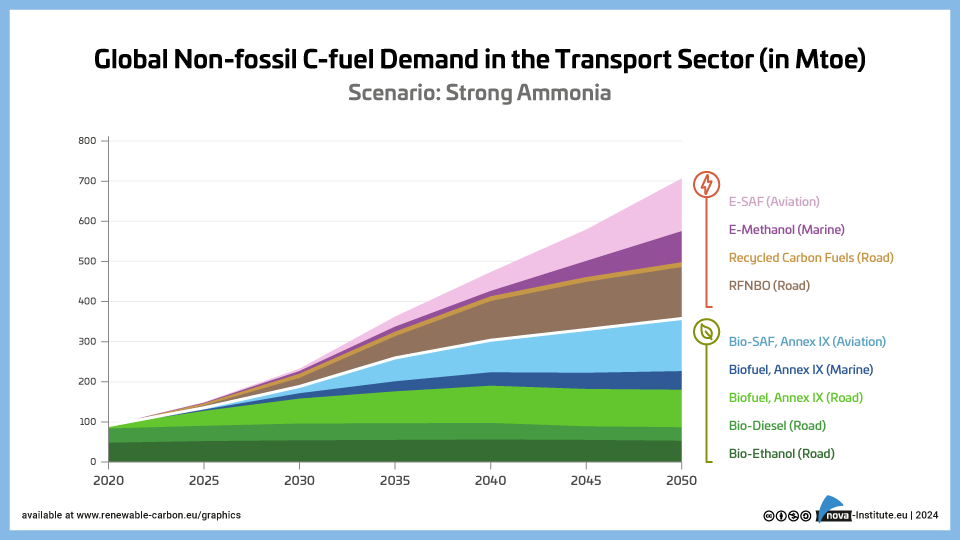
Global Non-fossil C-fuel Demand in the Transport Sector – Strong Ammonia – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
15 Downloads
15 Downloads
2025-01
FREE
15
Downloads -
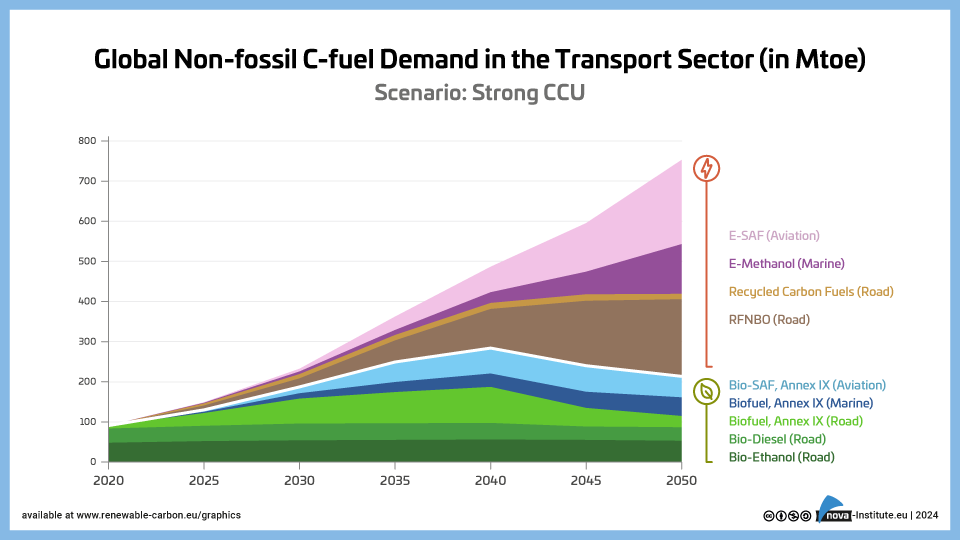
Global Non-fossil C-fuel Demand in the Transport Sector – Strong CCU – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
280 Downloads
280 Downloads
2025-01
FREE
280
Downloads -
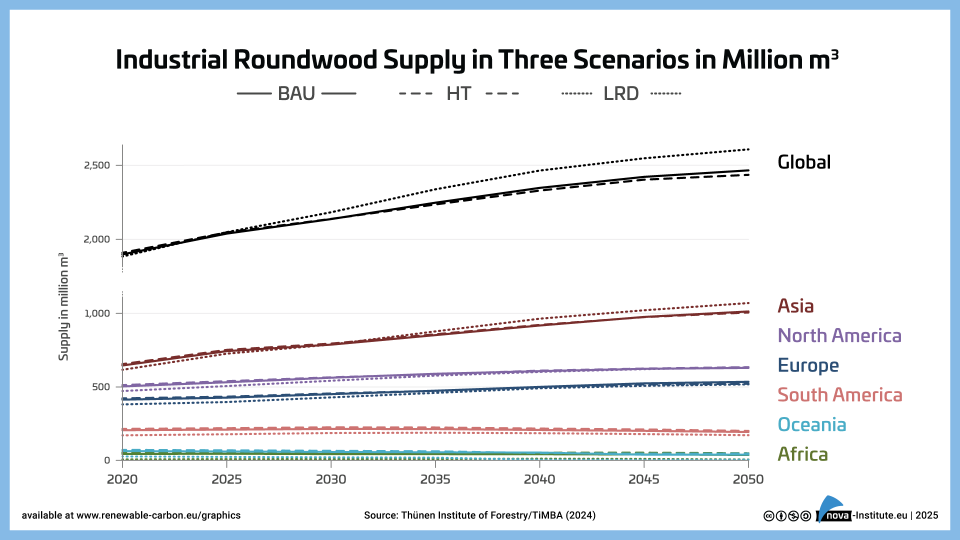
