
Before the global problems derived from marine contamination, strategies have been proposed to replace conventional polymers as alternatives for biodegradable bioplastics, among which are highlighted: starch, cellulose, polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHBV) a type of polymer between them.
In this regard, these materials are designed for decomposing CO2, water and biomass with the intervention of aerobic microorganisms and the process of biodegradation is bound to the conditions of the environment, these play a very important role since they determine the type of microorganisms that are in charge of mining, as well as the kinetics of biodegradation. Said factors are:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- pH
- Oxygen
The biodegradation of bioplastics in the marine environment
It is carried out through a chain that consists of the following steps:
- Bio-deterioration: at the beginning of the study, a change in the physical and chemical properties of polymers occurs.
- Bio-fragmentation: reduction of molecular weight of biopolymers where oligomers and monomers are produced.
- Bio-assimilation: microorganisms ingest molecules.
Thus, the conditions of the marine environment affect the kinetics of biodegradation, these are divided into abiotic factors such as the salinity of water, the depth, and the temperature, among others, and biotic factors such as the diversity of marine habitats. In the same way, the properties of the biopolymers like the physical-chemical properties (weight, crystallinity, chemical structure, molecular distribution, etc.).

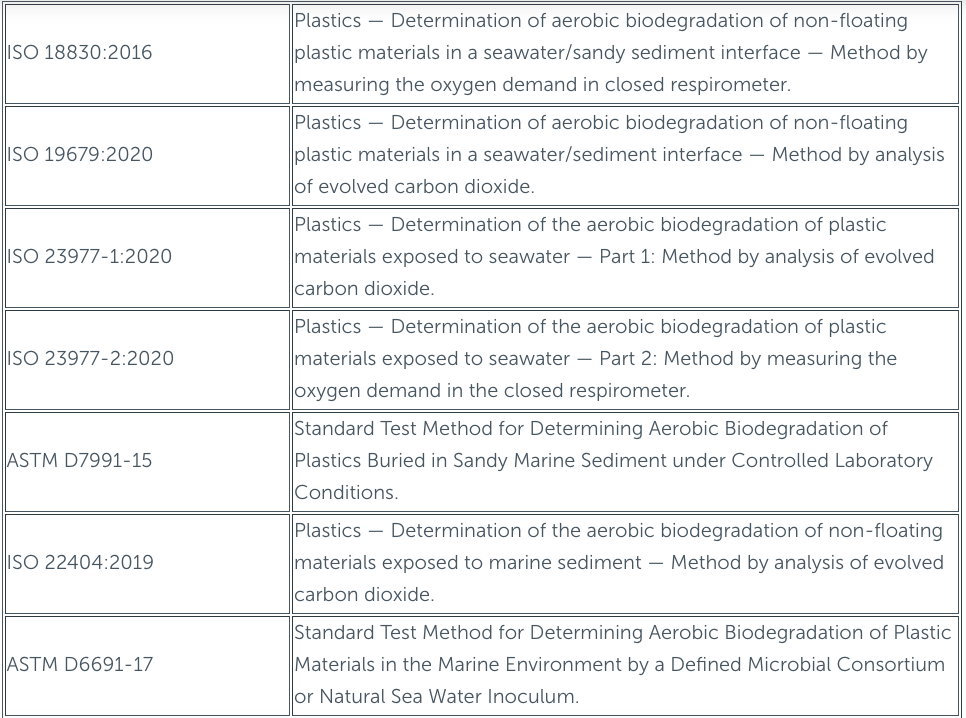
Regulations on biodegradability in the marine environment
As has already been mentioned, biodegradation in the marine environment is influenced by biotic and abiotic factors related directly to the sea area where bioplastic is positioned. This fact has led to the development of a large number of rules that aim to simulate conditions of biodegradation in different areas of the sea, in the same way, the project develops new rules that allow the generation of more adjusted tests to the conditions of the real environment.
Below, some standards are shown that have been developed for the determination of biodegradation of bioplastics in a marine environment.

AIMPLAS biodegradation laboratory
Given this, to offer a guarantee to the consumer, our Biodegradation and Compostability laboratory can help businesses obtain certification and eco-label as biodegradable in the marine environment through the certified entity TÜV Austria.
Author
María Mozo Toledo
Source
AIMPLAS, press release, 2022-10-10.
Supplier
AIMPLAS (Asociación de Investigación de Materiales Plásticos y Conexas)
TÜV AUSTRIA Group
Share
Renewable Carbon News – Daily Newsletter
Subscribe to our daily email newsletter – the world's leading newsletter on renewable materials and chemicals









