
- Right now, many plastic products, especially contaminated and multilayer plastics, cannot be traditionally recycled at scale.
- Instead, these plastics are typically incinerated or sent to landfills.
- More plastic can be recycled using chemical recycling, helping Europe reduce this waste.
At ExxonMobil, we’re prepared to expand our chemical recycling capabilities to Europe, building on successful deployment in the United States. But achieving this requires policy frameworks that support innovation and investment.
ExxonMobil Europe President Philippe Ducom shares his views. Read on to find out why mass balance is a key piece of the puzzle.
Right now, one key decision is in the hands of the European Commission: how to regulate mass balance and the accounting approach that underpins the business case for chemical recycling.
We believe the Commission should support a flexible, outcome-oriented approach. One that enables producers to use existing infrastructure, including refineries, to help address plastic waste and deliver economic benefits.
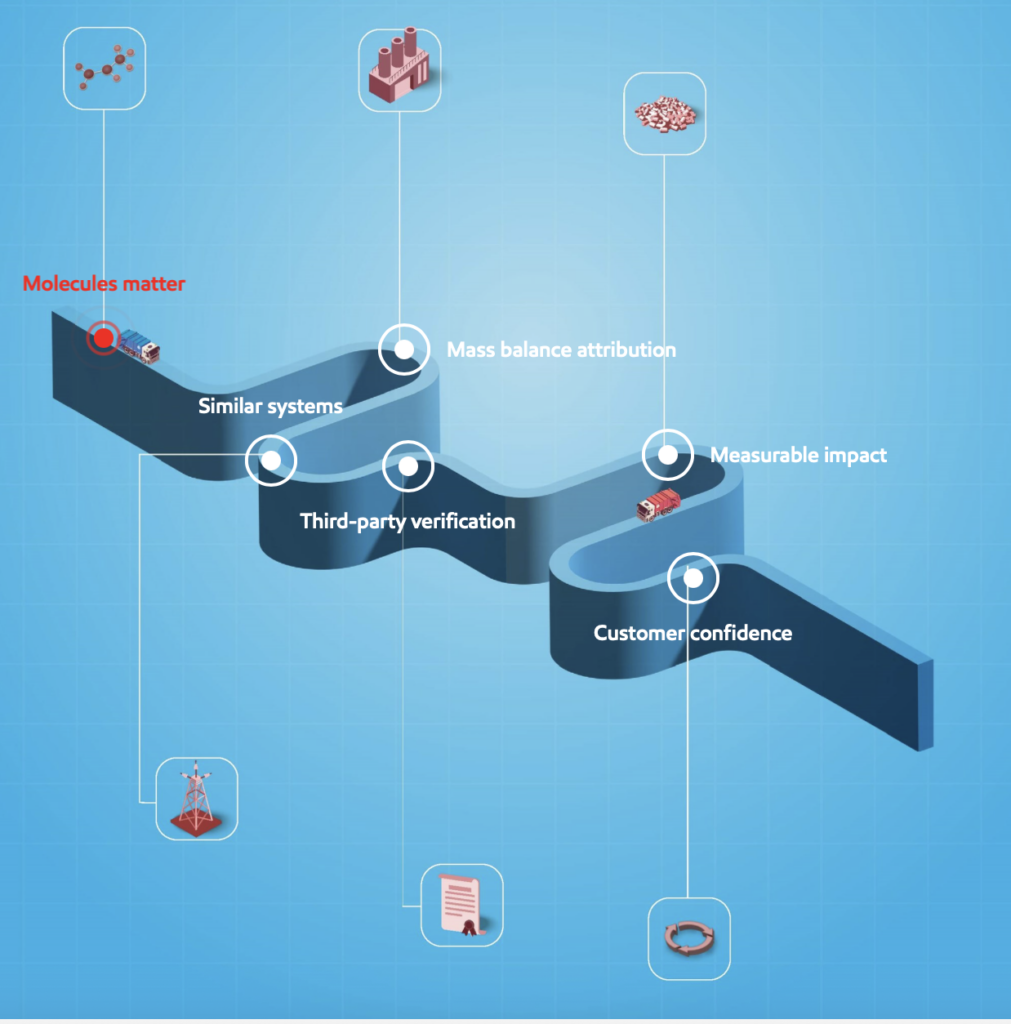
Chemical recycling breaks down plastic waste to the molecular level. During the process, the plastic waste is mixed with fossil-based feedstock, and you can’t identify which molecules come from plastic and which come from fossil feedstock. © Exxon Mobil Corporation
Why is mass balance needed for chemical recycling?
Chemical recycling could help Europe meet its recycling targets and address plastic waste. And mass balance – which attributes the amount of usable raw materials made from the plastic waste we process to the virgin-quality, certified-circular plastics we sell – is key to chemical recycling.
But there’s an urgent need for policies that outline a clear mass balance system for calculating what qualifies as recycled content. This would help spur investment in chemical recycling across the European Union.
At scale, we can help make a difference
Today, the EU recycles just 26.9% of plastic waste. Meanwhile, incineration is growing; up more than 15% since 2018. But chemical recycling could help address this challenge. This technology, deployed alongside mechanical recycling, can help expand the range of plastics that find a second life as new products.
Europe’s refining sector, which has struggled to compete with other parts of the world, could play an important role in this equation. According to a recent statement by several EU Member States, the region could lose over 50,000 petrochemical jobs by 2035. Chemical recycling could help transform these sites, save jobs, and redefine the role of refineries within a circular economy.
The role of mass balance and why policy matters
Europe currently uses a “fuel-exempt” method for mass balance. Under this system, plastic waste used to make fuel does not count toward recycled content goals.
To support investments in chemical recycling, the system must be practical and efficient. A clear and workable approach to mass balance is key for companies to build a viable business case.
Mass balance isn’t new—it’s been proven in other industries
Analogous methods are already widely used in other sectors. A helpful analogy is renewable electricity production.
Because all sources of power connect to the same grid, we cannot tell where exactly our electricity comes from (nuclear, renewable, gas, etc.) at a specific moment. But providers use credits to confirm that a target amount of renewable energy has been added to the system. The same principle applies to chemical recycling.
Third-party verification adds credibility
Our approach is certified and audited by ISCC PLUS, a system that verifies compliance with a robust mass balance methodology. ISCC ensures that companies follow strict rules and that they accurately account for recycled inputs. The ISCC has more than 250 members, including companies, researchers, and NGOs.
We know chemical recycling works
It’s already a reality at our Baytown facility in Texas. And the numbers speak for themselves:
| Around 45,000 metric tons | Plastic waste processed since 2022 |
| $200 million | In additional investment announced for various sites in the U.S. |
| 220,000 metric tons per year | Total chemical recycling capacity, either in operation or under development |
| Nearly 500,000 metric tons per year | Our chemical recycling capacity goal |
In Europe, we are exploring how we might bring this technology to our sites in Rotterdam and Antwerp.
Source
Exxon Mobil, press release, 2025-07-03.
Supplier
Exxon
ExxonMobil
International Sustainability & Carbon Certification (ISCC)
Share
Renewable Carbon News – Daily Newsletter
Subscribe to our daily email newsletter – the world's leading newsletter on renewable materials and chemicals









