Showing 1–20 of 234
-
Advanced Recycling Conference 2025 (Proceedings, PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2025-12
150 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Add to
cartThe proceedings of the Advanced Recycling Conference 2025 (19-20 November, https://advanced-recycling.eu) contain 41 conference presentations, the conference journal, sponsor documents and the press release.
-
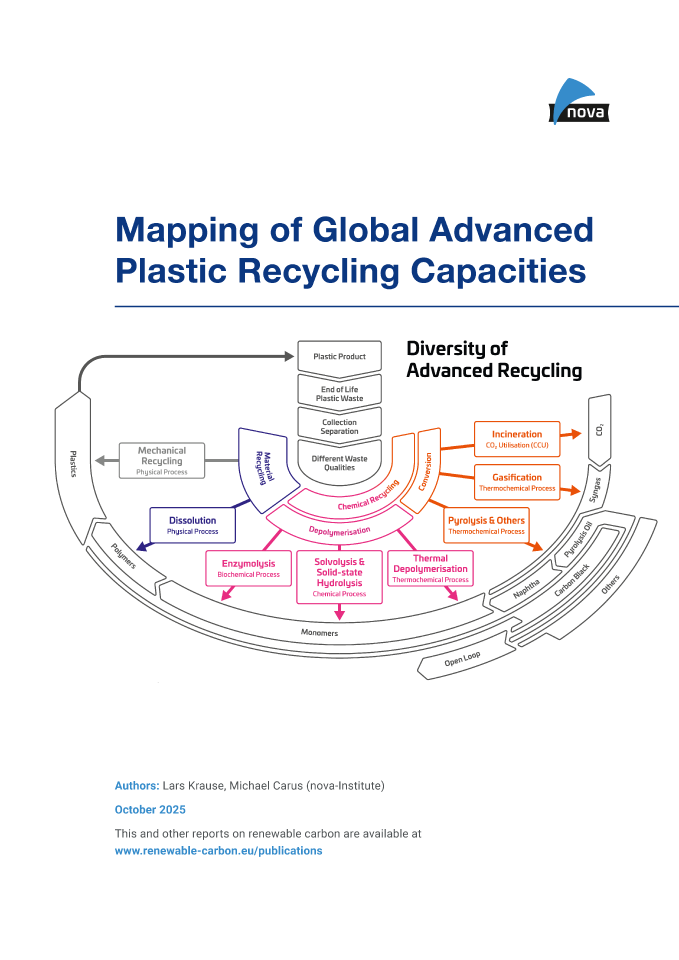
Mapping of Global Advanced Plastic Recycling Capacities (PDF)
NewMarkets & Economy, Policy, Technology
35 Pages

2025-11
500 € – 1,000 €Price range: 500 € through 1,000 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Select
licenceChemical and physical recycling are essential to keeping carbon in the loop and fully establishing a circular economy. Despite delays in policy regulations and investment, experts foresee a bright future for new capacity, both globally and in Europe.
The development of advanced recycling technologies is very dynamic and at a fast pace, with new players constantly appearing on the market, from start-ups to chemistry giants and everything in between. New plants are being built, and new capacities are being achieved. Due to these dynamic developments, it is difficult to keep track of everything. The nova report “Mapping of global advanced plastic recycling capacities” aims to clear up this jungle of information. A comprehensive evaluation of the global input and output capacities was carried out for which 390 planned as well as installed and operating plants including their specific product yields were mapped to provide an overview about global advanced recycling capacities in the past, present, and future.
Further information: The new report represents a short study updating the current and future Advanced Recycling input- and output-capacities for the year 2024-2031. The report does not include any technology- or company-profiles which are published in another study (https://doi.org/10.52548/WQHT8696).
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/YKWB6074
-
Renewable Materials Conference 2025 (Proceedings, PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2025-10
200 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Add to
cartThe proceedings of the Renewable Materials Conference 2025 (22-24 September 2025, https://renewable-materials.eu) contain all released 68 presentations, the conference journal and the press release of the three winners of the Innovation Award “Renewable Material of the Year 2025″.
