Showing 61–80 of 412
-
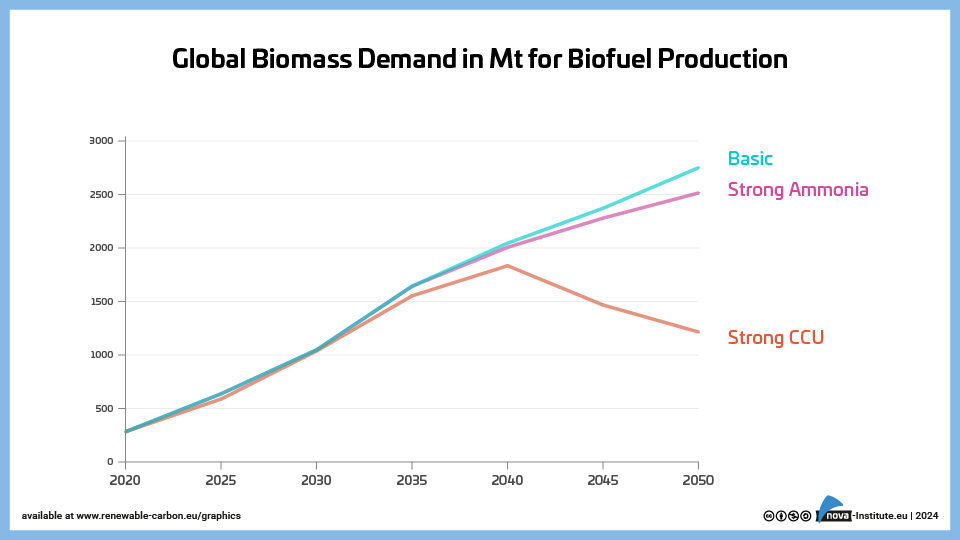
Global Biomass Demand in Mt for Biofuel Production – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
24 Downloads
24 Downloads
2025-01
FREE
24
Downloads -
Advanced Recycling Conference 2024 (Proceedings)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2024-12
150 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Add to
cartThe proceedings of the Advanced Recycling Conference 2024 (20-21 November, https://advanced-recycling.eu) contain 42 conference presentations, the conference journal, sponsor documents and the press release.
-
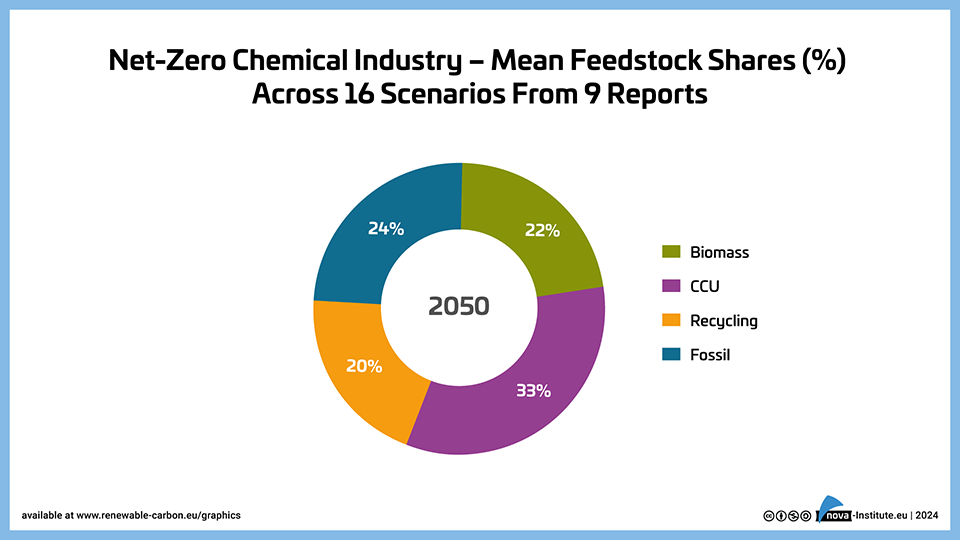
Net-Zero Chemical Industry – Mean Feedstock Shares (%) Across 16 Scenarios From 9 Reports – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
61 Downloads
61 Downloads
2024-11
FREE
61
DownloadsThe graph illustrates the mean feedstock shares projected for the 2050 net-zero chemical industry, based on 16 scenarios across 9 reports. The chart shows a diverse mix of feedstocks, with CCU (33%) and recycling (20%) playing significant roles alongside biomass (22%), while fossil & CCS still account for 24% of the feedstock share.
