Showing 1–20 of 413
-
Bio-based Building Blocks and Polymers – Global Capacities, Production and Trends 2024–2029 (PDF)
NewMarkets & Economy
434 Pages

2025-03
3,000 € – 10,000 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Select
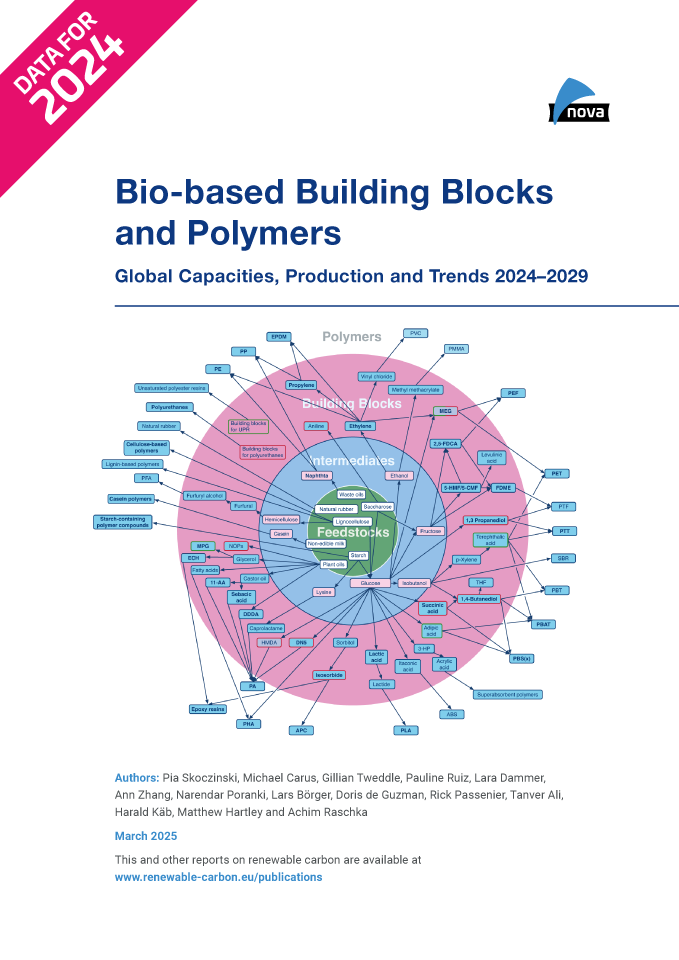
licence2024 was a respectable year for bio-based polymers, with an overall expected CAGR of 13 % to 2029. Overall, bio-based biodegradable polymers have large installed capacities with an expected CAGR of 17 % to 2029, but the current average capacity utilisation is moderate at 65 %. In contrast, bio-based non-biodegradable polymers have a much higher utilisation rate of 90 %, but will only grow by 10 % to 2029.
Epoxy resin and PUR production is growing moderately at 9 and 8 %, respectively, while PP and cyclic APC capacities are increasing by 30 %. Despite a decline in production of biodegradables, especially for PLA in Asia, capacities have increased by 40 %. The same applies to PHA capacities. Commercial newcomers such as casein polymers and PEF recorded a rise in production capacity and are expected to continue to grow significantly until 2029.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/UMTR4695
-
Bio-based Building Blocks and Polymers Global Capacities, Production and Trends 2024–2029 – Short Version (PDF)
NewMarkets & Economy
28 Pages
892 Downloads
892 Downloads
2025-03
FREE
Free Shipping892
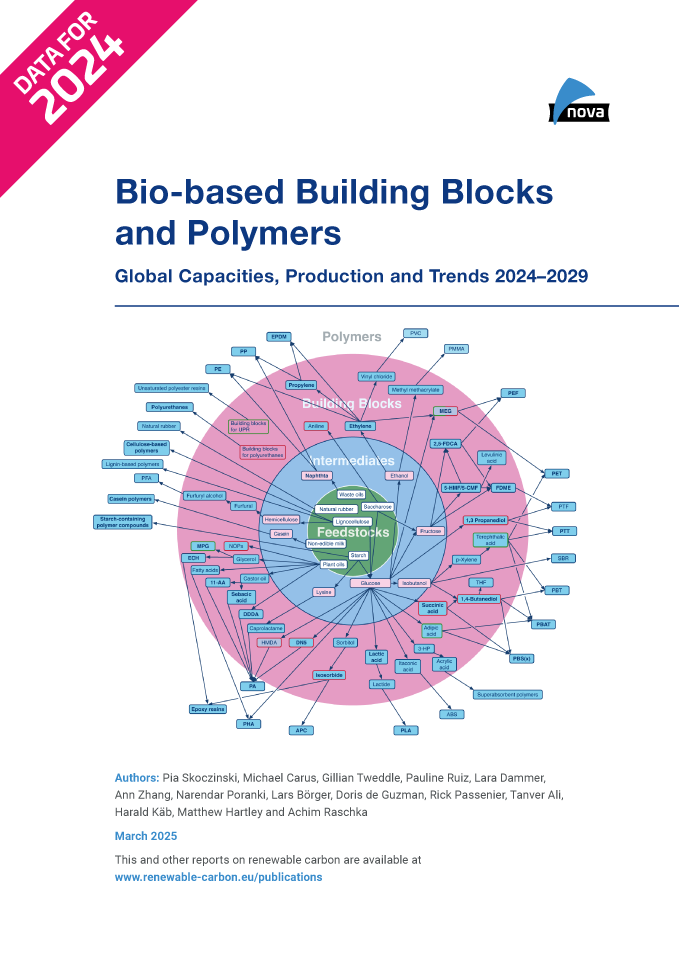
Downloads2024 was a respectable year for bio-based polymers, with an overall expected CAGR of 13 % to 2029. Overall, bio-based biodegradable polymers have large installed capacities with an expected CAGR of 17 % to 2029, but the current average capacity utilisation is moderate at 65 %. In contrast, bio-based non-biodegradable polymers have a much higher utilisation rate of 90 %, but will only grow by 10 % to 2029.
Epoxy resin and PUR production is growing moderately at 9 and 8 %, respectively, while PP and cyclic APC capacities are increasing by 30 %. Despite a decline in production of biodegradables, especially for PLA in Asia, capacities have increased by 40 %. The same applies to PHA capacities. Commercial newcomers such as casein polymers and PEF recorded a rise in production capacity and are expected to continue to grow significantly until 2029.