-
Benefits of Using First-Generation Biomass for Food, Fuel, Materials and Chemicals in Europe (PNG)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
101 Downloads
101 Downloads
2025-09
FREE
Free Shipping101
Downloads -
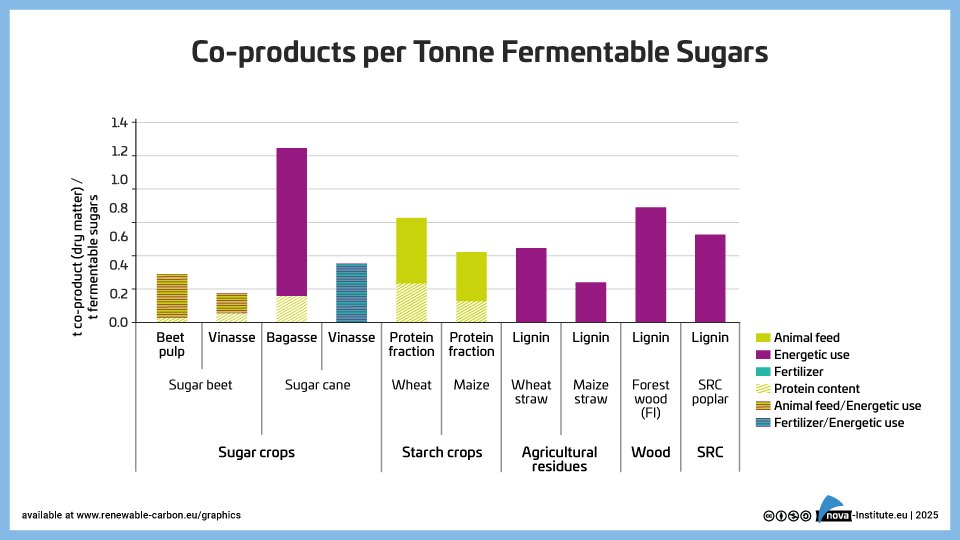
Co-production per Tonne Termantable Sugars (PNG)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
18 Downloads
18 Downloads
2025-09
FREE
Free Shipping18
Downloads -
Benefits of Using First-Generation Biomass for Food, Fuels, Chemicals and Derived Materials in Europe (PDF)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
16 Pages
716 Downloads
716 Downloads
2025-09
FREE
Free Shipping716
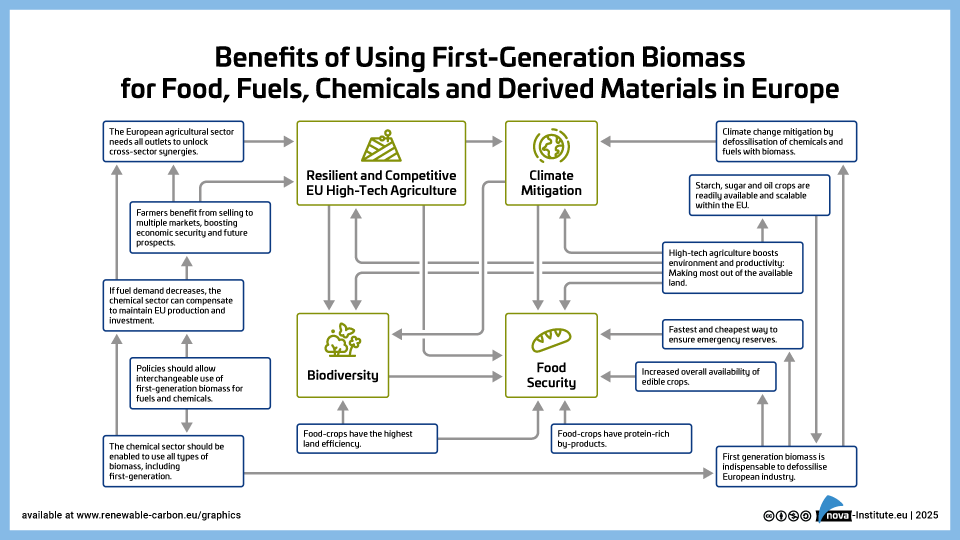
DownloadsKey messages – Benefits of using first-generation biomass for food, fuels, chemicals and derived materials
First-generation biomass in non-food applications increases food security.