-
Evaluation of Recent Reports on the Future of a Net-Zero Chemical Industry in 2050 (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
20 Pages
1789 Downloads
1789 Downloads
2024-11
FREE
Free Shipping1789
DownloadsThe Renewable Carbon Initiative’s Scientific Background Report assesses 24 scenarios from 15 studies to envision a net-zero chemical industry by 2050. The analysis anticipates continued growth in chemical production, projecting a 2.4-fold increase in global feedstock demand by 2050 compared to 2020 levels, with most expansion expected outside Europe while European feedstock volumes remain stable. To achieve net-zero emissions, the industry is projected to undergo a significant shift in feedstocks, with key renewable carbon sources identified as biomass (22%), carbon capture and utilisation (33%), and recycling (20%), while the remaining 24% comes from fossil sources with carbon capture and storage. For plastics specifically, recycling is expected to play an even larger role, accounting for 42% of feedstocks on average. This transition will require continued innovation and investment in renewable carbon technologies to meet ambitious defossilisation goals.
The report provides invaluable insights for industry leaders, policymakers, and researchers, highlighting the urgent need for action to achieve a net-zero future in the chemical sector by 2050.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/SXWV6083
-
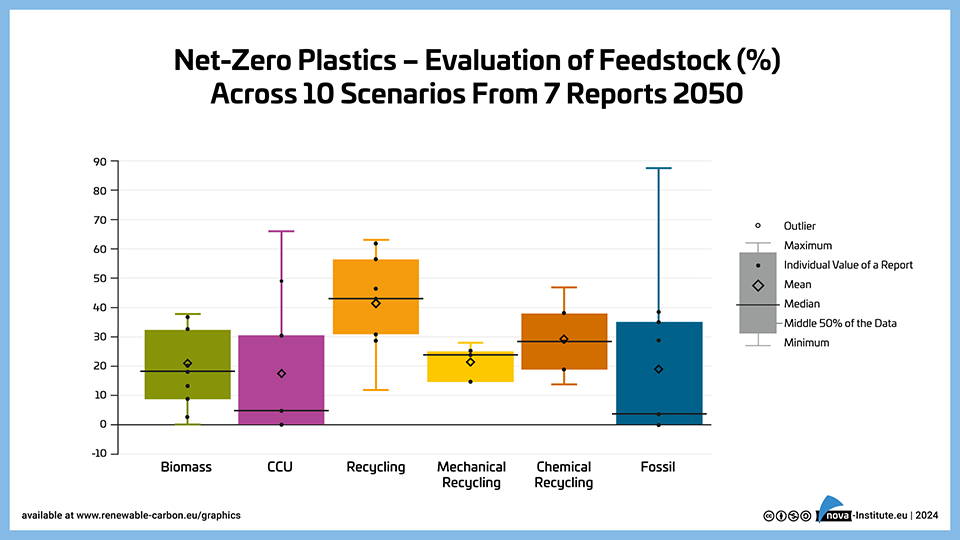
Net-Zero Plastics – Evaluation of Feedstock (%) Across 10 Scenarios from 7 Reports 2050 – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
114 Downloads
114 Downloads
2024-11
FREE
114
DownloadsThe graph illustrates feedstock projections specifically for the plastics sector by 2050, analysing 10 scenarios from 7 reports, where recycling emerges as the dominant feedstock at 42% (combining mechanical and chemical recycling), while biomass (21%), CCU (17%), and fossil with CCS (19%) play supporting roles. The data shows less variation in projections compared to the chemical industry overall, suggesting stronger agreement on the future role of recycling in plastics production.