-
160 Downloads
2025-06
FREE
Free Shipping160
DownloadsThere is an urgent need for horizontal sustainability criteria for biomass in bio-based chemicals and derived materials – in the framework of future incentives.
The Renewable Carbon Initiative’s position paper on sustainability criteria for biomass emphasises that biomass is essential for Europe’s net-zero transition by replacing fossil resources in chemicals and materials.
The EU must establish clear, aligned sustainability criteria for biomass use in chemicals, based on the Renewable Energy Directive (REDIII) but adapted for this sector. These criteria should address sustainable cultivation of feedstock, full life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions, and feedstock eligibility, and be linked to market incentives to ensure effectiveness.
No caps should limit the use of primary agricultural biomass for chemicals, as it does not threaten food security and provides multiple benefits. Access to a wide range of sustainable feedstocks is crucial. Biodiversity impacts should be managed through climate-smart farming, while forest biomass criteria must focus on current sustainable practices using existing certification schemes. This approach will create a fair and dependable framework to support Europe’s sustainable bio-based economy.
-
Summary of RCI Scientific Background Report “RCI Policy Proposals for Facilitating the Transition to Renewable Carbon” (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Sustainability & Health
3 Pages
45 Downloads
45 Downloads
2025-06
FREE
Free Shipping45
DownloadsHow to defossilise the chemical industry – policy proposals
This is a summary of the RCI Scientific Background Report “RCI Policy Proposals for Facilitating the Transition to Renewable Carbon” published by the Renewable Carbon Plastics | bioplastics MAGAZINE [03/25] Vol. 20.