Using first-generation biomass for non-food applications strengthens food security by increasing overall availability of feedstock and market stability. At the same time, it also delivers valuable protein-rich by-products addressing the most critical needs for human and animal nutrition. The ability to shift crops between the food, feed, and industrial markets enables the EU and market players to respond swiftly to changes in demand and mitigate the risks associated with supply chain disruptions. Most importantly, using first-generation biomass for non-food applications offers a fast and economical way to set up and ensure an emergency food reserve.- First-generation biomass in non-food applications enhances a resilient and competitive EU agriculture
- First-generation biomass in non-food applications supports climate change mitigation
- First-generation biomass in non-food applications supports biodiversity protection
- High-tech agriculture further enhances the benefits of first-generation biomass.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/GCJC4981
-
RCI’s Position Paper: Mass Balance and Attribution (MBA) – Update 2025 (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy
5 Pages
217 Downloads
217 Downloads
2025-08
FREE
Free Shipping217
DownloadsThis position paper highlights the importance of mass balance and attribution “MBA” as one possible way to incentivise the transformation of the chemical sector away from fossil and on towards renewable carbon.
The term “mass balance” has become established to describe systems in which biomass, CO2 and secondary materials are used as a feedstock, but is not or not fully physically traced to the end product. Using the MBA approach makes it possible to substitute large quantities of fossil raw materials and attractive renewable content shares can be attributed to desired materials or products for which demand on the market exists. Through this, chemistry can stepwise, but continuously, increase the shares of renewable carbon
However, the term “mass balance” is somewhat unfortunate because it is too general, and does not mention the essence of the method: the free attribution of the bio-based, CO2-based or chemically recycled share in the feedstock mix to certain selected end products. Without this attribution, a pure mass balance makes no sense, and in practice, with several hundred products and intermediate products that have been certified accordingly, attribution is frequently carried out globally. The RCI recommends to only speak of “mass balance and attribution (MBA)” as this is transparent and honest, building trust from customers, end consumers and society in general. Both, mass balance and the free attribution are based on solid and established certifications.
Besides terminology, there is still a need for regulatory harmonisation between the schemes of the existing certification systems. MBA cannot only be applied for bio-based feedstock, but also for CO/CO2 or feedstock from chemical recycling, both will gain strongly in importance in the coming years. Every MBA scheme should cover these three renewable feedstocks: biomass, CO/CO2 and recycling.
This 2025 update now includes a brief overview and figure of MBA as defined at EU level, via the SUPD Implementing Decision on the recycling of a single-use plastics bottle- This establishes overall regulatory support for MBA in the EU as well as an applicable methodological framework for MBA in practice.
-
The fossil fuel trap: Why defossilising chemistry is essential – and feasible! (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Technology
8 Pages
205 Downloads
205 Downloads
2025-07
FREE
Free Shipping205
DownloadsHow can we escape the fossil fuel trap, our dependence on fossil fuels and the vulnerability that comes with it? In the long term, recycling, together with biogenic carbon and CO₂, can completely replace fossil carbon from crude oil or natural gas as a raw material for plastics production. This will enable the European Union to become independent of fossil carbon imports and increase its resilience and competitiveness. To achieve this, it is crucial to shape the transition phase in a politically astute and rapid manner so that the transformation of the chemical industry in Europe is successful – after all, Europe is the birthplace of modern chemistry. This is the only way to prevent the EU from remaining stuck in a fossil fuel trap while other regions successfully transform their economies.