-
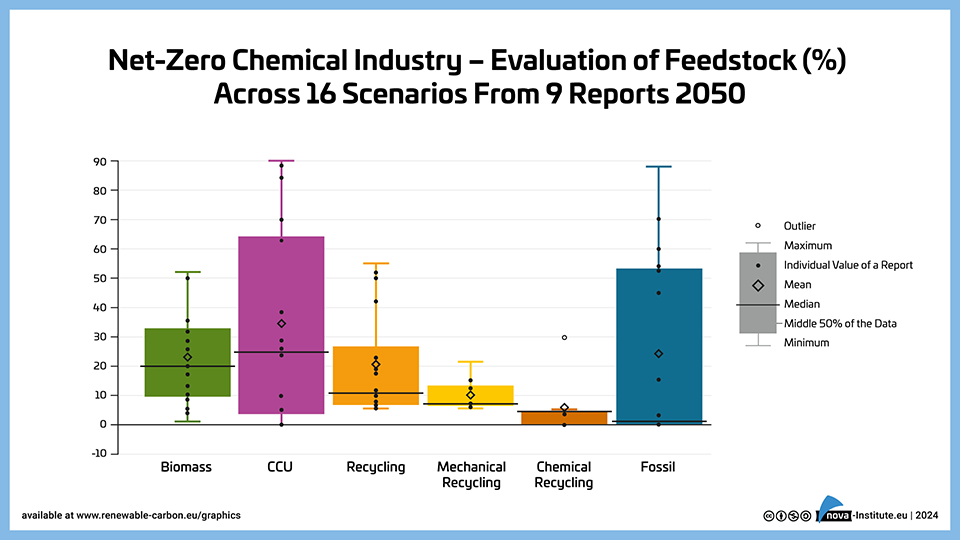
Net-Zero Chemical Industry – Evaluation of Feedstock (%) Across 16 Scenarios from 9 Reports 2050 – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
95 Downloads
95 Downloads
2024-11
FREE
95
DownloadsThe graph shows the distribution of feedstock sources for the net-zero chemical industry by 2050, based on 16 scenarios from 9 reports, with CCU having the highest mean share at 33%, followed by biomass (22%), recycling (20%, split between mechanical and chemical), and fossil with CCS (24%). The data reveals significant variability across scenarios, particularly for CCU which ranges from near 0% to 90%, while both biomass and recycling show more moderate ranges, indicating a general consensus on their roles in the future chemical industry.
-
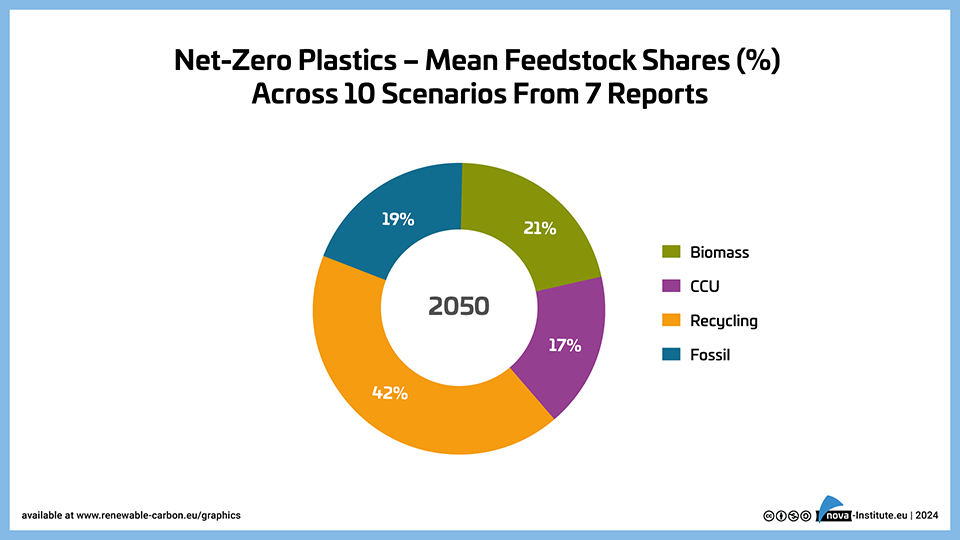
Net-Zero Plastics – Mean Feedstock Shares (%) Across 10 Scenarios From 7 Reports – Graphic (PNG)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
1 Page
81 Downloads
81 Downloads
2024-11
FREE
81
DownloadsThe graph presents the mean feedstock shares for the 2050 net-zero plastics sector, derived from 10 scenarios across 7 reports. In this projection, recycling dominates with a 42% share, followed by biomass (21%), fossil & CCS (19%), and CCU (17%), highlighting the increased potential for circularity in the plastics industry compared to the broader chemical sector.