-
3-CO Social Innovation Brochure: Social Innovation – Solutions Contributing to Responsible Production and Consumption in the Bioeconomy and Beyond
Sustainability & Health
64 Pages
34 Downloads
34 Downloads
2025-06
FREE
Free Shipping34
DownloadsThis brochure by the EU-funded 3-CO project includes 17 carefully sected social innovations from various countries and sectors. These aim to introduce different approaches with the potential to change society at large but also inspire replication. They further identify hurdles in realising social innovation and introduce opportunities for upscaling and transfer. Derived policy recommendations complete the publication.
DOI No.: 10.5281/zenodo.15601644
-
110 Downloads
2025-06
FREE
Free Shipping110
DownloadsThis short document explains the OK renewable label, developed by RCI, nova and TÜV Austria and launched on 1 April 2025. The OK renewable label provides a clear, trustworthy way to identify products whose carbon content is derived from non‑fossil sources.
The Renewable Carbon Share (RCS) metric quantifies the proportion of a product’s renewable carbon that originates from the biosphere, atmosphere or technosphere but not the geosphere on a five‑tier scale from 20% to 100 %. Products earn an RCS classification based either on their actual renewable carbon content or through documented substitution of fossil‑based feedstock with renewable alternatives.
-
Joint Webinar hosted by Bio-based Industries Consortium (BIC) and the Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) (May 2025) (PDF)
Policy, Sustainability & Health
51 Pages
411 Downloads
411 Downloads
2025-05
FREE
Free Shipping411
DownloadsThe webinar was presented by Michael Carus (nova-Institute, RCI), supported by Christopher vom Berg (RCI), Dirk Carrez (BIC), and Marco Rupp (BIC). It was based on a Scientific Background Report “Is there enough biomass to defossilise the chemicals and derived materials sector by 2050?” commissioned by the Bio-based Industries Consortium (BIC) and the Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI).
It explored whether agricultural and woody biomass could sustainably meet 20% of the carbon demand for the chemical and derived materials sectors by 2050. Using models like CAPRI (for agriculture) and TiMBA (for forestry), the study examined different scenarios, balancing food, feed, and biofuel priorities. Results showed that with moderate technological advancements, this 20% target is achievable without compromising sustainability or biodiversity. Stronger high-tech scenarios could even provide up to 40%, though existing biofuel policies may limit this. Overall, the study concluded that biomass could play a key role in defossilising the chemical sector, given the right innovations and policy frameworks.
-
CO2-based Fuels and Chemicals Conference 2025 (Proceedings, PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2025-05
150 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Add to
cartThe proceedings of the CO2-based Fuels and Chemicals Conference 2025 (29-30 April 2025, https://co2-chemistry.eu) contain all released presentations, the conference journal, and the press release of the three winners of the Innovation Award “Best CO2 Utilisation 2025″.
-
Summary of BIC/RCI Report – Food and feed supply not at risk (PDF)
Sustainability & Health
3 Pages
93 Downloads
93 Downloads
2025-05
FREE
Free Shipping93
DownloadsBiomass can meet 20 % of carbon demand in the chemicals sector by 2050 without compromising food and feed supply.
This is a summary of the RCI/BIC study “Is There Enough Biomass to Defossilise the Chemicals and Derived Materials Sector by 2050?” published by the Renewable Carbon Plastics | bioplastics MAGAZINE [02/25] Vol. 20.
-
Summary of RCI Scientific Background Report “Evaluating LCA Approaches and Methodoloies for Renewable Carbon Sources” (PDF)
Sustainability & Health
3 Pages
207 Downloads
207 Downloads
2025-05
FREE
Free Shipping207
DownloadsHow leading LCA standards address renewable carbon: An RCI study
This is a summary of the RCI Scientific Background Report “Evaluating LCA Approaches and Methodologies for Renewable Carbon Sources” published by the Renewable Carbon Plastics | bioplastics MAGAZINE [02/25] Vol. 20.
-
RCI Webinar: LCA Approaches and Methodologies for Renewable Carbon (PDF)
Sustainability & Health
54 Pages
315 Downloads
315 Downloads
2025-05
FREE
Free Shipping315
DownloadsThis webinar presentation is based on the key findings of the RCI Scientific Background Report “Evaluating LCA Approaches and Methodologies for Renewable Carbon Sources” and was held on 7 May 2025 by Ferdinand Kähler (nova-Institute). The session examined how major LCA and carbon footprint standards address renewable carbon sources.