-
Die fossile Falle: Warum die Defossilisierung der Chemie unverzichtbar – und machbar – ist! (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Technology
8 Pages
55 Downloads
55 Downloads
2025-07
FREE
Free Shipping55
DownloadsWie kommen wir raus aus der fossilen Falle, aus der fossilen Abhängigkeit und Verwundbarkeit? Langfristig kann Recycling zusammen mit biogenem Kohlenstoff und CO₂ den fossilen Kohlenstoff aus Erdöl oder Erdgas als Rohstoff für die Kunststoffproduktion komplett ersetzen. So kann die Europäische Union unabhängig von fossilen Kohlenstoffimporten werden und ihre Widerstandsfähigkeit und Wettbewerbsfähigkeit steigern. Dafür ist es entscheidend, die Übergangsphase politisch klug und rasch zu
gestalten, damit die Transformation der Chemieindustrie in Europa gelingt – schließlich ist Europa die Ursprungsregion der modernen Chemie. Nur so kann vermieden werden, dass die EU in der fossilen Sackgasse stecken bleibt, während anderen Regionen die Transformation gelingt.
-
284 Downloads
2025-06
FREE
Free Shipping284
DownloadsThere is an urgent need for horizontal sustainability criteria for biomass in bio-based chemicals and derived materials – in the framework of future incentives.
The Renewable Carbon Initiative’s position paper on sustainability criteria for biomass emphasises that biomass is essential for Europe’s net-zero transition by replacing fossil resources in chemicals and materials.
The EU must establish clear, aligned sustainability criteria for biomass use in chemicals, based on the Renewable Energy Directive (REDIII) but adapted for this sector. These criteria should address sustainable cultivation of feedstock, full life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions, and feedstock eligibility, and be linked to market incentives to ensure effectiveness.
No caps should limit the use of primary agricultural biomass for chemicals, as it does not threaten food security and provides multiple benefits. Access to a wide range of sustainable feedstocks is crucial. Biodiversity impacts should be managed through climate-smart farming, while forest biomass criteria must focus on current sustainable practices using existing certification schemes. This approach will create a fair and dependable framework to support Europe’s sustainable bio-based economy.
-
Joint Webinar hosted by Bio-based Industries Consortium (BIC) and the Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) (May 2025) (PDF)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
51 Pages
585 Downloads
585 Downloads
2025-05
FREE
Free Shipping585
DownloadsThe webinar was presented by Michael Carus (nova-Institute, RCI), supported by Christopher vom Berg (RCI), Dirk Carrez (BIC), and Marco Rupp (BIC). It was based on a Scientific Background Report “Is there enough biomass to defossilise the chemicals and derived materials sector by 2050?” commissioned by the Bio-based Industries Consortium (BIC) and the Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI).
It explored whether agricultural and woody biomass could sustainably meet 20% of the carbon demand for the chemical and derived materials sectors by 2050. Using models like CAPRI (for agriculture) and TiMBA (for forestry), the study examined different scenarios, balancing food, feed, and biofuel priorities. Results showed that with moderate technological advancements, this 20% target is achievable without compromising sustainability or biodiversity. Stronger high-tech scenarios could even provide up to 40%, though existing biofuel policies may limit this. Overall, the study concluded that biomass could play a key role in defossilising the chemical sector, given the right innovations and policy frameworks.
-
CO2-based Fuels and Chemicals Conference 2025 (Proceedings, PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2025-05
150 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Add to
cartThe proceedings of the CO2-based Fuels and Chemicals Conference 2025 (29-30 April 2025, https://co2-chemistry.eu) contain all released presentations, the conference journal, and the press release of the three winners of the Innovation Award “Best CO2 Utilisation 2025″.
-
Background Document to RCI/BIC Report „Measuring the Use of Biogenic Feedstocks in the Global and EU Chemical Industry in 2023″ (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy
16 Pages
103 Downloads
103 Downloads
2025-05
FREE
Free Shipping103
DownloadsThis background document is a supplement to the main publication: “Is there Enough Biomass to Defossilise the Chemicals and Derived Materials Sector by 2050? – A Joint BIC and RCI Scientific Background Report“.