-
Alternatives Naphtha – Den Kreislauf für Kunststoffe und Reifen schließen: Pyrolyseöl als chemischer Rohstoff (Gastbeitrag Teil 3) (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Technology
1 Page
95 Downloads
95 Downloads
2024-11
FREE
95
DownloadsIn den beiden vorangegangenen Artikeln dieser Serie wurde das Konzept des alternativen Naphthas als Ersatz für fossile Rohstoffe in Raffinerien und Steamcrackern vorgestellt. In diesem dritten Artikel konzentriert sich die Diskussion auf Pyrolyseöl, das durch chemisches Recycling von Kunststoffabfällen und Reifen gewonnen wird, und warum dies ein wichtiges „alternatives Naphtha“ für Raffinerien und Steamcracker ist.
Relevante Anteile erneuerbarer Chemikalien und Polymere sind ohne „alternatives Naphtha“ nicht möglich. Ohne eine Abkehr von fossilem Naphtha wird es keine signifikante Defossilisierung des Chemiesektors geben.
Dieser Artikel ist im Rahmen einer Serie von Gastbeiträgen im CHEManager erschienen. Es handelt sich um „Alternatives Naphtha Teil 3“ – aus CHEManager 11/2024.
Hier finden sie den Artikel auch bei CHEManager.
-
Alternatives Naphtha – Herstellung und Nutzung – Wie erneuerbare Rohstoffe zu Naphtha verarbeitet werden (Gastbeitrag Teil 2) (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Technology
1 Page
49 Downloads
49 Downloads
2024-10
FREE
49
DownloadsIm ersten Artikel dieser dreiteiligen Serie wurde das Konzept „Alternatives Naphtha“ als Ersatz für fossile Rohstoffe in Raffinerien und Steamcrackern vorgestellt. Relevante Mengen erneuerbarer Chemikalien und Polymere sind ohne alternatives Naphtha nicht realisierbar, eine signifikante Defossilisierung des Chemiesektors erfordert den Verzicht auf fossiles Naphtha. Im zweiten Artikel wird die Herstellung und Nutzung von alternativem Naphtha genauer beleuchtet.
Biobasierte Rohstoffe wie Fette, Öle und Schmierstoffe (Triglyceride) können fossile Erdölrohstoffe ersetzen und in bestehenden Raffinerien mitverarbeitet werden. Dies ist attraktiv, da Raffinerien ohne große Investitionen Biokraftstoffe und biobasierte Grundchemikalien produzieren können. Eine Vorbehandlung der Rohstoffe kann dabei erforderlich sein.
Dieser Artikel ist im Rahmen einer Serie von Gastbeiträgen im CHEManager erschienen. Es handelt sich um „Alternatives Naphtha Teil 2“ – aus CHEManager 10/2024.
-
Forest-Based Biorefineries: Innovative Bio-Based Products for a clean Transition (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Technology
8 Pages
385 Downloads
385 Downloads
2024-10
FREE
Free Shipping385
DownloadsA new study conducted by the nova-Institute and commissioned by the Confederation of European Paper Industries (Cepi) unveils a significant surge in the European biorefinery sector, with forest-based biorefineries more than doubling their turnover to €6 billion since 2020. This remarkable growth underscores the rising demand for sustainable, bio-based alternatives to fossil-based products.
The research, focused on the pulp and paper industry that produce additional bio-based products which land on the market beyond pulp and paper, identifies a total of 143 biorefineries across Europe, with 126 currently operational and 17 in development. The largest number of biorefineries is in Sweden, Finland, Germany, Portugal and Austria. The study points to a bright future for biorefineries, with projected annual growth rates of up to 5% until 2050.