Topics covered include:
- Comparison of ISO standards (14040, 14044, 14067), PEF, TfS, Pact Pathfinder, GHG Protocol, and EPDs
- Areas of consistency, such as biogenic carbon and recycling approaches
- Key divergences, including allocation methods and co-product substitution credits
This deck is a useful reference for sustainability teams, LCA practitioners and anyone working with carbon accounting and renewable materials.
-
Background Document to RCI/BIC Report „Measuring the Use of Biogenic Feedstocks in the Global and EU Chemical Industry in 2023″ (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy
16 Pages
68 Downloads
68 Downloads
2025-05
FREE
Free Shipping68
DownloadsThis background document is a supplement to the main publication: “Is there Enough Biomass to Defossilise the Chemicals and Derived Materials Sector by 2050? – A Joint BIC and RCI Scientific Background Report“.
The report provides a comprehensive assessment of biogenic feedstock usage in the global and EU chemical industries for 2023, detailing sources like starch, sugar, vegetable oils, animal fats and more.
Globally, the chemical industry used 7.3 million tonnes of starch and 4.0 million tonnes of sugar for bioethanol-derived chemicals, while the EU used 480,000 and 150,000 tonnes respectively. Vegetable oils accounted for the highest single feedstock usage globally at 17.6 million tonnes, and 1.6 million tonnes in the EU. Other significant feedstocks include glycerol (3.4 million tonnes globally, 490,000 tonnes in the EU) and natural rubber (14 million tonnes globally, 1.1 million tonnes in the EU).
The data aims to establish a baseline for future biomass modeling and highlights discrepancies and assumptions due to data gaps.
-
A Deep Dive into the Agriculture sector – „Is There Enough Biomass to Defossilise the Chemicals and Derived Materials Sector by 2050?“ (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
41 Pages
177 Downloads
177 Downloads
2025-05
FREE
Free Shipping177
DownloadsThis presentation is a supplement to the main publication: “Is there Enough Biomass to Defossilise the Chemicals and Derived Materials Sector by 2050? – A Joint BIC and RCI Scientific Background Report“ and provides deeper insights into the agriculture sector.
The presentation analyses the potential of sustainable agricultural biomass to meet future carbon demand in the global and EU chemical industries by 2050.
It uses the CAPRI model to simulate various land-use and technological scenarios, finding that only the Green High Tech (HT) scenarios can meet the projected biomass needs while fulfilling food, feed, and fuel demands. Key feedstocks include starch, sugar, and oil crops, with starch having the most significant expansion potential. Residues and biowaste play a limited but important role, especially when supplemented by advanced technologies and logistical improvements. External factors such as reduced meat consumption, Ukraine’s potential EU accession and innovations like agro-photovoltaics and urban farming also influence biomass availability.
-
A Deep Dive into the Forestry sector – „Is There Enough Biomass to Defossilise the Chemicals and Derived Materials Sector by 2050?” (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
46 Pages
181 Downloads
181 Downloads
2025-05
FREE
Free Shipping181
DownloadsThis presentation is a supplement to the main publication: “Is there Enough Biomass to Defossilise the Chemicals and Derived Materials Sector by 2050? – A Joint BIC and RCI Scientific Background Report“ and provides deeper insights into the forestry sector.
The TiMBA model evaluates the global forest products market under three scenarios—Business-as-Usual (BAU), Green Low Resource Depletion (LRD), and Green High Tech (HT)—to project wood production, trade, and forest development from 2020 to 2050. Under all scenarios, global forest area increases, especially in Asia, with the LRD and HT scenarios showing stronger forest protection due to deforestation bans and improved forest management. Industrial roundwood production rises by 38% globally by 2050, with Asia leading the growth, and highest demand seen in the LRD scenario, particularly for new applications like dissolving pulp and cellulose derivatives. Despite increased production, forest stocks remain stable or improve slightly due to technological efficiency, increased recycling, and reduced raw material inputs. However, competition for wood residues among biorefineries, pellet production, and sustainable aviation fuels poses challenges to meeting future biomass demand sustainably.