The report provides a comprehensive assessment of biogenic feedstock usage in the global and EU chemical industries for 2023, detailing sources like starch, sugar, vegetable oils, animal fats and more.
Globally, the chemical industry used 7.3 million tonnes of starch and 4.0 million tonnes of sugar for bioethanol-derived chemicals, while the EU used 480,000 and 150,000 tonnes respectively. Vegetable oils accounted for the highest single feedstock usage globally at 17.6 million tonnes, and 1.6 million tonnes in the EU. Other significant feedstocks include glycerol (3.4 million tonnes globally, 490,000 tonnes in the EU) and natural rubber (14 million tonnes globally, 1.1 million tonnes in the EU).
The data aims to establish a baseline for future biomass modeling and highlights discrepancies and assumptions due to data gaps.
-
A Deep Dive into the Agriculture sector – „Is There Enough Biomass to Defossilise the Chemicals and Derived Materials Sector by 2050?“ (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
41 Pages
369 Downloads
369 Downloads
2025-05
FREE
Free Shipping369
DownloadsThis presentation is a supplement to the main publication: “Is there Enough Biomass to Defossilise the Chemicals and Derived Materials Sector by 2050? – A Joint BIC and RCI Scientific Background Report“ and provides deeper insights into the agriculture sector.
The presentation analyses the potential of sustainable agricultural biomass to meet future carbon demand in the global and EU chemical industries by 2050.
It uses the CAPRI model to simulate various land-use and technological scenarios, finding that only the Green High Tech (HT) scenarios can meet the projected biomass needs while fulfilling food, feed, and fuel demands. Key feedstocks include starch, sugar, and oil crops, with starch having the most significant expansion potential. Residues and biowaste play a limited but important role, especially when supplemented by advanced technologies and logistical improvements. External factors such as reduced meat consumption, Ukraine’s potential EU accession and innovations like agro-photovoltaics and urban farming also influence biomass availability.
-
A Deep Dive into the Forestry sector – „Is There Enough Biomass to Defossilise the Chemicals and Derived Materials Sector by 2050?” (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
46 Pages
361 Downloads
361 Downloads
2025-05
FREE
Free Shipping361
DownloadsThis presentation is a supplement to the main publication: “Is there Enough Biomass to Defossilise the Chemicals and Derived Materials Sector by 2050? – A Joint BIC and RCI Scientific Background Report“ and provides deeper insights into the forestry sector.
The TiMBA model evaluates the global forest products market under three scenarios—Business-as-Usual (BAU), Green Low Resource Depletion (LRD), and Green High Tech (HT)—to project wood production, trade, and forest development from 2020 to 2050. Under all scenarios, global forest area increases, especially in Asia, with the LRD and HT scenarios showing stronger forest protection due to deforestation bans and improved forest management. Industrial roundwood production rises by 38% globally by 2050, with Asia leading the growth, and highest demand seen in the LRD scenario, particularly for new applications like dissolving pulp and cellulose derivatives. Despite increased production, forest stocks remain stable or improve slightly due to technological efficiency, increased recycling, and reduced raw material inputs. However, competition for wood residues among biorefineries, pellet production, and sustainable aviation fuels poses challenges to meeting future biomass demand sustainably.
