Metal-organic frameworks, more commonly known as MOFs were first developed in the 1990s. Three decades later, these highly functional materials have been recognized with the 2025 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. One of the remarkable features of MOFs is their design flexibility and scope for chemical functionalization, which enables the creation of a large library of structures with tailored properties, and control over pore size and shape. The structural versatility and tunability afforded by MOFs have attracted widespread interest in numerous applications across carbon capture, batteries, biogas sweetening and other gas separation processes, catalysis, medical/drug delivery, sensing, and many more. However, as the MOF market moves closer to full commercialization, several hurdles still need to be addressed. Even so, IDTechEx projects that the MOF market could exceed US$900 million by 2035.
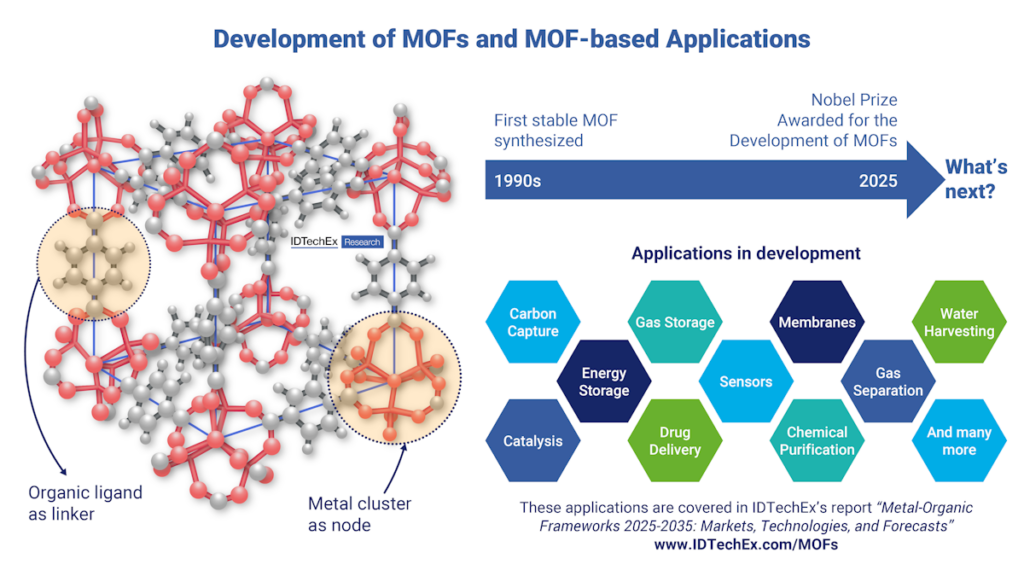
The Road to the Nobel Prize
The first stable structures of MOF were synthesized around the mid-1990s. Since then, over 100,000 different structures of MOFs have been reported, with the number continuously growing. MOFs are known for their highly tunable periodic structures, that have an exceptionally high surface area (e.g. up to 7,000m2 per gram of MOF). Compared to other solid sorbents, MOFs have tunable pore size distribution, high adsorption capacity, selectivity, and cycling stability. Additionally, MOFs can also be regenerated with a lower energy penalty compared to other sorbents, which also adds benefits from a sustainability standpoint and lowers operational costs. The Nobel Prize award recognizes the promise and potential of MOFs, but the question remains over whether MOFs can deliver on the gap between the promise and real-world adoption.
The road to commercializing these materials has not been easy. The translation from research laboratories to industrial applications has been hindered by several challenges, such as the high cost and low availability of some of the materials/precursors used for MOF synthesis. Additionally, most MOFs developed in research labs are synthesized using solvothermal methods on the milligrams scale. To produce MOFs on an industrial scale, the production methods need to be scalable. Over the past decade or so, multiple efforts to commercialize MOFs have fallen short, leading some to view them as difficult material to bring to market. For example, in 2013, BASF was focused on commercializing MOFs for the transportation industry, facilitating natural gas storage for natural gas vehicles (NGVs). However, the company was unable to successfully commercialize the materials for gas-powered vehicles a decade ago due to the high cost of manufacturing MOFs and the gas-powered vehicle market did not evolve as expected.