Industrial Roundwood Production in Three Scenarios in Million m3 – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
7 Downloads
7 Downloads
2025-01
FREE
7
Downloads -
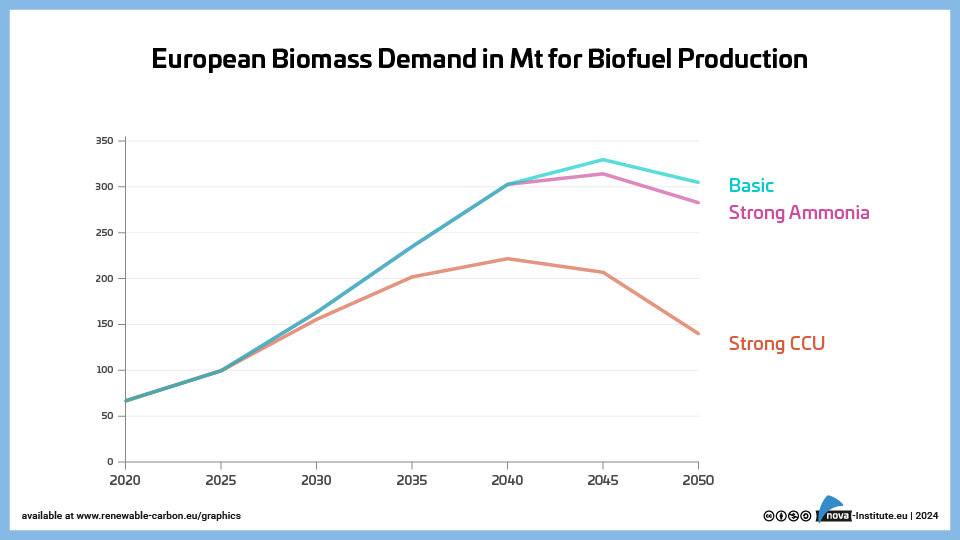
European Biomass Demand in Mt for Biofuel Production – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
30 Downloads
30 Downloads
2025-01
FREE
30
Downloads -
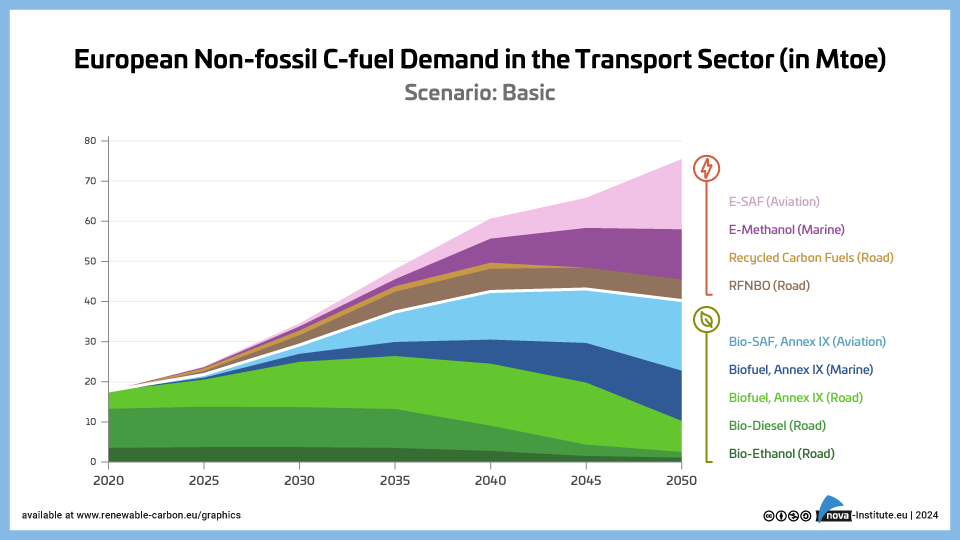
European Non-fossil C-fuel Demand in the Transport Sector – Basic – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
24 Downloads
24 Downloads
2025-01
FREE
24
Downloads