The products of these biorefineries provide sustainable solutions across various industries, from aviation to fashion, offering alternatives in materials, chemicals, fuels, food, and pharmaceuticals. Importantly, biorefineries contribute to Europe’s climate targets, with bio-based products already substituting over 3.1 megatons of CO2 emissions that would have been produced by fossil-based industries.The study emphasises that these advancements are not replacing traditional pulp and paper-making activities but are creating new revenue streams and increasing resource efficiency, providing a pathway to sustainable economic growth.
-
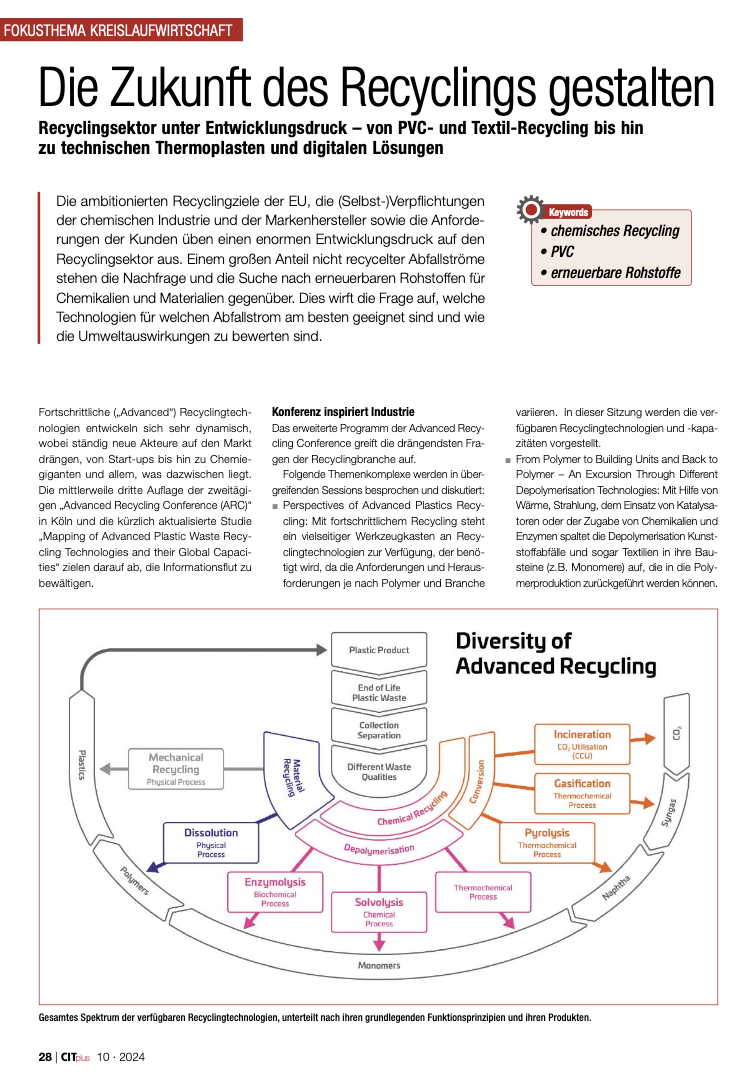
Die Zukunft des Recyclings gestalten (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
2 Pages
569 Downloads
569 Downloads
2024-10
FREE
Free Shipping569
DownloadsDie ambitionierten Recyclingziele der EU, die (Selbst-)Verpflichtungen der chemischen Industrie und der Markenhersteller sowie die Anforderungen der Kunden üben einen enormen Entwicklungsdruck auf den Recyclingsektor aus. Einem großen Anteil nicht recycelter Abfallströme stehen die Nachfrage und die Suche nach erneuerbaren Rohstoffen für Chemikalien und Materialien gegenüber. Dies wirft die Frage auf, welche Technologien für welchen Abfallstrom am besten geeignet sind und wie die Umweltauswirkungen zu bewerten sind.
-
nova-paper #17: Science-based Definition of Natural Polymers (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
22 Pages
749 Downloads
749 Downloads
2024-09
FREE
Free Shipping749
DownloadsEuropean policy has defined „natural polymers“ in a way that has caused much concern and debate among scientists and industry, and has created a barrier to innovation. The authors of this report have carried out a comprehensive scientific evaluation of how the scientific literature defines „natural polymers“, and the result is: The European policy definition is partly in clear contrast to the scientific definitions.