-
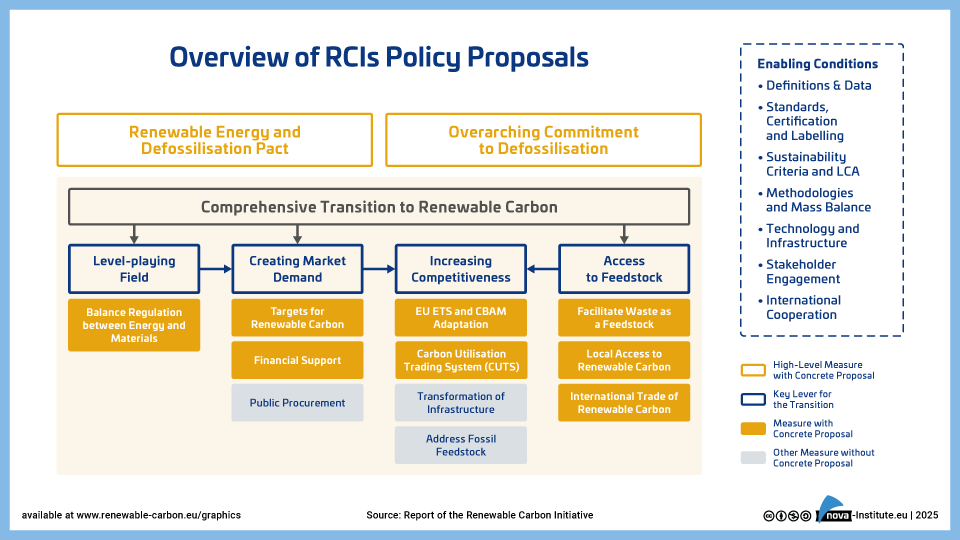
Overview of RCIs Policy Proposals (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
44 Downloads
44 Downloads
2025-04
FREE
Free Shipping44
Downloads -
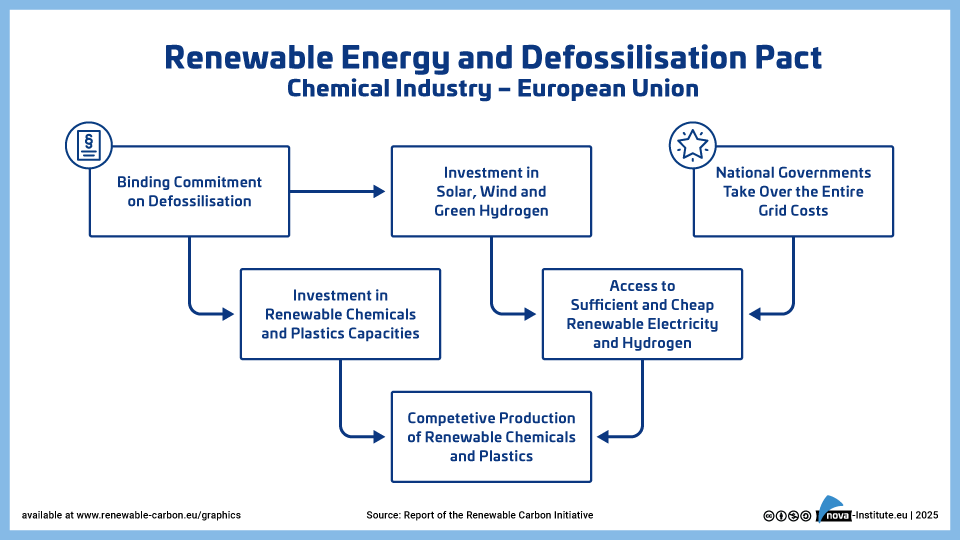
Renewable Energy and Defossilisation (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
35 Downloads
35 Downloads
2025-04
FREE
Free Shipping35
Downloads -
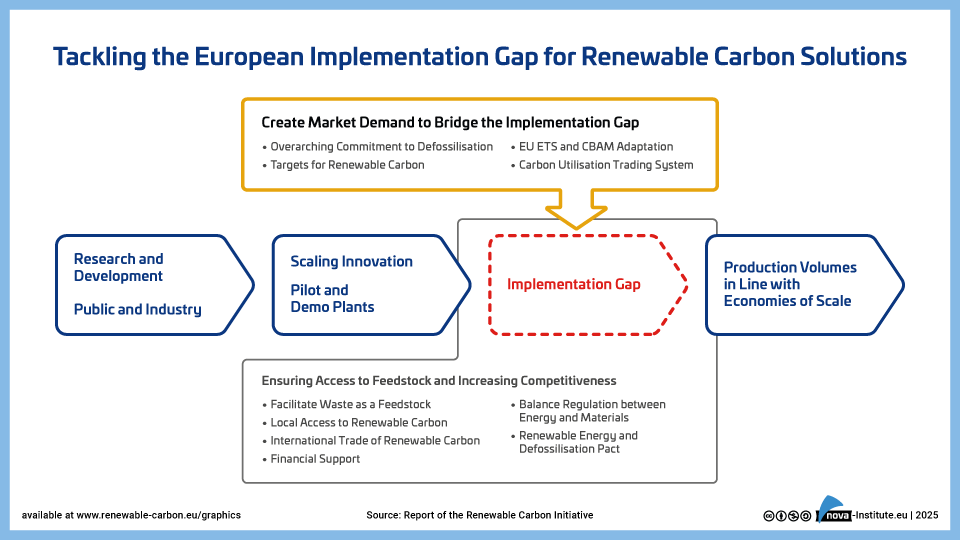
Trackling the European Implementation Gap for Renewable Carbon Solutions (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
1 Page
42 Downloads
42 Downloads
2025-04
FREE
Free Shipping42
Downloads -
RCI Policy Proposals for Facilitating the Transition to Renewable Carbon (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
70 Pages
1043 Downloads
1043 Downloads
2025-04
FREE
Free Shipping1043
DownloadsThe report outlines a strategic roadmap for transforming Europe’s chemical industry by transitioning from fossil-based to renewable carbon sources. It highlights the industry’s current crisis which is driven by global competition, high energy costs, and regulatory pressure, and stresses the urgency of reducing dependence on fossil feedstocks. The report aruges that the transition to renewable carbon is not just about environmental sustainability; it is about securing Europe’s industrial future and maintaining its global competitiveness in a rapidly changing world. By pioneering renewable carbon technologies, the EU can unlock economic benefits and unleash its innovation potential while advancing climate neutrality ambitions.
The Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) proposes ten comprehensive policy measures including mandatory renewable carbon targets, adaptation of emissions trading systems, and financial support mechanisms. These proposals aim to create market demand, drive innovation and build industrial resilience. Key enablers include harmonised standards, robust certification, infrastructure development, and stakeholder engagement.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/DZRU4577