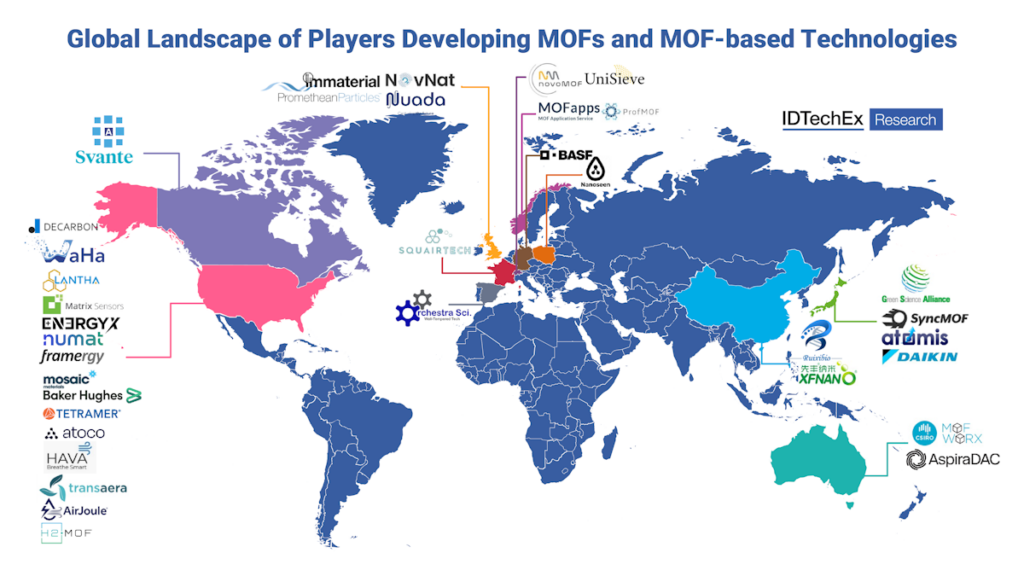
Nonetheless, the ecosystem of players working to scale up MOF production has expanded markedly over the past three to five years. These include players such as Svante, Nuada, Promethean Particles, BASF, UniSieve, and many more. The focus is shifting toward delivering cost-effective, scalable MOF-based technologies aimed at tackling global challenges such as carbon capture, efficient gas separation, and atmospheric water harvesting.
The Path Ahead
Thanks to their favorable properties and material characteristics, MOFs are attracting growing interest across a wide range of applications, from carbon capture, water harvesting, hydrogen storage, chemical purifications, gas separation, and many more. They are especially promising in areas where they can help lower energy consumption and reduce operational costs. applications where MOFs can result in material reduction in energy consumption and operational costs.
In particular, carbon capture is fast emerging as a key application of MOFs resulting from the high CO2selectivity, cycling stability, and low energy requirements for regeneration, with technologies being developed by the likes of Svante and Nuada gaining momentum. It offers the potential for significant reductions in operational costs compared to incumbent amine scrubbing.
For all their potential, MOFs are not without obstacles. Producing them economically at scale and integrating them into durable, industrial-grade technologies remain key challenges. Although early testing and pilot data are showing promising results, the technologies are yet to be demonstrated at an industrial scale. Additionally, incumbent technologies have a stronghold in the key target markets, and MOFs will need to be competitive to gain market share. With the advent of several commercial products over the next decade, MOF-based technologies will need to demonstrate their performance at scale. This must also be complemented by a sustained growth in manufacturing capacity using scalable methods.
As MOF-based technologies approach commercialization, IDTechEx’s report “Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) 2025-2035: Markets, Technologies, and Forecasts” offers an independent analysis of key trends and considers applications of MOFs for several applications including carbon capture, water harvesting, chemical separation and purification, hydrogen storage, energy storage (e.g. batteries), semiconductors, sensors, and more. Informed by insights gained from primary research, the report provides benchmarks, analyzes key players in the field and provides market forecasts in terms of yearly mass demand and market value segmented by application.
For more information on this report, including downloadable sample pages, please visit www.IDTechEx.com/MOFs, or for the full portfolio of research available from IDTechEx, see www.IDTechEx.com.
About IDTechEx
IDTechEx provides trusted independent research on emerging technologies and their markets. Since 1999, we have been helping our clients to understand new technologies, their supply chains, market requirements, opportunities and forecasts. For more information, contact research@IDTechEx.com or visit www.IDTechEx.com.
Source
IDTechEx, press release, 2025-10-10.
Supplier
Share
Renewable Carbon News – Daily Newsletter
Subscribe to our daily email newsletter – the world's leading newsletter on renewable materials and chemicals









