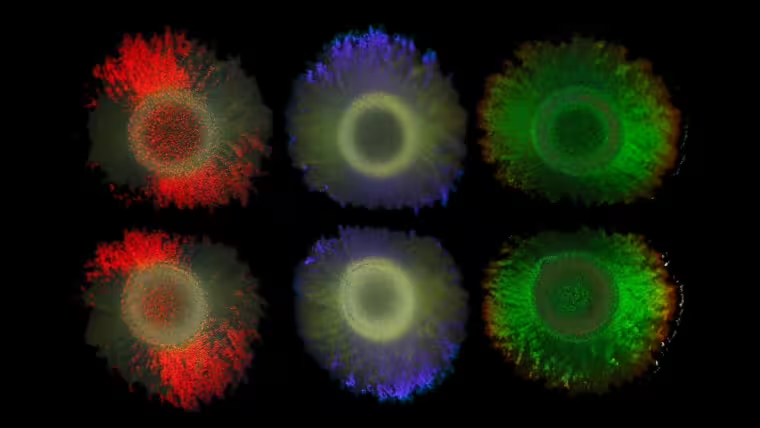
An international team of researchers has investigated the mechanism that makes some types of bacteria reflect light without using pigments. The researchers were interested in the genes responsible and discovered important ecological connections. These findings were published in the current issue of the renowned journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The iridescent colours known from peacock feathers or butterfly wings are created by tiny structures that reflect light in a special way. Some bacterial colonies form similar glittering structures. In collaboration with the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces, Leibniz Institute DSMZ-German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures, Utrecht University, University of Cambridge, and the Netherlands Institute for Sea Research, the scientists sequenced the DNA of 87 structurally coloured bacteria and 30 colourless strains and identified genes that are responsible for these fascinating colonies. These findings could lead to the development of environmentally friendly dyes and materials, a key interest of the collaborating biotechnology company Hoekmine BV.
Predictions with artificial intelligence
The researchers trained an artificial intelligence model to predict which bacteria produce iridescent colours based on their DNA. “With this model, we analyzed over 250,000 bacterial genomes and 14,000 environmental samples from international open science repositories”, says Prof. Bas E. Dutilh, Professor of Viral Ecology at the University of Jena and researcher in the Cluster of Excellence ‘Balance of the Microverse’. “We discovered that the genes responsible for structural color are mainly found in oceans, freshwater, and special habitats such as intertidal zones and deep-sea areas. In contrast, microbes in host-associated habitats such as the human microbiome displayed very limited structural colour.”
Ecological significance and future applications
The study results indicate that the colourful bacterial colony structures are not only used to reflect light. Surprisingly, these genes are also found in bacteria that live in deep oceans without sunlight. This could imply that the colours could reflect deeper processes of cell organization with important functions, such as protecting the bacteria from viruses, or efficiently colonizing floating food particles. These findings could inspire new, sustainable technologies based on these natural structures.
Excellent collaborative research
The international research project exemplifies how two profile lines of the Friedrich Schiller University Jena, LIFE and LIGHT, can find each other. It also addresses the goals of the Cluster of Excellence “Balance of the Microverse”, where Prof. Dutilh has held one of four ‘Microverse Professorships’ as an Alexander von Humboldt Professor since 2021. The cluster investigates the complex relationships within microbial communities, and the role of colony structure in microbial interaction is one of the key research questions.
Original Publication
Zomer A, Ingham CJ, von Meijenfeldt FAB et al. Structural color in the bacterial domain: The ecogenomics of a 2-dimensional optical phenotype, PNAS 2024, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2309757121
Source
University of Jena, press release, 2024-07-08.
Supplier
Cambridge University
Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena
Hoekmine BV
Leibniz-Institut DSMZ-Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH
Max-Planck-Institut für Kolloid- und Grenzflächenforschung
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA (PNAS)
Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ)
Utrecht University
Share
Renewable Carbon News – Daily Newsletter
Subscribe to our daily email newsletter – the world's leading newsletter on renewable materials and chemicals







