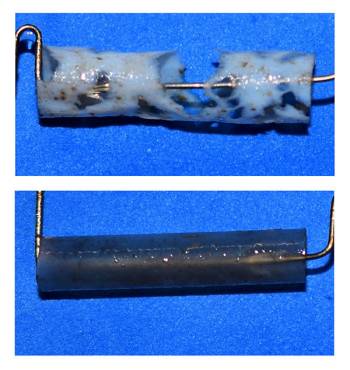
Plastic drinking straws that get into marine ecosystems make beaches unsightly and pose problems for turtles and seabirds. So, people increasingly favor alternatives marketed as biodegradable or compostable. But do marine microorganisms break apart those straws?
Researchers conducted experiments with seawater and report in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering that some commercial bioplastic or paper straws might disintegrate within eight to 20 months in coastal ocean systems and switching to foam makes a major difference.
To combat plastic pollution, some regions in the U.S. have restricted traditional polymers, such as polypropylene (PP), in drinking straws. These policies have led to a growing market for single-use items made from paper or bioplastics. However, replacement materials need to retain functionality so they don’t flop over after the first sip but will fall apart later if they end up in soil, fresh water or salt water. While the next generation of bioplastics, such as cellulose diacetate (CDA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), may be able to meet both requirements, little is known about how long products made of these materials last in the ocean before fully degrading compared to other materials. So, Bryan James, Collin Ward and colleagues conducted experiments using real seawater to investigate the environmental lifetimes of different straws and to find a way to accelerate the breakdown of next-generation bioplastics.
In initial tests, the researchers cut inch-long pieces from commercially available straws made from either coated or uncoated paper, PP polymer, or CDA, PHA or polylactic acid (PLA) bioplastics. Then the pieces were suspended on wires in large tanks with room temperature seawater flowing through them. The team found that after 16 weeks, paper, CDA and PHA straws lost 25-50% of their initial weights. The researchers projected that these degradable straws should fully disintegrate in coastal oceans within 10 months for paper, 15 months for PHA and 20 months for CDA. Additionally, the biofilms on the disintegrating samples contained microbes known to metabolize diverse polymers. Conversely, PP and PLA straws didn’t have measurable weight changes, which suggests they could persist for years in ocean water.
Using the same experimental conditions, the researchers next examined how changing the CDA material’s structure, from solid to a foam, impacted the bioplastic’s environmental lifetime. They observed that the CDA foam broke down at least twice as fast as the solid version, and they estimated that a straw made from the prototype foam would disintegrate in seawater in eight months — the shortest lifetime of any material tested. Having demonstrated that some bioplastic straws are unlikely to remain intact over a long period, the researchers recommend that simple changes, such as switching to foam materials, could further reduce that time frame.
The authors acknowledge funding from Eastman. Some authors are employees of Eastman, a manufacturer of biodegradable plastics.
Some authors have patents in the field of biodegradable plastics.
About the American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
Source
American Chemical Society, press release, 2024-01-30.
Supplier
American Chemical Society (ACS)
Eastman Chemical Company
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI)
Share
Renewable Carbon News – Daily Newsletter
Subscribe to our daily email newsletter – the world's leading newsletter on renewable materials and chemicals