-
2025-04
FREE
Plus 19% MwSt.Free Shipping0
More
Downloads
infoDas Rheinische Revier soll im Zuge des Kohleausstiegs zu einer „Modellregion Bioökonomie“ entwickelt werden. Der dadurch steigende Biomassebedarf könnte negative Auswertungen haben und muss daher gründlich untersucht werden. Aus diesem Grund hat das LANUV mit Unterstützung des nova-Instituts im Zeitraum vom 01.03.2023 bis 28.02.2025 das Projekt „Biomassepotenziale Rheinisches Revier“ durchgeführt. Ziel des Projekts war es, Grundlagen und Instrumente zu schaffen, um zu einer nachhaltigen Nutzung von Biomasse aus der Land- und Ernährungswirtschaft in der Region beizutragen.

![Cellulose Fibres Conference 2025 (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital]](https://renewable-carbon.eu/publications/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/21-01-07_RC-Publications-Cover-Proceedings_Cellulose-Fibres-100x141.png) Cellulose Fibres Conference 2025 (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital]
Cellulose Fibres Conference 2025 (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital] 
![Renewable Materials Conference 2025 (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital]](https://renewable-carbon.eu/publications/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/21-01-07_RC-Publications-Cover-Proceedings_RMC-100x141.png)





![CO2-based Fuels and Chemicals Conference 2025 (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital]](https://renewable-carbon.eu/publications/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/21-01-07_RC-Publications-Cover-Proceedings_CO2-based-100x141.png)