-
nova-Institute: Science-based Consultancy on Renewable Carbon for Chemicals and Materials (PDF)
6 Pages
388 Downloads
388 Downloads
2025-04
FREE
388
Downloads -
RCI Policy Proposals for Facilitating the Transition to Renewable Carbon (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology
70 Pages
726 Downloads
726 Downloads
2025-04
FREE
Free Shipping726
DownloadsThe report outlines a strategic roadmap for transforming Europe’s chemical industry by transitioning from fossil-based to renewable carbon sources. It highlights the industry’s current crisis which is driven by global competition, high energy costs, and regulatory pressure, and stresses the urgency of reducing dependence on fossil feedstocks. The report aruges that the transition to renewable carbon is not just about environmental sustainability; it is about securing Europe’s industrial future and maintaining its global competitiveness in a rapidly changing world. By pioneering renewable carbon technologies, the EU can unlock economic benefits and unleash its innovation potential while advancing climate neutrality ambitions.
The Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI) proposes ten comprehensive policy measures including mandatory renewable carbon targets, adaptation of emissions trading systems, and financial support mechanisms. These proposals aim to create market demand, drive innovation and build industrial resilience. Key enablers include harmonised standards, robust certification, infrastructure development, and stakeholder engagement.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/DZRU4577
-
2025-04
FREE
Plus 19% MwSt.Free Shipping0
More
Downloads
infoDas Rheinische Revier soll im Zuge des Kohleausstiegs zu einer „Modellregion Bioökonomie“ entwickelt werden. Der dadurch steigende Biomassebedarf könnte negative Auswertungen haben und muss daher gründlich untersucht werden. Aus diesem Grund hat das LANUV mit Unterstützung des nova-Instituts im Zeitraum vom 01.03.2023 bis 28.02.2025 das Projekt „Biomassepotenziale Rheinisches Revier“ durchgeführt. Ziel des Projekts war es, Grundlagen und Instrumente zu schaffen, um zu einer nachhaltigen Nutzung von Biomasse aus der Land- und Ernährungswirtschaft in der Region beizutragen.
-
Cellulose Fibres Conference 2025 (Proceedings, PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health, Technology

2025-03
150 € ex. tax
Plus 19% MwSt.Press
release Add to
cartThe Cellulose Fibres Conference 2025 – New with Biosynthetics! (https://cellulose-fibres.eu, 12-13 March 2025, Cologne, hybrid) covered the entire value chain of the sustainable textile industry, from lignocellulose, pulp, cellulose fibres such as rayon, viscose, modal or lyocell and new developments to a wide range of applications:
Textiles from renewable fibres, non-wovens such as wet wipes, as well as areas such as composites, hygiene, packaging or nano cellulose in the food industry. This year, for the first time, the conference included a dedicated session on biosynthetics – a promising area to complement the alternative for bio-based textiles. Deep insights have been offered into the future of cellulose fibres, which fits perfectly with the current shift towards circular economy, recycling and sustainable carbon cycles.The Cellulose Fibres Conference Proceedings include all released conference presentations, the conference journal, sponsor documents and the conference press release.