„Occurring in nature“ is the basis for every definition of „natural polymers“ in the scientific literature and in policy. All scientific definitions include biotechnological processes for the production of natural polymers. Not a single definition mentions the place of polymerisation as a criterion – in clear contrast to European policy. Industrial practice confirms this finding: A long list of widely accepted natural polymers includes biotechnologically processed polymers and the place of polymerisation is not a criterion.
Conclusion: A policy definition of „natural polymers“ that is at odds with almost all scientific definitions and at odds with business reality, and which is a major barrier to innovation, green investment and lower carbon footprints, needs to be revised.
The essence of the scientific definitions evaluated in this report is simple and leads to the following proposed definition: „Natural polymers are those that occur in nature, are produced in and extracted from nature, or can be produced identically using biotechnological processes“.DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/UGBZ5516
-
European Bioeconomy in Figures 2014–2021 (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
29 Pages
821 Downloads
821 Downloads
2024-09
FREE
Free Shipping821
DownloadsThe bioeconomy in the European Union is a strong contributor to the overall economy and accounts for over 16 million employees and more than 2.3 trillion Euro in turnover across all 27 Member States. In terms of turnover almost half of the 2.3 trillion Euro can be attributed to the food and feed industries, which remain a large part of the EU bioeconomy. Adding to this are the agriculture and forestry sectors providing primary biomass to bioeconomic processes. However, the sectors processing these feedstocks and manufacturing intermediate and end-use products, collectively referred to as the bio-based industries, find themselves contributing on a stable level to the overall bioeconomy and account for almost a third of the overall turnover.
-
Alternatives Naphtha – Erneuerbare Kohlenstoffquellen sollen der Defossilisierung der Chemieindustrie einen Schub verleihen (Gastbeitrag Teil 1) (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Technology
1 Page
45 Downloads
45 Downloads
2024-09
FREE
45
DownloadsFür die Defossilisierung der chemischen Industrie ist es entscheidend, Alternativen zu fossilem Naphtha zu finden. Relevante Anteile erneuerbarer Chemikalien und Polymere sind ohne „alternatives Naphtha“ nicht möglich.
Das Konzept „alternatives Naphtha“ nutzt die bestehende Raffinerie-, Steamcracker- und Chemieindustrieinfrastruktur, in der ein Teil der fossilen Rohstoffe – Rohöl oder fossiles Naphtha – durch erneuerbare Kohlenstoffalternativen ersetzt werden kann, die aus den drei Quellen Biomasse, CO2 und Recycling stammen.
Dieser Artikel ist im Rahmen einer Serie von Gastbeiträgen im CHEManager erschienen. Es handelt sich um „Alternatives Naphtha Teil 1“ – aus CHEManager 09/2024.
Hier finden sie den Artikel auch bei CHEManager.
-
RCI’s position paper: “Swift implementation of EU biotech and biomanufacturing initiative is key to strengthen EU competitiveness and accelerate defossilisation (PDF)”
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
3 Pages
473 Downloads
473 Downloads
2024-09
FREE
Free Shipping473
DownloadsThe Renewable Carbon Initiative’s position paper emphasizes that the EU must swiftly implement its biotechnology and biomanufacturing initiative to accelerate the shift from fossil carbon to renewable sources and boost competitiveness. The Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) highlights three key actions:
1.) Align with Circular Economy Policies: Ensure consistency across EU initiatives to promote renewable carbon from biomass, recycling, and CCU.
2.) Boost Market Demand: Address the lack of demand for renewable feedstocks by implementing policies to make fossil alternatives less competitive.
3.) Enable Fossil-to-Renewable Transition: Repurposing current fossil-based manufacturing to use renewable feedstocks. Clear sustainability criteria, access to various biomass sources, and broader definitions of biomanufacturing processes are essential to achieving this transition.
These actions are vital for achieving net-zero goals and strengthening EU industry.
