Tremendous effort has been put into making plastics not only durable and convenient but also environmentally-friendly materials for everyday products. Osaka Metropolitan University scientists made a significant advance in this journey with their innovative artificial photosynthesis technology that produces biodegradable plastics from acetone and CO2, addressing the plastic waste crisis while moving toward the goal of carbon neutrality. Their findings were published in Chemical Communications.
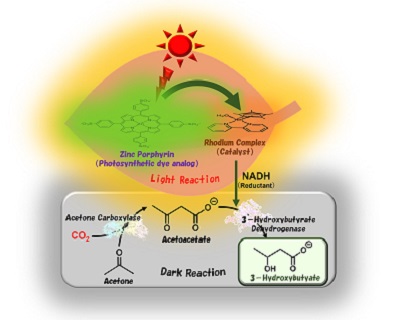
The research team led by Professor Yutaka Amao from the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis at Osaka Metropolitan University has successfully synthesized 3-hydroxybutyrate, a raw material for poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB)—a strong water-insoluble polyester used for packaging materials—from acetone and CO2. With a visible light-driven catalytic system utilizing sunlight and two biocatalysts, the researchers achieved a yield of about 80%.
Mimicking natural photosynthesis, the team artificially reproduced a light reaction, which involves sunlight, and a dark reaction, which fixes CO2, and synthesized 3-hydroxybutyrate.
This study is the latest in a series of the researchers’ articles on using artificial photosynthesis to produce useful substances, generate renewable energy, and achieve a carbon neutral society.
“This research result of synthesizing 3-hydroxybutyrate, a raw material for PHB, from CO2 is a significant contribution to addressing both the plastic and CO2 reduction issues,” said Professor Amao. “In the future, we aim to produce 3-hydroxybutyrate through artificial photosynthesis using CO2 contained in exhaust gas emitted from factories.”
Funding
This work was partially supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (22H01872) and Fund for the Promotion of Joint International Research (Fostering Joint International Research (B)) (19KK0144).
Paper Information
Title: Visible-light driven 3-hydroxybutyrate synthesis from CO2 and acetone with the hybrid system of photocatalytic NADH regeneration and multi-biocatalysts
Journal: Chemical Communications
DOI: 10.1039/D2CC03660F
Author: Yu Kita and Yutaka Amao
URL: https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CC03660F
Contribution to SDGs

7: Affordable and clean energy
12: Responsible consumption and production
Source
OMU, press release, 2022-10-03.
Supplier
Share
Renewable Carbon News – Daily Newsletter
Subscribe to our daily email newsletter – the world's leading newsletter on renewable materials and chemicals