-
Evaluating LCA Approaches and Methodologies for Renewable Carbon Sources Report 1 of 3 – Renewable Carbon in LCA Guidelines (March 2025) (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
145 Pages
719 Downloads
719 Downloads
2025-03
FREE
Free Shipping719
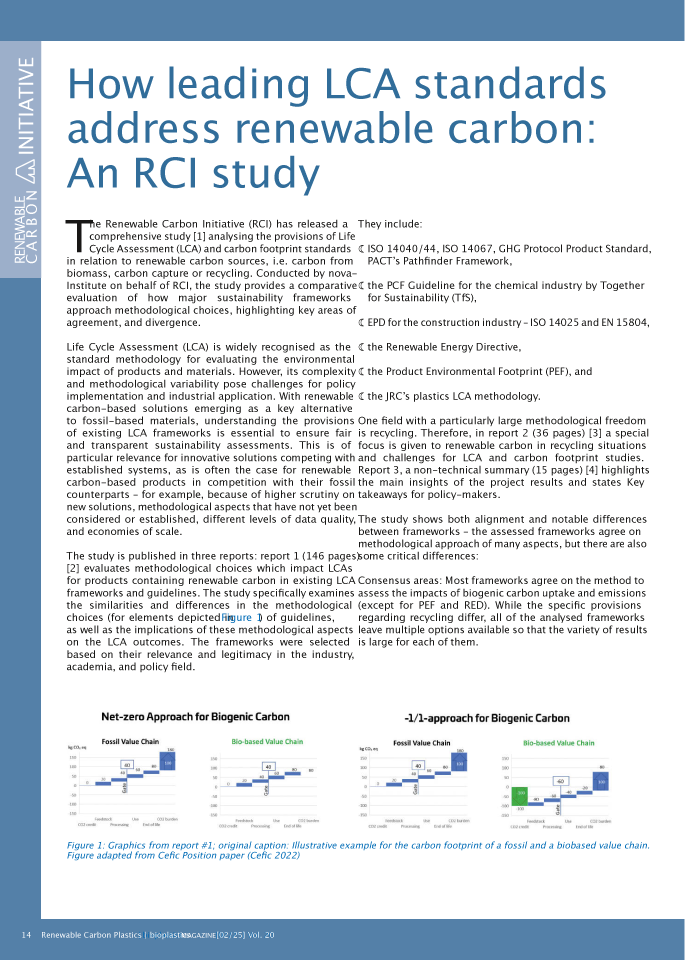
DownloadsRenewable Carbon in LCA Guidelines (146 pages) evaluates methodological choices which impact LCAs for products containing renewable carbon in existing LCA frameworks and guidelines. The study specifically examines the similarities and differences in the methodological choices of guidelines, as well as the implications of these methodological aspects on the resulting LCA outcomes.The frameworks were selected based on their relevance and legitimacy in the industry, academia and policy field, and include: ISO 14040/44, ISO 14067, GHG Protocol Product Standard, PACT’s Pathfinder Framework, the PCF Guideline for the chemical industry by Together for Sustainability (TfS), EPD for the construction industry – ISO 14025 and EN 15804, the Renewable Energy Directive, the Product Environmental Footprint (PEF) and the JRC’s plastics LCA methodology. One field with a particularly large methodological freedom is recycling.
This report is the first report of a larger RCI project on LCA methodology, which includes two additional publications:
Report 2 of 3 – Renewable Carbon in Recycling Situations
Report 3 of 3 – Non-technical SummaryPlease find these additional reports by following the respective links at the bottom of this page.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/VCYM7822
-
Evaluating LCA Approaches and Methodologies for Renewable Carbon Sources Report 2 of 3 – Renewable Carbon in Recycling Situations (March 2025) (PDF)
Markets & Economy, Policy, Sustainability & Health
37 Pages
493 Downloads
493 Downloads
2025-03
FREE
Free Shipping493
DownloadsThis report focuses on renewable carbon in recycling scenarios and the key challenges in LCA and carbon footprint assessments. It examines system boundaries, allocation methods, and biogenic carbon accounting approaches, highlighting their influence on sustainability evaluations. The report emphasises the cut-off and avoided-burden approaches for recycling while recommending the -1/+1 method for biogenic carbon transparency. However, it also identifies contradictions between LCA results and broader sustainability goals, such as the EU waste hierarchy, which prioritises recycling. To address these inconsistencies, the report suggests integrating LCA with additional sustainability metrics like land use and recyclability. Ultimately, refining these methodologies will enhance the accuracy and reliability of environmental assessments for bio-based and recycled materials.
This report is the second report of a larger RCI project on LCA methodology, which includes two additional publications:
Report 1 of 3 – Renewable Carbon in LCA Guidelines
Report 3 of 3 – Non-technical SummaryPlease find these additional reports by following the respective links at the bottom of this page.
DOI No.: https://doi.org/10.52548/QTVU8642