-
Alternative Naphtha – Technologies and Market, Status and Outlook (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Technology
188 Pages

2024-07
2,500 € – 9,000 €Price range: 2,500 € through 9,000 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Select
licenceFor the defossilisation of the chemical industry, it is crucial to find alternatives to fossil-based naphtha. The “alternative naphtha” concept makes use of existing refinery, steam cracking and chemical industry infrastructure where a proportion of fossil-based feedstocks – crude oil or fossil-based naphthas can be replaced by renewable carbon alternatives derived from the three sources of renewable carbon: CO2, biomass and recycling.
This new report by nova-Institute presents an analysis of the routes, associated technologies, market players and volumes by which renewable carbon can be introduced to refinery and steam cracking operations as replacement for fossil based feedstocks.
With 188 pages, 22 tables and illustrated by 48 graphics the report provides a comprehensive view on the growth in capacity for these alternative sources of naphtha as chemical industry feedstock, production routes and the need for “upgrading”, key companies and partnerships and the regulatory environment.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/JICP8041
-
Alternative Naphtha – Technologies and Market, Status and Outlook (PDF) – Short Version
Markets & Economy, Technology
20 Pages
1163 Downloads
1163 Downloads
2024-07
FREE
1163
DownloadsFor the defossilisation of the chemical industry, it is crucial to find alternatives to fossil-based naphtha. The “alternative naphtha” concept makes use of existing refinery, steam cracking and chemical industry infrastructure where a proportion of fossil-based feedstocks – crude oil or fossil-based naphthas can be replaced by renewable carbon alternatives derived from the three sources of renewable carbon: CO2, biomass and recycling.
This new report by nova-Institute presents an analysis of the routes, associated technologies, market players and volumes by which renewable carbon can be introduced to refinery and steam cracking operations as replacement for fossil based feedstocks.
With 188 pages, 22 tables and illustrated by 48 graphics the report provides a comprehensive view on the growth in capacity for these alternative sources of naphtha as chemical industry feedstock, production routes and the need for “upgrading”, key companies and partnerships and the regulatory environment.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/JICP8041
-
RCI’s position paper: “Towards an ambitious Industrial Carbon Management for the EU – A Call for Speedy and Coherent Implementation of Policy Measures (PDF)”
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
3 Pages
496 Downloads
496 Downloads
2024-07
FREE
496
DownloadsThe Renewable Carbon Initiative’s position paper emphasizes the need for a comprehensive industrial carbon management strategy in the EU that goes beyond CO2 emissions to include all carbon sources, promoting the use of renewable carbon from biomass, CCU, and recycling. It calls for the establishment of a regulatory framework with specific sub-targets and incentives by 2025 to accelerate the adoption of circular carbon technologies and reduce dependence on fossil feedstocks. The paper argues that recognising carbon as a raw material is essential for achieving sustainable carbon cycles and meeting the EU’s climate neutrality goals by 2050.
-
Joint Statement PEF TAB – biogenic carbon modelling (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
4 Pages
498 Downloads
498 Downloads
2024-06
FREE
498
DownloadsThe RCI along with the organisations APAG Oleochemicals Europe, Bio-based Industries Consortium, BioChem Europe, EuropaBio, GO!PHA, IKT Kunststofftechnik Stuttgart and Plastics Europe submitted this Joint Statement to the members of the Technical Advisory Boyard of the Product Environmental Footprint (PEF TAB). The purpose of this submission is to address the ongoing discussions on carbon modelling in the EF, which have been frequently discussed in recent PEF TAB meetings. With this joint statement we advocate for enabling -1/+1 accounting of biogenic and atmospheric carbon in the LCA methodology.
-
Renewable Materials Conference 2024 (Proceedings, PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2024-06
200 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Add to
cartThe proceedings of the Renewable Materials Conference 2024 (11-13 June 2024, https://renewable-materials.eu) contain all released presentations, the conference journal, and the press release of the three winners of the Innovation Award “Renewable Material of the Year 2024″.

![Renewable Materials Conference 2024 (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital]](https://renewable-carbon.eu/publications/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/21-01-07_RC-Publications-Cover-Proceedings_RMC-100x141.png) Renewable Materials Conference 2024 (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital]
Renewable Materials Conference 2024 (Proceedings, PDF) [Digital]